Colégio Ressurreição
Atividade de Inglês
Profª.: Sandra Miguel
3º. bimestre 2012
Conteúdo: Simple Past, Past Continuous e Past Perfect
Nome do(a) aluno(a): ________________________________________________nº.______3ª. Série _____.
SIMPLE PAST: Ações que começaram e terminaram no passado.
► Regular Verbs: (Verbo regulares: são chamados assim porque seguem as regras abaixo.)
1. Regra geral: acrescenta-se “ED” no final do verbo: To clean + ed = cleaned.
To watch + ed = watched.
2. Verbos terminados em CONSOANTE + Y, elimina o “y” e adiciona “IED”: To study = studied.
3. Verbos monossílabos (uma sílaba) terminados em CONSOANTE (C) + VOGAL (V) + CONSOANTE (C), ‘dobra’ a última
consoante e adiciona ED: To stop + p + ed = stopped
4. Verbos Oxítonos (última sílaba “forte”) terminados em consoante (C) + vogal (V) + consoante (C), ‘dobra’ a última
consoante e adiciona ED: To occur + r + ed = occurred
FICA IGUAL PARA TODAS AS PESSOAS
To clean
To watch
To wash
To pass
To try
To cry
Limpar
Assistir
Lavar
Passar
Tentar (fazer algo)
Chorar
I
You
He
She
It
We
You
They
Michael
Jane
cleaned, watched,
studied, washed,
passed, tried, cried
Affirmative
Pronome/nome
You
+
verbo (+ ed)
liked
Pronome/nome
You
+
did not / didn’t
didn’t
+
complemento
lizards.
Negative
Interrogative
Did
+ Pronome/nome
Did
you
+ verbo
like
+
+ complemento
lizards
verb
like
+
complemento
lizards.
?
?
► Irregular verbs: são chamados assim porque não seguem nenhuma regra. Para sabê-los é preciso consultar a SEGUNDA
COLUNA a lista de verbos.
PAST
INFINITIVE
PAST PARTICIPLE
TRANSLATION
Was/were
To be
Been
Ser/estar
Bought
To buy
Bought
Comprar
Made
To make
Made
Fazer
You bought a car.
Affirmative
You didn’t buy a car.
Negative
Did you buy a car?
Interrogative
► KEY WORDS: YESTERDAY, LAST NIGHT/ WEEK/MONTH/YEAR, AGO, IN THE PAST ETC.
You liked lizards in the past.
They didn’t wash the car yesterday
Did Michael study Science last year?
Jane ate banana two hours ago. We made a cake last night.
Did she swim a lot last week?
PAST CONTINUOUS: (PHOTO) registro de um momento particular no passado. Por exemplo, ontem à noite eu estava
assistindo a um filme. Ele começou às 19:00 e terminou às 21:00. Portanto, às 20:00 “Eu estava assistindo ao filme”.
Yesterday (Past)
7:00 p.m.
8:00 p.m.
9:00 p.m.
I was watching the film.
The film started.
The film ended.
Affirmative
Pronoun or Name+ was / were+ verb(ing)
They were having a bath. She was living in London.
You were waiting for the bus.
Negative
Pronoun or Name+ was / were+not+ verb(ing)
They were not having a bath.
She was not living in London.
Interrogative
Was / Were+ Pronoun or Name+verb(ing)?
Were they having a bath? Was she living in London?
You were not waiting for the bus.
Were you waiting for the bus?
OBS.: as regras para se adicionar ING ao verbo são as mesmas do Present Continuous.
To do = doing
to make = making
to run = running
to lie = lying
KEY WORDS: YESTERDAY, LAST, AGO.
Yesterday, at 3:00 a.m. he was sleeping.
Last night, at 3:00 a.m. he was not sleeping.
Was he sleeping two hours ago?
PAST PERFECT: “passado dentro do passado”.
Affirmative:
Pronoun/name + had + Past participle
I had finished my work.
You had stopped before me.
Negative:
Pronoun/name + had + not + Past participle
I had not finished my work.
You had not stopped before me.
Interrogative:
Had + pronoun/name + Past participle?
Had you finished your work?
Had you stopped before me?
More examples:
She had gone to school.
We had not left. Had you arrived?
Had they eaten dinner?
PAST PARTICPLE:
Regular: é igual ao passado simples dos verbos irregulars, terminando com ED.
Irregular: Para sabê-los é preciso consultar a TERCEIRA COLUNA a lista de verbos.
The train left at 9:00 a. m. We arrived at 9:15a.m. When we arrived, the train had left.
9:00 – The train left the station. (passado “distante” – antes)
9:15 – We arrived at the station. (passado “recente” – depois)
The train had left
Passado remoto
when we arrived.
Passado recente
Imagine que vocês chegaram à estação às 9:15. O funcionário da estação diz a vocês:
"You are too late. The train has left." Você está muito atrasado. O trem tem partido.
Mais tarde, você conta a seus amigos:
"We were too late. The train had left." Nós estávamos muito atrasados. O trem tinha partido.
Mais exemplos:
I wasn't hungry. I had just eaten.
They were hungry. They had not eaten for five hours.
I didn't know who he was. I had never seen him before.
A: Mary wasn't at home when I arrived.
B: Really? Where had she gone?
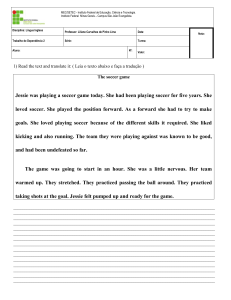
EXERCISE: Complete as lacunas com os verbos entre parênteses nos tempos pedidos. (SOMENTE A RESPOSTA)
SIMPLE PAST
1) …… you …… (to see) that little girl with the red hair?
2) My husband ……(to spend) our honeymoon fund in a new beetle.
3) How …… you …… (to know) that?
4) When I …… (to come) to, I was surrounded by the fire.
5) How ……. They …… (to live) with little money?
1. DID/SEE
2. SPENT
3. DID/KNOW
4. CAME
5. DID/LIVE
PAST CONTINUOUS
1) I …… (to wait) for some support.
2) They …… just …… (to talk) about you.
3) …… the baby …… (to cry) 10 minutes ago?
4) Alan…… (not/to smoke) his pipe in his room.
5) Tom and Ted…… (to look) at the car in the garage
1. WAS WAITING
2. WERE/TALKING
3. WAS/CRYING
4. WAS NOT SMOKING
5. WERE LOOKING
PAST PERFECT
1) Paul ……. (to finish) half the work, when they ……. (to come) in.
2) He'd been a businessman before he ……. (to become) an actor.
3) Roberto …… (to write) another song.
4) The nurses …… (not/ to lock) the front door.
5) …… they …… (to do) anything before they met me?
1. HAD FINISHED/CAME
2. BECAME
3. HAD WRITTEN
4. HAD NOT LOCKED
5. HAD/DONE