Student_________________________________________ group_____ unit_____ date____/____
The Past Tense indicates that an action is in the past relative to the speaker or writer.
- when the time period has finished: “We went to Chicago last Christmas.”
- when the time period is definite: “We visited Mom last week.”
- with for , when the action is finished: “I worked with the FBI for two months.”
Note:
a) Ele descreve uma ação que já ocorreu e que não se repete mais em um tempo específico no
passado. Às vezes é mencionado o tempo específico desta ação no passado.
b) A ação teve início e fim no passado.
c) Nele o verbo não é flexionado em nenhuma pessoa, repetindo-se em todas elas igualmente.
Regular Verbs
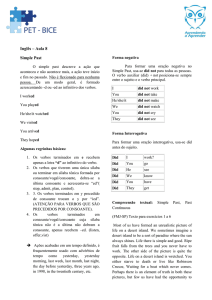
O Simple Past dos verbos regulares, de um modo geral, é formado acrescentando -d ou -ed ao
infinitivo dos verbos:
REGULAR VERB
INFINITIVE
PAST
trabalhar
to work
worked
gostar
to like
liked
FORMS
Aff.: I worked last week.
Eu trabalhei semana passada.
Neg.: I did not work last week. (didn’t)
Eu não trabalhei semana passada.
Int.: Did i work last week?
Eu trabalhei semana passada?
ORTHOGRAPHY
1. Os verbos terminados em e recebem apenas a letra -d ao infinitivo do verbo. Veja alguns
exemplos abaixo:
hope – hoped / behave – behaved / lie – lied / live – lived / change – changed / love - loved
arrive – arrived / invite – invited / snore – snored
2. Se o verbo tiver uma única sílaba ou terminar em sílaba tônica formada
por consoante/vogal/consoante, dobra-se a última consoante e acrescenta-se -ed:
stop – stopped / permit – permitted / occur – occurred / rob – robbed / admit - admitted
prefer – preferred / omit – omitted / control – controlled / drop – dropped / plan - planned
shop - shopped
Note: No Inglês Britânico, se o verbo termina com a letra "L", dobra-se essa consoante mesmo
que a última sílaba não seja tônica.
travel – travelled / rival - rivalled
3. Os verbos terminados em y precedido de consoante trocam o y por -ied:
study – studied / carry – carried / worry – worried / try – tried / hurry – hurried / cry - cried
Note: Quando o y for precedido de vogal, não há mudança ortográfica, bastando apenas
acrescentar -ed ao verbo:
pray – prayed / enjoy – enjoyed / obey – obeyed / play - played
4. Os verbos terminados em consoante/vogal/consoante
última não dobram a consoante, apenas recebem -ed:
cuja sílaba tônica não é a
listen – listened / develop – developed / open – opened / fasten – fastened / suffer - suffered
visit – visited / wonder – wondered / offer – offered
Irregular Verbs
Estes verbos não seguem a regra geral dos verbos regulares no passado ou mesmo particípio,
pois apenas são diferentes e sem regras para sua mudança. Entretanto, podem ser aprendidos ao
observarmos a forma como eles se apresentam.
a) São iguais a base (infinitive)
infinitive
past
past participle
bet
bet
bet
cast
cast
cast
b) São diferentes da base (infinitive) mas iguais no past e past participle
buy
bought
bought
bring
brought
brought
c) Apenas a base é igual ao past participle
come
came
come
run
ran
run
d) Todos são diferentes da base (infinitive)
drink
drank
drunk
sing
sang
sung
swim
swam
swum
5. SENTENCES ( regular and irregular verbs )
a) Completed Action in the Past
I saw a movie yesterday.
I didn't see a play yesterday.
Last year, I traveled to Japan.
Last year, I didn't travel to Korea.
Did you have dinner last night?
She washed her car.
He didn't wash his car.
b) A Series of Completed Actions in the Past
I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim.
He arrived from the airport at 8:00, checked into the hotel at 9:00, and met the others at
10:00.
Did you add flour, pour in the milk, and then add the eggs?
c) Duration in Past ( for two years; all day; thirty minutes; one hour; four weeks, etc)
I lived in Brazil for two years.
Shauna studied Japanese for five years.
They sat at the beach all day.
They did not stay at the party the entire time.
We talked on the phone for thirty minutes.
A: How long did you wait for them?
B: We waited for one hour.
d) Habits in the Past (always, often, usually, never, when I was a child, when I was younger, etc.)
I studied French when I was a child.
He played the violin.
He didn't play the piano.
Did you play a musical instrument when you were a kid?
She worked at the movie theater after school.
They never went to school, they always skipped class.
e) Past Facts or Generalizations
She was shy as a child, but now she is very outgoing.
He didn't like tomatoes before.
Did you live in Texas when you were a kid?
People paid much more to make cell phone calls in the past.
f) Examples of Questions in the Past Tense
Did you study?
Aff.: Yes, I did. Neg.: No, I didn’t.
When did you study? – I studied last night.
Where did you study? – I studied at the library.
Did you go to work yesterday? - Yes, I did go to work yesterday.
Did they arrive on time? - Yes, I did.
Did she like the surprise? - No, I didn’t.
Where did she go? - She went to the zoo.
What did you do yesterday? – I played violin.
What did you say? - I didn't say anything. / I said that i love her.
Why did we have to come? – Because is time to go home.
Remember: Aff.: I worked yesterday.
Neg.: I didn’t work yesterday.
Int.: Did i word yesterday?
A realidade é que para aprender qualquer coisa em inglês o segredo é a repetição e a
frequência de revisão!
The reality is that to learn anything in English the secret is repetition and frequency
of revision!