PowerPoint Slides
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
English Text
Cancer Prevention: Part 2
VideoTranscript
Professional Oncology Education
Cancer Prevention: Part 2
Time: 11:32
Therese B. Bevers, M.D.
Professor, Clinical Cancer Prevention
Medical Director, Cancer Prevention Center
The University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer
Center
Hi, I am Dr. Terry Bevers, Professor of Clinical
Cancer Prevention and Medical Director of the
Cancer Prevention Center at the University of Texas
MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today, our talk is
about Cancer Prevention: Part II.
Brazilian Portuguese Translation
Prevenção do Câncer: Segunda Parte
Transcrição do vídeo
Educação Profissional em Oncologia
Prevenção do Câncer: Segunda Parte
Duração: 11:32
Therese B. Bevers, M.D.
Professora, Prevenção Clínica do Câncer
Diretora Médica, Centro de Prevenção de Câncer
MD Anderson Cancer Center, Universidade do
Texas
Oi, meu nome é Dra. Terry Bevers, sou Professora
de Prevenção Clínica do Câncer e Diretora Médica
do Centro de Prevenção de Câncer do MD
Anderson Cancer Center da Universidade do
Texas. A palestra de hoje será sobre segunda parte
da prevenção do câncer.
Cancer Prevention: Part II
Therese B. Bevers, M.D.
Professor, Clinical Cancer Prevention
Medical Director, Cancer Prevention Center
1
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Objectives
Upon completion of this lesson, participants will
be able to:
• Discuss lifestyle modification strategies for
risk reduction
• List types of prophylactic surgical interventions
used to prevent malignancies
• Identify chemoprevention strategies for several
common cancers
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
In a previous lecture, you heard Sally Scroggs talk
about lifestyle modifications for risk reduction.
Today, the lecture will focus on understanding types
of prophylactic surgical interventions used to
prevent
malignancies
and
identification
of
chemoprevention strategies for several common
cancers.
Em uma palestra anterior, vocês ouviram Sally
Croggs falar sobre mudanças no estilo de vida para
a redução dos riscos. Hoje, a ênfase da palestra
será na compreensão dos tipos de intervenções
cirúrgicas profiláticas utilizadas para evitar
neoplasias malignas e na identificação de
estratégias quimiopreventivas para vários tipos
comuns de câncer.
I want to first focus on prophylactic surgical
interventions.
Primeiro quero dirigir a atenção às intervenções
cirúrgicas profiláticas.
Risk Reduction Strategies
•
Health Promotion
-
Diet
Lifestyle modification
•
Prophylactic surgical interventions
•
Chemoprevention
2
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Prophylactic Surgical Interventions
•
Breast Cancer
Surprisingly, there are a number of surgical
interventions that can be used to reduce an
individual’s risk of developing cancer. Today, I
would like to focus on prophylactic mastectomy and
prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy.
Surpreendentemente, há muitas intervenções
cirúrgicas que podem ser utilizadas para reduzir o
risco de uma pessoa contrair câncer. Hoje, gostaria
de dar destaque à mastectomia profilática e à
salpingo-ooforectomia profilática.
Prophylactic mastectomy is the removal of the
breast tissue, both sides, to reduce a woman’s risk
of developing breast cancer. This strategy is highly
effective for breast cancer risk reduction; reducing a
woman’s chance of developing the disease by about
90%. However, it does carry some significant risk
associated with it. It alters a woman’s body form
permanently and her own self-image.
It is
irreversible. And for these reasons we typically only
consider it in exceptional circumstances. Such
circumstances would be a woman who is a gene
mutation carrier for a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
The risk is quite high carrying a 50% to 80% lifetime
risk. Given this high lifetime risk, certainly, we
would consider a very highly effective risk reduction
strategy such as prophylactic mastectomy.
A mastectomia profilática consiste na remoção do
tecido da mama, de ambos os lados, para reduzir o
risco de a mulher contrair câncer de mama. Esta
estratégia é altamente eficaz para a redução do
risco de câncer de mama, reduzindo em cerca de
90% a possibilidade de uma mulher contrair a
doença. No entanto, existem alguns riscos
significativos associados a ela. Altera a forma do
corpo da mulher permanentemente e sua
autoimagem. É irreversível. E, por essas razões,
normalmente só é considerada em circunstâncias
excepcionais. Tais circunstâncias seriam o caso de
uma mulher que é portadora de mutação no gene
BRCA1 ou BRCA2. O risco é bastante elevado,
com um risco cumulativo vital de 50% a 80%. Dado
o elevado risco cumulativo vital, certamente,
poderíamos considerar uma estratégia altamente
eficaz de redução de risco, como a mastectomia
profilática.
– Prophylactic mastectomy
– Prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy
•
Ovarian Cancer
– Prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy
•
Colorectal Cancer
– Prophylactic colectomy
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Prophylactic Mastectomy
• Highly effective
– 90% risk reduction
• Alters body form and image
• Irreversible
• Need only be considered in exceptional
circumstances
– Genetic predisposition
3
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Prophylactic Oophorectomy
• Risk Reduction
– Breast cancer
47-68%
– Ovarian cancer 85-96%
• Causes premature menopause with systemic effects
• Use of postmenopausal HRT does not appear
to increase breast cancer risk
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Risk Reduction Strategies
•
Another prophylactic surgical intervention is
prophylactic oophorectomy or prophylactic salpingooophorectomy where the tubes and ovaries on both
sides are removed.
This not only reduces a
woman’s chance of developing ovarian cancer by
about 85 to 96%, but also reduces a woman’s
chance of developing breast cancer if done early in
her 30s or 40s. The breast cancer risk reduction
can be as much as 47% to 68%. There are risks
associated with this particular surgical intervention.
It does cause premature menopause with all the
associated systemic effects, such as increased risk
of heart disease, increased risk of osteoporosis, and
associated menopausal symptoms, such as hot
flashes, night sweats, and the like. One study has
shown that the use of postmenopausal hormone
therapy does not appear to affect a woman’s risk of
developing breast cancer if she were to take it after
a prophylactic oophorectomy.
Now, I want to switch our attention to
chemoprevention, which is the use of medications to
reduce an individual’s risk of developing the
disease, in this case, cancer.
Outra intervenção cirúrgica profilática é a
ooforectomia profilática, ou salpingo-ooforectomia
profilática, em que as tubas e os ovários em ambos
os lados são removidos. Esse procedimento não só
reduz a chance de as mulheres contraírem câncer
de ovário em cerca de 85% a 96%, mas também
reduz a chance de contraírem câncer de mama se
for realizado precocemente aos 30 ou 40 anos de
idade. A redução do risco de câncer de mama pode
variar de 47% a 68%. Existem riscos associados a
esta intervenção cirúrgica específica. Ela causa a
menopausa precoce com todos os efeitos
sistêmicos associados, como aumento do risco de
cardiopatias e osteoporose e sintomas de
menopausa associados, como ondas de calor,
suores noturnos e semelhantes. Em um estudo foi
demonstrado que, se administrada após uma
ooforectomia profilática, a terapia de reposição
hormonal na pós-menopausa não parece afetar o
risco de as mulheres contraírem câncer de mama.
Agora, quero mudar de assunto e focalizar na
quimioprevenção, que é o uso de medicamentos
para reduzir o risco de uma pessoa contrair a
doença, neste caso, o câncer.
Health Promotion
-
Diet
Lifestyle modification
•
Prophylactic surgical interventions
•
Chemoprevention
4
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Chemoprevention
The use of medication to reduce the development of
disease mechanisms:
•
Modify estrogen response
(selective estrogen receptor
modulators - SERMs)
•
Protect cells from oxidative stress
•
Suppress cell proliferation
(difluoromethylornithine - DFMO)
•
Interfere with estrogen production
(aromatase inhibitors)
•
Block carcinogens from
binding DNA
•
Block cyclo-oxygenase (NSAIDs)
•
Retinoids (vitamin A derivatives)
•
Alter ovulation
•
Deltanoids (vitamin D derivatives)
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Chemoprevention
•
-
Quero falar brevemente sobre dois agentes, o
tamoxifeno e o raloxifeno, que comprovadamente
reduzem o risco de contrair câncer de mama.
Tamoxifen
Raloxifene
Finasteride (Proscar®, Propecia®)
Liver Cancer
-
•
I want to briefly talk about two agents, tamoxifen
and raloxifene, that have been shown to reduce the
risk of developing breast cancer.
Prostate Cancer
-
•
Há uma grande quantidade de medicamentos ou
substâncias que estão sendo exploradas para
reduzir a incidência de câncer. Esta é apenas uma
lista parcial. De fato, alguns, como os SERMs, ou
moduladores seletivos do receptor de estrogênio,
contam com a aprovação da FDA para serem
utilizados com o objetivo de reduzir o risco de
câncer de mama. Outros ainda estão sendo
pesquisados. Os mecanismos propostos estão
indicados neste slide.
Breast Cancer
-
•
There are a large number of medications or
substances that are being explored to reduce the
development of cancer. This list is just a partial list.
Some such as SERMs, or Selective Estrogen
Receptor Modulators, actually have FDA approval
for their use to reduce the risk of developing breast
cancer. Others are still under investigation. The
proposed mechanisms are listed on this slide.
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Cervical Cancer
–
HPV Vaccine
5
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Tamoxifen and Raloxifene
• Both drugs reduce the risk of invasive and non-invasive
breast cancer by 50%
• Both drugs reduce the risk of osteoporotic bone fractures
• Raloxifene has fewer risks than tamoxifen
– Fewer DVT and PE
– No increased risk of:
• Endometrial cancer
• Cataracts
These drugs reduce the risk of both invasive and
noninvasive breast cancer by one-half. They also
reduce the risk of developing osteoporotic-type
bone fractures.
There are, however, risks
associated with both of these drugs. Raloxifene has
fewer risks than tamoxifen, has fewer deep vein
thromboses or DVTs, and fewer pulmonary embolus
or PEs. It does not have the increased risk of
endometrial cancer or cataracts that is seen with
tamoxifen. The side effects in regards to hot
flashes, vaginal dryness, and other annoying side
effects are fairly comparable between the two drugs.
Esses fármacos reduzem pela metade o risco de
câncer de mama invasivo e não invasivo. Também
reduzem o risco de fraturas ósseas do tipo
osteoporótico. Contudo, existem riscos associados
a ambos os fármacos. O raloxifeno apresenta
menos riscos do que o tamoxifeno, com menor
índice de trombose venosa profunda ou TVP e
menor índice de embolia pulmonar ou EP. Não
apresenta maiores riscos de câncer de endométrio
ou de catarata, observados com o tamoxifeno. Os
efeitos colaterais em relação às ondas de calor,
secura vaginal e outros efeitos colaterais
desconfortantes são bastante semelhantes nas
duas drogas.
Women, who are at increased risk, have options
now to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer.
Premenopausal woman have the option of taking
tamoxifen.
Postmenopausal woman have the
option of either tamoxifen for five years or raloxifene
for lifelong use.
Agora, as mulheres com risco maior, contam com
opções para reduzir o risco de contrair câncer de
mama. A mulher na pré-menopausa tem a opção de
tomar o tamoxifeno. A mulher na pós-menopausa
tem a opção de tomar o tamoxifeno durante cinco
anos ou o raloxifeno por toda a vida.
• Side effects comparable
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Breast Cancer Chemoprevention
Options for women at increased risk of developing
breast cancer:
• Premenopausal
– Tamoxifen
• Postmenopausal
– Tamoxifen
– Raloxifene
6
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Chemoprevention
•
-
This study, called the Prostate Cancer Prevention
Trial, actually showed that there were fewer cases
of prostate cancer in the finasteride arm. In looking
at 1000 men followed over seven years, taking
either finasteride or no finasteride, there were
actually 15 fewer cases of prostate cancer in the
finasteride arm when compared to the no finasteride
arm. However, somewhat surprisingly, four more
cases of high-grade cancers were seen. It was this
observation that has led to some reluctance in the
use of finasteride generally for men to reduce the
risk of developing prostate cancer.
De fato, nesse estudo, chamado "Prostate Cancer
Prevention Trial" [Estudo de prevenção do câncer
de próstata], foi observado que, no grupo com
finasterida, houve um menor número de casos de
câncer de próstata. Em 1000 homens examinados
durante um acompanhamento de sete anos que
tomaram finasterida ou não, houve, na realidade, 15
menos casos de câncer de próstata no grupo com
finasterida quando comparado com o grupo sem
finasterida. Contudo, e um tanto
surpreendentemente, foram observados mais
quatro casos de alto grau. Foi esta observação que
gerou alguma relutância em utilizar a finasterida
para reduzir o risco de câncer de próstata nos
homens.
Finasteride (Proscar®, Propecia®)
Liver Cancer
-
•
Tamoxifen
Raloxifene
Prostate Cancer
-
•
Voltando nossa atenção para o câncer de próstata,
temos um estudo que analisou o Proscar® ou
finasterida para a prevenção do câncer de próstata.
Breast Cancer
-
•
Turning our attention now to prostate cancer, we
®
have a study that has looked at Proscar or
finasteride for the prevention of prostate cancer.
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Cervical Cancer
–
HPV Vaccine
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Estimated Benefit and Risk from Finasteride on Development of Prostate Cancer
Thompson IM et al. N Engl J Med 2003 349(3):215
7
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Chemoprevention
•
-
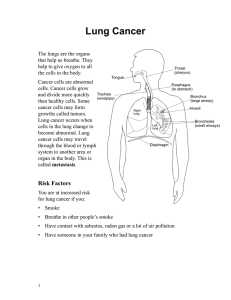
I want to briefly talk about hepatitis B and the
hepatitis B vaccine. We know that hepatitis B and
hepatitis V --- hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections
are major risk factors for the development of
hepatocellular or liver carcinoma. In fact, the risk is
even greater if there is infection with both hepatitis B
and C. Chronic infections with these account for
about 40% of cases of hepatocellular or liver cancer
that are seen. It has been hypothesized that
vaccination against hepatitis B may reduce the
incidence of liver cancer by as much as one-half.
Quero falar brevemente sobre a hepatite B e a
vacina contra a hepatite B. Sabemos que a hepatite
B e a hepatite V... que as infecções com hepatite B
e hepatite C constituem importantes fatores de risco
de carcinoma hepatocelular ou hepático. Na
verdade, o risco é ainda maior se houver infecção
com as hepatites B e C. Infecções crônicas com
estas hepatites representam cerca de 40% dos
casos observados de câncer hepatocelular ou
hepático. Sugeriu-se a hipótese de que a vacinação
contra a hepatite B pode reduzir a incidência de
câncer de fígado em até a metade.
Finasteride (Proscar®, Propecia®)
Liver Cancer
-
•
Tamoxifen
Raloxifene
Prostate Cancer
-
•
Voltamos nossa atenção agora para algumas
vacinas que podem ser benéficas na redução do
risco da pessoa contrair câncer.
Breast Cancer
-
•
Turning our attention now to some vaccines that can
be beneficial in reducing individuals’ risk of
developing cancer.
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Cervical Cancer
–
HPV Vaccine
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Hepatitis B
• Hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections are major
risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
• Risk is greater with coinfection with both
hepatitis B and C
• Chronic hepatitis B and C infection account for
0-40% of cases of HCC
• Vaccination against hepatitis B may reduce risk
of HCC by 50%
8
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Hepatitis B Vaccine
• Part of childhood immunization series
• High risk adult populations
–
–
–
–
–
–
Have >1 sex partner in 6 months
Men who have sex with other men
Sex contacts of infected people
IV drug users
Healthcare workers
Household contacts of persons
with chronic HBV infection
– Hemodialysis patients
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Chemoprevention
•
-
Finalmente, gostaria de falar sobre o câncer de colo
do útero e a vacina contra o HPV ou vacina contra o
vírus do papiloma humano.
Tamoxifen
Raloxifene
Finasteride (Proscar®, Propecia®)
Liver Cancer
-
•
Finally, I would like to talk about cervical cancer and
HPV vaccine or human papillomavirus vaccine.
Prostate Cancer
-
•
Viemos utilizando a vacina contra a hepatite B
como parte da série de imunização infantil já há
vários anos. Certamente, as pessoas que
receberam rotineiramente a vacina contra a hepatite
B ainda estão numa idade em que é normalmente
esperado que o câncer de fígado aconteça. Por
isso, ainda vai demorar até começarmos a ver os
efeitos da vacinação contra a hepatite B na
população. No entanto, existem algumas
populações adultas de alto risco que estão
enumeradas aqui e que devem ser consideradas
seriamente para receberem a vacina contra a
hepatite B, reduzir o risco de infecções com
hepatite B e, dessa forma, reduzir potencialmente o
risco de contraírem câncer de fígado.
Breast Cancer
-
•
We have been using hepatitis B vaccine as part of
the childhood immunization series for a number of
years.
Certainly, the individuals who routinely
received hepatitis B vaccine are still under the age
that we would normally expect to see liver cancer
develop. So it will be a while before we begin to see
the effects of hepatitis B vaccination on the
population. There are, however, some high-risk
adult populations that are listed here, and these
populations should seriously be considered for
hepatitis B vaccination to reduce the risk of being
infected with hepatitis B and, thus, potentially
reduce the risk of developing liver cancer.
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Cervical Cancer
–
HPV Vaccine
9
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
HPV Vaccine
• Quadrivalent HPV vaccine (Gardasil®)
– HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18
• Bivalent HPV vaccine (Cervarix®)
– HPV 16 and 18
• Nearly 100% effective in protecting against
precancerous lesions caused by HPV 16 and 18
– HPV 16 and 18 cause 70% of cervical cancers
• Quadrivalent HPV vaccine (Gardasil®) also protects
against HPV 6 and 11
– Cause over 90% of genital warts
There are actually two different types of HPV
vaccines that are now available on the market.
®
Gardasil is a quadrivalent vaccine, meaning it has
four types of HPV included in the vaccine. It has
two high-risk or oncogenic cancer causing types,
which is HPV 16 and 18, and two low-risk types
®
HPV 6 and 11. Cervarix is a bivalent vaccine
focusing only on the high-risk types, HPV 16 and
18. It has been found in studies that women who
were immunized with HPV vaccine obtained nearly
100% prevention against the development of
precancerous lesions caused by HPV 16 and 18. It
is important to realize that HPV 16 and 18 account
for about 70% of the cervical cancers that occur in
®
the United States. Because Gardasil also includes
HPV 6 and 11 in the vaccine, it can prevent against
the diseases that those are associated with,
specifically genital warts. In fact, they are the cause
of over 90% of genital warts. While these are not
oncogenic or cancer-causing, certainly they can be
problematic, and there is the potential to reduce the
incidence of these developing.
De fato, existem dois tipos diferentes de vacinas
contra o HPV que agora estão disponíveis no
mercado. O Gardasil® é uma vacina quadrivalente,
ou seja, tem quatro tipos de HPV incluídos na
vacina. Tem dois tipos de alto risco ou oncogênicos,
que causam câncer, que é o HPV 16 e 18, e dois
tipos de baixo risco, o HPV 6 e o 11. O Cervarix® é
uma vacina bivalente dirigida apenas aos tipos de
alto risco, o HPV 16 e o 18. Descobriu-se em
estudos que a prevenção contra o aparecimento de
lesões pré-cancerosas causadas pelo HPV 16 e 18
foi de quase 100% em mulheres imunizadas com a
vacina contra o HPV. É importante perceber que o
HPV 16 e o 18 respondem por cerca de 70% dos
cânceres de colo do útero que ocorrem nos Estados
Unidos. Como o Gardasil® também inclui HPV 6 e
11 na sua composição, pode prevenir contra
doenças às quais aqueles estão associados,
especificamente verrugas genitais. Na verdade,
eles são a causa de mais de 90% das verrugas
genitais. Embora estas não sejam oncogênicas ou
causadoras de câncer, certamente podem ser
problemáticas, e existe a possibilidade de reduzir a
sua incidência.
10
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
HPV Vaccine
• Will not protect against HPV infection by other
high risk types, so screening is still needed
• Vaccine does not treat HPV infection only
prevents it
• To be effective, the vaccine should be given
prior to the initiation of sexual activity
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
CDC Recommendations: HPV Vaccination
• Routine vaccination of females aged 11-12
• Catch-up vaccination of females aged 13-26
– Counseling regarding diminished benefits of
vaccination after HPV exposure should be provided
• HPV vaccination is not currently recommended for
women aged < 9 or > 26
• New recommendation for quadrivalent HPV vaccine
(Gardasil®) vaccination in males to prevent genital warts
– May decrease transmission of HPV infection
CDC=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
HPV vaccine will not protect against HPV infection
caused by other high-risk types, so we still continue
to need --- we still need to screen women with the
Pap smear because certainly they can have an HPV
infection from other high-risk types that would lead
to cervical dysplasia or cervical cancer.
The
vaccine does not treat an HPV infection. In fact,
there is no treatment currently for HPV infections. It
only prevents the infection from occurring. For that
reason, to be most effective, the vaccine should be
given prior to the initiation of sexual activity, as HPV
is largely transmitted through sexual activity.
A vacina contra o HPV não protege contra a
infecção por HPV causada por outros tipos de alto
risco, por isso ainda precisamos... fazer o
rastreamento de mulheres com o exame de
Papanicolaou, porque certamente elas podem ter
uma infecção por HPV de outros tipos de alto risco
que resultaria em displasia cervical ou câncer
cervical. A vacina não trata a infecção pelo HPV. Na
verdade, não existe no momento tratamento para
infecções pelo HPV. Ela só impede que a infecção
ocorra. Por essa razão, para ser mais eficaz, a
vacina deve ser administrada antes do início da
atividade sexual, pois o HPV é transmitido
sobretudo por meio da atividade sexual.
The current Centers for Disease Control
recommendations for HPV vaccination are that
females aged 11 to 12 should receive routine
vaccination with a series of three vaccinations over
a six-month interval. Females aged 13 through 26
may obtain vaccination as a catch-up mechanism,
but they should also be counseled that, if they have
become sexually active, they may have already
been infected with one of the HPV types in the
vaccine, and would not, thus, obtain protection
against that particular HPV type. For that reason,
they may have diminished benefits from the
vaccination.
HPV vaccination is not currently
recommended for women under the age of 9 or over
the age of 26, although studies are currently
ongoing. Recently, there have been some new
®
recommendations for Gardasil vaccination in males
to prevent the development and transmission of
®
genital warts. Certainly, since Gardasil vaccination
would also prevent HPV infection with 16 and 18 in
the males, it may help to decrease the transmission
As recomendações atuais dos Centros para o
Controle de Doenças para a vacinação contra o
HPV indicam que meninas de 11 e 12 anos de
idade devem receber vacinação de rotina com uma
série de três doses da vacina em um intervalo de
seis meses. Pessoas do sexo feminino com idades
de 13 a 26 anos devem obter a vacinação como um
mecanismo de recuperação, mas elas também
devem ser informadas de que se já forem
sexualmente ativas, poderiam ter sido infectadas
com um dos tipos de HPV presentes na vacina, e,
por conseguinte, não obteriam proteção contra esse
tipo específico de HPV. Por essa razão, talvez não
recebam todos os benefícios da vacinação.
Atualmente, a vacinação contra o HPV não é
recomendada para crianças menores de 9 anos ou
para mulheres maiores de 26 anos, embora os
estudos ainda estejam em andamento.
Recentemente, saíram novas recomendações para
a vacinação com Gardasil® em homens para
prevenir o desenvolvimento e a transmissão de
11
of these two HPV types to their sexual partners,
thus potentially reducing the risk further for the
population.
Cancer Prevention:
Principles and Clinical Practice
Conclusions
• Many primary prevention strategies are available
to reduce the risk of developing cancer to include
lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise and
avoidance of smoking and excessive sun exposure
• For those at increased risk for the disease,
prophylactic surgery and chemoprevention
may be beneficial as well
In conclusion, there are many primary prevention
strategies that are available to reduce a person’s
risk of developing cancer. These include lifestyle
modifications, that you heard Sally talk about, such
as diet and exercise, avoidance of smoking, or
smoking cessation if you already smoke, and
excessive sun exposure. Also for those who are at
increased risk of the disease, we have other
options, such as prophylactic surgical interventions
and chemoprevention.
I hope that you have
enjoyed this lecture and we welcome your feedback.
Thank you.
verrugas genitais. Certamente, uma vez que a
vacinação com Gardasil® também serve para
prevenir a infecção pelo HPV em jovens do sexo
masculino com 16 e 18 anos de idade, pode ajudar
a diminuir a transmissão desses dois tipos de HPV
aos parceiros sexuais, reduzindo ainda mais o risco
para a população.
Em conclusão, existem muitas estratégias de
prevenção primária disponíveis para reduzir o risco
de uma pessoa contrair câncer. Elas incluem
mudanças no estilo de vida, de que vocês ouviram
a Sally falar a respeito, como dieta e exercício
físico, evitar fumar ou parar de fumar se a pessoa já
fuma, e a exposição excessiva ao sol. Também
para aqueles com maior risco para a doença temos
outras opções, como as intervenções cirúrgicas
profiláticas e a quimioprevenção. Espero que
tenham gostado desta palestra e agradeceríamos
os seus comentários. Obrigada.
12