REPORTED SPEECH
Reported Speech é a repetição de algo que foi dito por alguém; algo que foi relatado a outra(s) pessoa(s) com nossas
próprias palavras.
He said, "I study hard." (direct speech)
He said (that) he studied hard. (reported speech)
Para passar uma sentença do direct speech (discurso direto) para o reported speech (discurso indireto) são necessárias
algumas alterações na construção da frase.
Veja as alterações a seguir.
Existem três tipos de reported speech:
Alterações
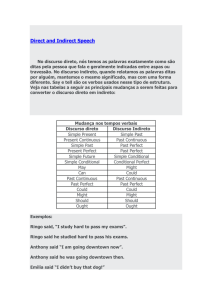
1. Alterações verbais
direct speech------- indirect speech
Simple Present
Simple Past
Present Continuous
Past Continuous
Present Perfect
Past Perfect
Present Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous
Simple Past
Past Perfect
Simple Future
Simple Conditional
Simple Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Can
Could
May
Might
Must
Had to
2. Expressões de tempo e lugar
direct speech------- indirect speech
these
those
here
there
now
then
today
that day
yesterday
the day before
tomorrow
the next day
last (...)
the (...) before
next (...)
the following (...)
ago
before
Observações:
1. Quando o verbo introdutório to say estiver no simple present, present continuous, present perfect ou simple
future, não haverá mudanças nos tempos verbais.
He says: "l love dancing."
He says (that) he loves dancing.
2. Os verbos should, ought to, might e could, assim como os verbos no past continuous e no past perfect não sofrem
alterações na passagem do discurso indireto.
He said to her, “I was studying hard."
He told her (that) he was studying hard.
3. Com verdades universais não há mudanças verbal:
He said, "Man is mortal"
He said (that) man is mortal.
Tipos de reported speech:
1. Statements
Seguem normalmente as regras já anteriormente mencionadas.
He said, "I study hard."
He said (that) he studied hard.
He said to us, "I think I have broken my arm".
He told us (that) he thought he had broken his arm.
2. Commands
imperativo afirmativo
infinitivo com to
He said to John, "Please, open the door."
He asked John to open the door.
imperativo negativo
not + infinitivo com to
She said to him, "Don't smoke here."
She told (ordered) him not to smoke there.
3. Questions
Com orações interrogativas, o verbo introdutório altera-se para ask.
a) Com question word
He said, "How is Paul?"
He asked how Paul was.
John said to Mary, "Where did you spend your holidays?"
John asked Mary where she had spent her holidays.
b) Quando não houver question word, usamos whether ou if no discurso indireto.
He said to me, "Did you go there yesterday?"
He asked me if (whether) I had gone there the day before.
c) Quando um convite ou uma sugestão são transformados em reported speech, o verbo da oração introdutória passa a
ser to suggest e a forma let's torna-se should.
They said, "Let's wait here till the rain stops."
They suggested (that) we should wait there till the rain stopped.