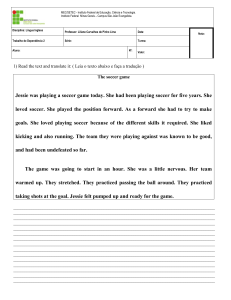
Aulas 26, 27, 28 e 29 de Inglês
26) Where you were yesterday?
Você deve se lembrar de que o verbo to be em inglês quer dizer ser ou estar, certo? Ele
é um verbo que usamos muito.
Antes de aprendermos o passado desse verbo, vamos revisar o presente:
I am a secretary.
You are a nurse.
He is at home.
She is a doctor.
It is a book.
We are at work.
You are students.
They are here.
No passado, o verbo vai funcionar do mesmo modo, só que é conjugado de modo
diferente:
Exemplos:
She was at home. (forma afirmativa)
She was not at home. (forma negativa)
Was she at home? (forma interrogativa)
As frases abaixo estão no presente. Reescreva-as usando o passado:
a) She is a nurse
.......................................................................................................................... .
b) They are teachers.
.......................................................................................................................... .
c) Are you at home?
.......................................................................................................................... .
d) Where are you?
.......................................................................................................................... .
e) He is here.
.......................................................................................................................... .
f) We are not doctors.
.......................................................................................................................... .
g) Mary is at school.
.......................................................................................................................... .
h) Are Paul and John at work?
.......................................................................................................................... .
27) I worked a lot yesterday
Em inglês, temos dois tipos de verbos: os regulares e os irregulares. Os verbos
regulares são assunto de nossa aula de hoje.
Os verbos regulares em inglês são a maioria (mas não todos, cuidado!).
Eles fazem o passado acrescentando-se -ed. É simples; só precisamos acrescentar -ed
ao final do verbo para termos seu passado.
Exemplos:Work no presente
Worked no passado
Virgínia and Nei work at Sunshine Travel Agency.
They worked a lot yesterday
É importante lembrar que acrescentamos -ed à forma básica do verbo no presente. Ou
seja, sem s ou es característicos da terceira pessoa do singular.
Veja:
Virgínia works at Sunshine.
She worked a lot yesterday.
O passado é conjugado da mesma maneira para todas as pessoas.
Além disso, existem outras regras:
· quando o verbo terminar em y precedido de consoante, tiramos o y e colocamos ied.
Exemplo: study - studied.
· quando o verbo terminar em e só precisamos acrescentar ddddd.
Exemplo: Love - Loved.
Complete o texto usando o passado dos verbos entre parênteses.
It ............... (to be) a beautiful day. In the morning João ............... (walk) to the park
and ............... (play) basketball with his friends. After the game, they ............... (relax) and
...............(walk) back home. In the afternoon, João ............... (stay) at home. He ...............
(study) Math and ............... (cook) dinner. After dinner, he ............... (watch) TV.
Reescreva as frases, no passado.
a) She studies English.
..........................................................................................................yesterday.
b) They watch T.V.
..........................................................................................................yesterday.
c) João and Mariana walk to the park
......................................................................................................... last night.
d) He is an astronaut.
........................................................................................................ in the past.
28) I didn't have time
Na Aula 26 aprendemos a descrever ações no passado usando verbos regulares.
Você se lembra da forma afirmativa do passado com verbos regulares?
Agora vamos ver como fazer a negativa do passado com verbos regulares. Usamos:
Did é o auxiliar do passado. Assim como usávamos do no presente, usamos did no
passado.
Vale lembrar que, quando usamos o auxiliar did, o verbo perde o ed, sua terminação de
passado. Veja:
She worked yesterday (na afirmativa).
She did not work yesterday (na negativa o verbo perdeu o ed).
Outro detalhe importante: did not é a mesma coisa que didn't.
Podemos dizer:
She did not work yesterday.
Ou
She didn’t work yesterday.
Passe para a negativa:
a) They stayed in Mexico City for two weeks.
........................................................................................................................... .
b)He planned his work well.
........................................................................................................................... .
c) The woman fainted on the street.
........................................................................................................................... .
d) Sally arrived home very late.
........................................................................................................................... .
e) She worked in that company for many years.
........................................................................................................................... .
f) Mariana called Gino at 10 p.m.
........................................................................................................................... .
g) She waited for him for one hour.
........................................................................................................................... .
h)Marcia walked to school with Mario.
........................................................................................................................... .
Complete as frases como no exemplo:
Exemplo: I didn’t go (not/go) to work yesterday because I wasn’t (not/be) very well.
a) Tom ................................... (not/shave) this morning because he .........................
(not/want) to.
b) She ........................... (not / try) the food because she .............................. (not / be )
hungry.
c) I ................................... (not/be) interested in the book because I .........................
(not/like) the subject.
29) Did you work yesterday?
Para fazermos perguntas no passado, com verbos regulares, usamos o auxiliar did.
Faça perguntas para as respostas abaixo:
a) ............................................................................................ (work yesterday)
No, I didn’t. I was sick.
b) ............................................................................................ (study last week)
Yes, I did. I have an exam today.
c) ........................................................................................... (see sky last vacation)
Yes, I did. It was nice!