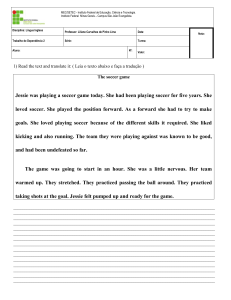
Resumo de gramática da Língua Inglesa.
Simple Present = Presente Simples
I comb my hair every morning. / Eu penteio meu cabelo toda manhã.
I don’t comb my hair every morning.
Do I comb my hair every morning?
He lives on Queen Street. / Ele Mora na rua Queen.
He doesn’t live on Queen Street.
Does he live on Queen Street?
Verbos terminados em (S, SS, SH, CH, X, O, Z) acrescenta-se “es” .
Exemplos: Watch = Watches / Go=Goes / Wash=Washes
Verbos terminados em (Y) precedido de consoante, acrescenta-se “ies”.
Exemplos: Study – Studies
Verbos terminados em (Y) precedido de vogal, acrescenta-se “s”.
Exemplos: Play – Plays.
Simple Present of the Verb To Be= Presente simples do verbo “to be”= ser, estar.
I am awake. = Eu estou acordado.
I am not awake
Am I awake?
I am not = I’m not
He is not = He isn’t
They are not = They aren’t.
She is an engineer. / Ela é engenheira.
She is not an engineer.
Is she an engineer?
They are ready = Eles estão prontos.
They are not ready
Are they ready?
Simple Present Continuous = Presente Simples Contínuo.
I am studying a new language. / Eu estou estudando uma língua nova.
I am not studying a new language.
Am I studying a new language?
She is watering the plants. / Ela está aguando as plantas.
She isn’t watering the plants.
Is She watering the plants?
We are running. / Nós estamos correndo.
We aren’t running.
Are we running?
Regras de acréscimo de “ing”.
Verbos terminados em (CVC), ou seja, consoante, vogal, consoante, dobra-se a última
letra.
Exemplos: Run-Running / Stop-Stopping
Verbos terminadoes em (ie), troca-se o “ie” pelo “y”.
Exemplos: Die-Dying.
Simple Past = Passado Simples (Geralmente, é especificado o tempo em que ocorreu a
ação).
You enjoyed the party very much last night. / Você curtiu muito a festa ontem à noite.
You didn’t enjoy the party very much last night.
Did you enjoy the party very much last night.
She went to the mall yesterday. / Ela foi ao shopping ontem.
She didn’t go to the mall yesterday.
Did she go to the mall yesterday?
Simple Past of the Verb “To Be” = Passado simples do verbo “to be” = ser, estar
I was tired. / Eu estava cansado.
I wasn’t tired.
Was I tired?
He was a waiter. / Ele era garçom.
He wasn’t a waiter.
Was he a waiter?
They were friends./ Eles eram amigos.
They weren’t friends.
Were they friends?
Simple Past Continuous = Passado Simples Contínuo.
I was studying a new language. / Eu estava estudando uma língua nova.
I was not studying a new language.
Was I studying a new language?
She was watering the plants. / Ela estava aguando as plantas.
She wasn’t watering the plants.
Was She watering the plants?
We were running. / Nós estávamos correndo.
We weren’t running.
Were we running?
Near Future = Futuro Próximo “GOING TO” (usado quando algo já está planejado).
I am going to buy a new car. / Eu vou comprar um carro novo.
I’m not going to buy a new car.
Are you going to buy a new car?
He is going to travel abroad. / Ele vai viajar para o exterior.
He isn’t going to travel abroad.
Is he going to travel abroad?
They are going to start a new course. / Eles vão começar um curso novo.
They aren’t going to start a new course.
Are they going to start a new course?
Future “in the past”
I was going to buy a new car. / Eu ia comprar um carro novo
He was going to travel abroad. / Ele ia viajar para o exterior.
They were going to start a new course. / Eles não iam começar um curso novo.
Simple Future = “WILL” (Normalmente usado quando algo é decidido no momento
da fala)
I will apply for a new job. / Eu me candidatarei para um novo emprego.
I won’t apply for a new job.
Will you apply for a new job.
She will work.
She won’t work.
Will she work.
I will = I’ll
She will = She’ll
OBS: WILL = SHALL. No entanto, o “shall” é usado apenas com a 1ª pessoa do
singular e do plural, ou seja, “I and We”
Exemplos: I will travel = I shall travel
We will sleep = We shall sleep.
Future Continuous = Futuro Contínuo
I will be watching the match at 8:30. / Eu estarei assistindo a partida às 8:30.
I won’t be watching the match….
Will you be watching the match…?
He will be working at 10 o’ clock tomorrow. / Ele estará trabalhando às 10 horas
amanhã.
He won’t be working at 10 o’ clock tomorrow.
Will he be working at 10 o’ clock tomorrow?
Future Perfect = Futuro Perfeito.
I will have retired 30 years from now. / Eu terei me aposentado daqui 30 anos.
I won’t have retired 30 years from now.
Will you be retired 30 years from now?
The game will have ended at 9:30. / O jogo terá terminado às 9:30.
The game won’t have ended at 9:30.
Will the game have ended at 9:30?
Present Perfect = Presente Perfeito. (É usado para falar de algo que aconteceu no
passado sem um tempo específico).
I have studied a lot for the test. / Eu estudei muito para a prova.
I haven’t studied a lot for the test.
Have you studied a lot for the test?
She has bought a new laptop. / Ela comprou um notebook novo.
She hasn’t bought a new laptop.
Has she bought a new laptop?
Já com o uso do “SINCE” e ‘FOR”, a tradução passa a ser de “tempo presente”.
I have worked at this company for two years. / Eu trabalho nesta companhia há dois
anos.
He has studied at this school since 2000. / Ela estuda nesta escola desde 2000.
Present Perfect Continuo = Presente Perfeito Contínuo. (É usado para falar de uma
ação que está em adamento, ou seja, teve início num tempo passado e contínua
acontecendo até o presente momento.
I have been working a lot. / Eu Estou estou trabalhando muito ou Eu tenho trabalhado
muito.
I haven’t been working a lot.
Have you been working a lot?
He has been studying at this school for 10 years. / Ele está estudando nessa escola há 10
anos, ou, Ele tem estudado nessa escola há 10 anos, ou, Ele estuda nessa escola há 10
anos.
OBS: O Present Perfect Continuo é muito usado em interrogativas acompanhadas
de “How Long” = Quanto tempo.
-How long have you been living in this city? / Há quanto tempo você tem morado nessa
cidade? ou Há quando tempo você mora nessa cidade?
-I have been living here for two years. / Eu moro aqui há dois anos. ou Eu tenho morado
aqui há dois anos.
-How long has he been working for this airline company? /Há quando tempo ele
trabalha para essa empresa aérea?
-He has been working for this airline company since 2008. / Ele trabalha para essa
empresa aérea desde 2008.
Past Perfect = Passado Perfeito
I had eaten a lot. / Eu havia comido muito. ou Eu tinha comido muito.
I hadn’t eaten a lot.
Had I eaten a lot?
He had left the office. / Ele havia saido do escritório. ou Ele tinha saído do escritório.
He hadn’t left the office.
Had he left the office?
(Usado para expressar um passado que ocorreu antes passado simples)
When I called you, you had already gone to bed. / Quando eu te liguei, você já tinha
ido domir.
Tom had already left by the time I arrived at his house. / Tom já tinha saído quando
eu cheguei à casa dele.
==============================================================
Used to + Verb (Expressa algo que ocorria no passado e que não acontece mais no
presente)
I used to play soccer. / Eu jogava futebol. Ou Eu costumava jogar futebol.
I didn’t use to play soccer.
Did you use to play soccer?
He used to smoke. / Ele fumava. Ou Ele costumava fumar.
He didn’t used to smoke.
Did he use to smoke?
==============================================================
To Be (in the present)+ used to + verb + ing (Expressa algo que você está acostumado
a fazer no presente)
I am used to playing golf. / Eu estou acostumado a jogar golf.
I am not used to playing golf.
Are you used to playing golf?
She is used to living in this city. / Ela está acostumada a morar nesta cidade.
She is not used to living in this city.
Is she used to living in this city?
To Be(in the past) + used to + verb + ing (Expressa algo que você estava acostumado
a fazer no passado)
I was used to playing soccer. / Eu era acostumado a jogar futebol.
I wasn’t used to playing soccer.
Were you used to playing soccer?
He was used to traveling a lot. / Ele era acostumado a viajar bastante.
He wasn’t used to traveling a lot.
Was he used to traveling a lot?
==============================================================================================