Revisão passado simples
Passado Simples - Simple Past
O Simple Past descreve uma ação que já ocorreu e que não ocorre mais. A ação teve início e fim no
passado. No Simple Past o verbo não é flexionado em nenhuma pessoa, repetindo-se em todas elas.
Verbos Regulares - Regular Verbs
Primeiramente iremos estudar o Simple Past dos verbos regulares que, de um modo geral, é formado
acrescentando -d ou -ed ao infinitivo dos verbos. Observe a tabela abaixo:
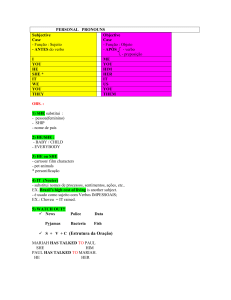
- FORMA AFIRMATIVA:
I
worked yesterday
You
worked yesterday
He
worked yesterday
She
worked yesterday
It
worked yesterday
We
worked yesterday
You
worked yesterday
They
worked yesterday
- PARTICULARIDADES DA ORTOGRAFIA DO SIMPLE PAST:
1. Os verbos terminados em e recebem apenas a letra -d ao infinitivo do verbo. Veja alguns exemplos
abaixo:
hope - hoped
change - changed
like - liked
behave - behaved
lie - lied
live - lived
love - loved
arrive - arrived
invite - invited
snore - snored
2. Se o verbo tiver uma única sílaba ou terminar em sílaba tônica formada
porconsoante/vogal/consoante, dobra-se a última consoante e acrescenta-se -ed:
stop - stopped
permit - permitted
occur - occurred
rob - robbed
admit - admitted
prefer - preferred
omit - omitted
control - controlled
drop - dropped
plan - planned
shop - shopped
OBSERVAÇÃO: No Inglês Britânico, se o verbo termina com a letra "L", dobra-se
essa consoante mesmo que a última sílaba não seja tônica.
travel - travelled
rival - rivalled
3. Os verbos terminados em y precedido de consoante trocam o y por -ied:
study - studied
carry - carried
worry - worried
try - tried
hurry - hurried
cry - cried
OBSERVAÇÃO: Quando o y for precedido de vogal, não há mudança ortográfica,
bastando apenas acrescentar -ed ao verbo:
pray - prayed
enjoy - enjoyed
obey - obeyed
play - played
4. Os verbos terminados em consoante/vogal/consoante cuja sílaba tônica não é a última nãodobram
a consoante, apenas recebem -ed:
listen - listened
develop - developed
open - opened
fasten - fastened
suffer - suffered
visit - visited
wonder - wondered
offer - offered
- USOS:
O Simple Past é usado para expressar:
1. Ações acabadas em um tempo definido, é frequentemente usado com advérbios de tempo
comoyesterday, yesterday morning, last week, last month, last night, the day before yesterday,
three years ago, in 1998, in the twentieth century, etc. O quando o fato ocorreu pode ser expresso
ou apenas subentendido.
Susan helped him last night. (Susan o ajudou ontem à noite.)
My parents traveled to Roma in 2005 and they enjoyed it a lot. (Meus pais viajaram para Roma em 2005 e
gostaram muito da viagem.)
I liked to read fairy tales when I was a child. (Eu gostava de ler contos de fadas quando era criança.)
Yesterday we entered the class late, today we have to enter on time. (Ontem entramos na sala de aula
atrasados, hoje temos que entrar na hora.)
Those students studied hard last semester. (Aqueles alunos estudaram bastante no último semestre.)
The Second World War ended in 1945. (A Segunda Guerra Mundial teve fim em 1945.)
2. Um fato anterior ao momento da fala, mas que ainda dura no momento do passado que está
sendo mencionado. Nesses casos é comum aparecer expressões como when, while, whenever.
Robert hated blues, but his sister loved it. (Roberto detestava blues, mas a irmã dele adorava.)
While the children played in the garden, their mother cleaned the house. (Enquanto as crianças brincavam
no jardim, a mãe delas limpava a casa.)
3. Indicar hábitos ou situações passadas. Nesses casos também é comum aparecer expressões
como when, while, whenever.
When I lived in London, I worked in a pub. (Quando morei em Londres, trabalhei em um bar.)
Whenever someone walked past the gate, the dog barked. (Toda vez que alguém passava no portão, o
cachorro latia.)
- FORMA NEGATIVA E INTERROGATIVA:
As formas negativas e interrogativas do Past Simple são feitas com o verbo auxiliar Did (passado de Do),
acompanhado do verbo principal no infinitivo sem to.
1. Forma Negativa:
Para formar uma oração negativa no Simple Past, usa-se did not para todas as pessoas, pois como já
vimos anteriormente, no Simple Past o verbo não é flexionado em nenhuma pessoa, repetindo-se em
todas elas. O verbo auxiliar (did) + not posiciona-se sempre entre o sujeito e o verbo
principal.Observe a tabela abaixo:
I
did not work
You
did not work
He
did not work
She
did not work
It
did not work
We
did not work
You
did not work
They
did not work
* FORMAS ABREVIADAS: did not - didn't. Ambas as formas são corretas e bastante comuns na Língua
Inglesa. Observe alguns exemplos com as formas abreviadas:
Steve didn't work as much as Paul. (Steve não trabalhou tanto como Paul.)
He didn't pay the bill. (Ele não pagou a conta.)
She didn't work yesterday. (Ela não trabalhou
ontem.)
He didn't taste the pasta at lunch. (Ela não provou a massa na hora do almoço.)
We didn't say that! (Nós não falamos isso!)
NEGATIVE FORM: SUJEITO + DID NOT + VERBO NO
INFINITIVO SEM TO
2. Forma Interrogativa:
Para formar uma oração interrogativa no Past Simple, usa-se did antes do sujeito. O verbo permanece no
infinitivo sem "to", uma vez que, no Simple Past o verbo não é flexionado em nenhuma pessoa,
repetindo-se em todas elas. Veja:
Did
I
work?
Did
You
work?
Did
He
work?
Did
She
work?
Did
It
work?
Did
We
work?
Did
You
work?
Did
They
work?
Did he call me yesterday? (Ele me ligou ontem?)
Why did he do that? (Por que ele fez isso?)
Did you drink wine last night? (Você tomou vinho ontem à noite?)
Did you clean your bedroom? (Você limpou o seu quarto?)
When did he confess the crime? (Quando ele confessou o crime?)
INTERROGATIVE FORM: DID + SUJEITO + VERBO NO INFINITIVO
SEM TO
Verbos Irregulares - Irregular Verbs:
Os verbos irregulares não seguem as regras gerais de formação do Simple Past, isto é, cada um tem
uma forma própria de passado. Sendo assim, é necessário estudá-los um a um. Ver lista dos verbos
irregulares.
A- Complete with the right form of the verb and use the word ago. Follow the example.
Example I saw (see) her two weeks ago.
1. He __________ (catch) a bus an hour __________.
2. I __________(drink) a cup of tea ten minutes __________.
3. He __________(speak) to the director two days __________.
4. She __________(meet) them a month __________.
5. They __________(have) lunch two hours __________.
6. John __________(open) the window half an hour __________.
7. My sister__________(cook) dinner an hour __________.
8. Mr. Field __________(telephone) just a minute __________.
9. they __________(be) in Paris a year __________.
10. I __________(eat) a sandwich an hour __________.
B- Fill in the blank spaces with the past simple of the verbs in brackets.
1. She __________(ask) me questions.
2. __________ (she / arrive) in time?
3. They __________(not/ eat) any chocolate.
4. __________(you/see) anybody there?
5. he __________(know)something about it.
6. We __________(meet) her last week.
7. Why __________(they / to be) so angry?
8. __________(she / clean) the blackboard?
9. Two years ago we __________(visit) Italy.
10. They __________(not / look) after the little girl.
11. The doctor __________(not / tell) her to stay in bed.
12. Who __________(you / give) it to?
13. __________(there to be) many people in front of the place?
14. It __________(not / rain) yesterday.
15. __________(he / not/ find9 the key?
16. __________ ( Tom / to be) at work?
17. Why __________( they / not / tell) me the truth about it?
18. He __________(never / drive) faster than he should.
19. We __________ (not/ walk) a long way.
20. __________(you/have) a comfortable trip?
21. When __________She / wash her car?
22. __________(you / visit) your grandparents last week?
23. __________ (the teacher / not / talk) to Peter after the lesson?
24. __________(she / not / buy) a blue jacket?
25. What colour __________(they/paint) their room?
26. He __________(find) the key on his way home?
27. __________(she / know) all the students’ names?
28. They __________(not / return) at 9.
29. They __________(not/leave) the books at home. They __________(leave) them at school.
30. He __________(not / wear) the old jeans. He __________(wear) the new ones.