Linguagens, Códigos e suas
Tecnologias – Inglês
Ensino Médio, 1ª Série
Simple Past/ Irregular form
O SIMPLE PAST EXPRESSA AÇÃO DETERMINADA E
CONCLUÍDA NO PASSADO.
EXEMPLOS:
• Nós trouxemos os livros ontem;
• We brought the books yesterday.
• Eu ensinei Inglês na semana passada;
• I taught English last week.
• Ele pagou seus débitos no ano passado;
• He paid his accounts last year.
• Eu vi quando você chegou.
• I saw when you arrived.
ALGUNS ADVÉRBIOS DE TEMPO IMPORTANTES QUE
DETERMINAM O PASSADO:
YESTERDAY = ONTEM;
• LAST WEEK = SEMANA PASSADA;
• LAST YEAR = ANO PASSADO;
• LAST MONTH = MÊS PASSADO;
• THE DAY BEFORE YESTERDAY = ANTEONTEM;
• TWO DAYS AGO = DOIS DIAS ATRÁS.
FORMAÇÃO:
Para a formação do “Simple Past”, como regra
geral, acrescenta-se “ed” ao infinitivo sem “to”.
EXEMPLO:
I need you – I needed you yesterday.
Todavia, nem todos os verbos seguem essa regra.
OBSERVAÇÃO:
Os verbos que não seguem essa regra são denominados
IRREGULARES, os quais serão analisados a seguir:
Ex.: I see you everyday .(Present) / I saw you last week.(Past)
Eu vejo você todos os dias.
/ Eu vi você ontem.
OS VERBOS IRREGULARES PODEM SER:
UNIFORMES:
•
Ou seja, possuindo apenas uma forma para
expressar o Presente, o Passado e o Particípio
Passado.
Exemplo:
PRESENTE
( cut )
Cortar
PASSSADO
(cut)
Cortava/cortou
P. PASSADO
(cut )
Cortado
Em alguns contextos o tempo verbal será
identificado pelo advérbio:
• I cut carrots every day.
• Eu corto cenouras todos os dias.
• I cut carrots yesterday.
• Eu cortei cenouras ontem
• I have cut carrots every day.
• Eu tenho cortado cenouras todos os dias.
IRREGULAR BIFORME:
Os que possuem duas formas diferentes para
expressar o Presente, Passado e o Particípio
Passado.
• PRESENTE
PASSSADO
P. PASSADO
To bring
• (Trazer)
Brought
( trazia)
Brought
(trazido)
IRREGULAR TRIFORME:
São os verbos que possuem uma forma
diferente para o Presente, outra para o Passado
e outra para o Particípio Passado.
EXEMPLO:
PRESENTE
PASSADO
P. PASSADO
To see
Saw
Seen
( Ver )
( via/viu )
( visto )
See some examples by clicking here
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZYfn7C9gKto&feature=relmfu
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST:
Diferente dos Verbos regulares, os Verbos
Irregulares são os que já possuem suas
formas do Presente diferentes e/ou iguais as
do passado e do Particípio Passado. Observe
alguns exemplos:
PRESENTE
PASSSADO
P. PASSADO
To awake
awoke
awoken
( acordar )
( acordou )
( Acordado )
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-2
To be
(Ser/ estar)
To bring
(Trazer)
To buy
(Comprar)
Was/ were
(Era /Estava)
Brought
(Trazia)
Brought
(comprou)
been
(Sido/ Estado)
Brought
(Trazido)
Brought
(Comprado)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-3
To come
(Vir)
Can
(Poder)
To do
(Fazer)
Came
(Veio)
Could
(Podia)
Did
(Fazia)
Come
(Vindo)
Could
(Podido)
Done
(Feito)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-4
To dig
(Cavar)
To dream
(Sonhar)
To drive
(Dirigir)
Dug
(Cavava)
Dreamt
(Sonhava)
Drove
(dirigia)
Dug
(cavado)
Dreamt
(Sonhado)
Driven
(Dirigido)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-5
To eat
(Comer)
To fight
(Lutar)
To feel
( Sentir)
To find
(Achar)
Ate
(Comia)
Fought
(Lutava)
Felt
(Sentia)
Found
(Achava)
Eaten
(Comodo)
Fought
(Lutado)
Felt
(Sentido)
Found
(Achado)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-6
• To forget
• (Esquecer)
• To get
• (Conseguir)
• To grow
• (Crescer)
Forgot
Forgot/forgotten
(Esquecia)
(Esquecido)
Got
Got
(Conseguia)
(Conseguido)
Grew
Grown
(Crescia)
(Crecido)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-7
To hear
Heard
(Ouvir)
(Ouvia)
To Hide
Hid
(Esconder)
(Escondia)
To know
Knew
(Saber/conhecer)
(Sabia)
Heard
(ouvido)
Hidden
(Escondido)
Known
(Sabido)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-8
To learn
(Aprender)
To mean
(Querer dizer)
To run
(Correr)
Learnt
(Aprendia)
Meant
(quis dizer)
Ran
(Corria)
Learnt
(Aprendido)
Meant
(Querido dizer)
Run
(Corrido)
IRREGULAR VERBS LIST-9
To ride
Rid
Ridden
(cavalgar)
(Cavalgava)
(Cavalgado)
To see
Saw
Seen
(Ver)
(via)
(Visto)
To sing
Sang
Sung
(Cantar)
(Cantava)
(Cantado)
To understand Understood
Understood
( Entender )
(Entendia)
(Entendido)
See how to pronunciate some of them by clicking here
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jLbe_EaP-7A
IMPORTANTE!
• A forma verbal do Simple Past só será
utilizada na Afirmativa.
EXEMPLO:
I went to school yesterday.
Eu fui a escola ontem.
Did you go...?
Você foi...?
Main wh-words:
How / Como
Where / Aonde; Onde
What / O que
Who/ Quem
When/ Quando
Why/Por que
HOW TO ASK QUESTIONS IN THE SIMPLE PAST?
• No “Simple Past”:
• Adicionamos “Did” antes do sujeito da oração com o
verbo principal no infinitivo sem “to”:
• EXEMPLOS:
• You WENT to Rio last week.
• Where Did you GO on your last vacation?
• Exceto com os verbos: ser, estar, haver, dever e
poder, com os quais a pergunta é feita pela inversão.
• Ex.: You could help me. – Could you help me?
•
•
Click here for exemples on practicing
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2v5AlmrqEug&feature=relmfu
A NEGATIVA TAMBÉM EXCLUI A FORMA DO “SIMPLE PAST”:
Exemplo: The brazilian indians knew how to
survive here;
The explorers did not know about it!
• Exceto com os verbos: ser, estar, haver, dever
e poder, com os quais a negativa é feita pelo
acréscimo de not após os mesmos.
• Ex.: I could help you. – I could not help you?
OBSERVAÇÃO:
• No “Simple Past” a forma vebal será a mesma
para todas as Pessoas do Verbo.
• EXEMPLO:
I went to S. Paulo last year.
You went to S. Paulo last year.
He went to S. Paulo last year.
She went to S. Paulo last year.
It went to S. Paulo last year.
We went to S. Paulo last year.
They went to S. Paulo last year.
COMO MELHORAR A PRONÚNCIA DAS FORMAS
VERBAIS DO PASSADO IRREGULAR?
Uma das dificuldades da Língua inglesa é pronunciar, não só as
formas verbais, mas as palavras de uma forma geral. Assim, é necessário
um estudo mais aprofundado sobre os sons da Língua Inglesa.
Os melhores dicionários de Inglês trazem consigo a simbologia
fonética, a qual tem sido muito útil ao esclarecimento da pronúncia do
Simple Past, bem como das palavras em geral.
Clique aqui para conhecer essa ferramenta
http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish/grammar/pron/sounds/
OBSERVAÇÃO:
• Há verbos irregulares que são uniformes
heterófonos, visto que os mesmos possuem a
mesma forma, entretanto, possuem sons
diferentes.
• Exemplo:
• PRESENTE
PASSSADO
P. PASSADO
Read/ri:d/
Read /rƐd/
Read /rƐd/
Ler
Lia /leu
Lido
IRREGULAR ADMITINDO FORMA REGULAR:
ALGUNS VERBOS ADMITEM AS FORMAS REGULAR
E IRREGULAR PARA O PASSADO E O PARTICÍPIO.
EXEMPLO:
PRESENTE
To dream
PASSSADO
dreamt / dreamed
P. PASSADO
dreamt / dreamed
COMO HÁ MAIS DE 270 VERBOS IRREGULARES, COMECE COM
OS MAIS COMUNS:
Click here for some more information on
Irregular Verbs
http://www.youtube.com/user/AlexESLvid#p/u/8/XAFPfyZ8D1Q
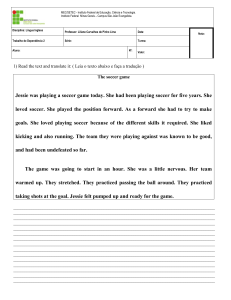
EXERCISES:
• 1- Complete the blanks with the correct Past form of
the verbs in parenthesis:
• a) The boy... to school alone yesterday.(go)
• b) I ...your mother at the shopping last Suturday.
(see)
• c) The students ... to study hard to pass the exam last
year. (have)
• d) The teacher.... The student how to spell this word
correctly last class. (teach)
The following are examples on how to use the Past Simple
Tense of some verbs. Before clicking, could you guess which ones
are Irregular?
• 1- I love nature.
• a.loved
• 2- I speak English
fluently.
• a. spoke
• 3- I protect
environement .
• a. protected
• 4- I see you every day.
• a. saw
• 5- we can make it
better!
• a. could
• 6- We need to emprove
our English
• a. needed
Read and answer:
A pretty little boy.
There was a fourteen- year-old boy, who lived in London. His name
was Robert. He loved to study. He had a nice family. His father´s name was
Peter and his mather was Nataly. He had two brothers – Phill and John –. They
were a really happy family!
Once upon a time, he knew a friend who did not think about study
as he did. However, he liked him so much... And then that new friend started
showing him other ‘values’, among them drug was included. That was the
beggining of an end. He could know another even bigger, but not greater
“family”, called Burning Gang, completly different from the lovely and
responsible one that he had. It was there that he got faster to the end of his
own life, by having an umpleasant experience with drugs.
The story may be the same that you might have already known
about.However, you can choose its end, by selecting his or her relationship.
NOW YOU ANSWER:
1- Which verbs are irregular ones.
• 2 – Construct five questions about the text
and then discuss with your classmates about
the answers.
• 3- Give it an outline about its sense in
Portuguese.
THIS IS THE END OF THE IRREGULAR SIMPLE PAST CLASS.
• I HOPE YOU HAVE ENJOY IT!