1º Ano
EF2
DATA: ____/12/2016
Professora: Juliana
Aluno(a): _________________________________
Roteiro
Reading Comprehension.
Grammar: Simple Present
Grammar: Simple Past
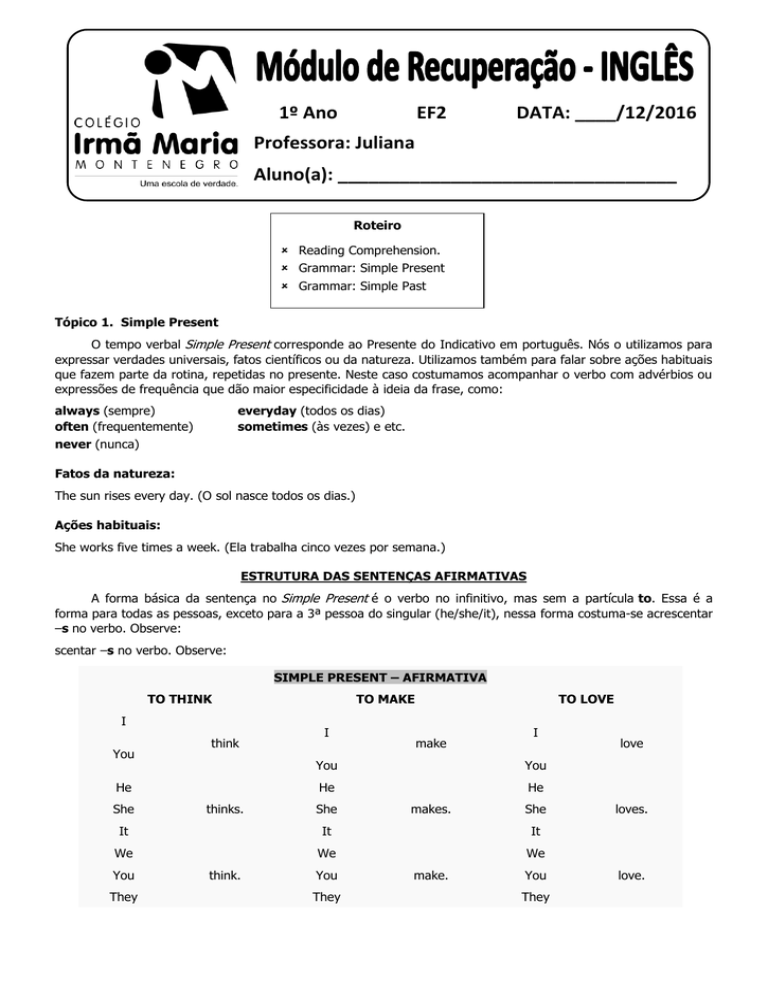
Tópico 1. Simple Present
O tempo verbal Simple Present corresponde ao Presente do Indicativo em português. Nós o utilizamos para
expressar verdades universais, fatos científicos ou da natureza. Utilizamos também para falar sobre ações habituais
que fazem parte da rotina, repetidas no presente. Neste caso costumamos acompanhar o verbo com advérbios ou
expressões de frequência que dão maior especificidade à ideia da frase, como:
always (sempre)
often (frequentemente)
never (nunca)
everyday (todos os dias)
sometimes (às vezes) e etc.
Fatos da natureza:
The sun rises every day. (O sol nasce todos os dias.)
Ações habituais:
She works five times a week. (Ela trabalha cinco vezes por semana.)
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS AFIRMATIVAS
A forma básica da sentença no Simple Present é o verbo no infinitivo, mas sem a partícula to. Essa é a
forma para todas as pessoas, exceto para a 3ª pessoa do singular (he/she/it), nessa forma costuma-se acrescentar
–s no verbo. Observe:
scentar –s no verbo. Observe:
SIMPLE PRESENT – AFIRMATIVA
TO THINK
I
You
think
He
She
thinks.
TO MAKE
I
TO LOVE
make
I
You
You
He
He
She
makes.
She
It
It
It
We
We
We
You
They
think.
You
They
make.
You
They
love
loves.
love.
2
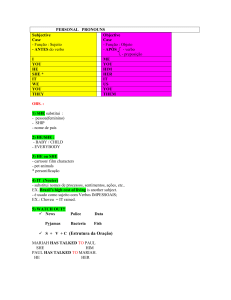
CASOS ESPECIAIS
O 1º caso especial é o verbo TO BE (ser, estar)
Ele já tem a 3ª pessoa especificado.
O 2º caso especial é o verbo TO HAVE (ter)
Na 3ª pessoa ele perde as duas últimas letras e acrescenta-se S.
TO BE
TO HAVE
I
am.
I
You
are.
You
He
have.
He
She
is.
She
It
It
We
We
You
are.
has.
You
They
have.
They
O 3º caso especial são os verbos terminados em o, ss, ch, sh, x, em que se acrescenta ES:
O
go (ir)
→
he/she/it goes
SS
kiss (beijar)
→
he/she/it kisses
CH
teach (ensinar)
→
he/she/it teaches
SH
wash (lavar)
→
he/she/it washes
X
fix (consertar)
→
he/she/it fixes
O 4º caso especial são os verbos terminados em Y, eles têm 2 possibilidades:
Y precedido de VOGAL acrescenta-se –S
Pay (pagar), buy (comprar)
He/she/it pays, buys
Y precedido de CONSOANTE acrescenta-se –IES
Cry (chorar), try (tentar)
He/she/it cries, tries
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS NEGATIVAS
Para escrever uma sentença negativa no Simple Present utiliza-se o verbo auxiliar do + not – mais utilizado
na escrita, pois é formal – ou sua forma contracta don’t – mais utilizada na fala, pois é informal – antes da forma
básica do verbo sem o to, exemplo:
1- I do not play the piano. (Eu não toco piano.)
2- My parents don’t like TV. (Meus pais não gostam de TV.)
3
Na 3ª pessoa do singular (he/she/it), usa-se o verbo auxiliar does + not ou doesn’t em vez de do+
notou don’t. Note que o verbo seguinte fica na forma básica sem o to e sem o S, exemplo:
1- She does not speak Portuguese, just Chinese. (Ela não fala português, somente chinês.)
2- Paulo doesn’t eat chocolate. (Paulo não come chocolate.)
Observação: Os verbos auxiliares do e does não tem tradução. Mas quando acompanhado do not, pode-se
traduzir por não simplesmente.
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS INTERROGATIVAS
Na forma interrogativa do Simple Present utilizam-se os verbos auxiliares do e does antes do sujeito na
frase. Note que o verbo fica na sua forma básica sem o to e sem o S, observe o exemplo:
1- Do you like orange juice? (Você gosta de suco de laranja?)
2- Does Mariah like movies? (A Maria gosta de filmes?)
RESUMO DO SIMPLE PRESENT
AFIRMATIVO
NEGATIVO
INTERROGATIVO
I work
I don’t work
Do I work ...?
You work
You don’t work
Do you work ...?
He works
He doesn’t work
Does he work ...?
She works
She doesn’t work
Does she work ...?
It works
It doesn’ twork
Does it work ...?
We work
We don’t work
Do we work...?
You work
You don’t work
Do you work ...?
Theywork
Theydon’twork
Do they work ...?
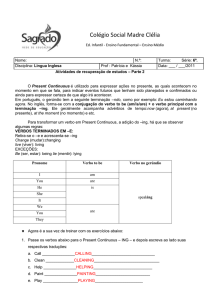
EXERCISE
01. Complete the sentences in the simple present.
a) I usually ____________________ to school. (go)
b) Tom ____________________ every day. (work)
c) You ____________________ basketball once a week. (play)
d) _________ you ____________________ twice a week? (swim)
e) I __________________________ very well. (not-dance)
f) John rarely ____________________ the country. (leave)
g) Marta ____________________ to Sobral every week. (travel)
h) I ____________________ vegetables. (not-eat)
i) You always ____________________ me new things. (teach)
j) Mary ____________________ a dog. (have)
k) My father ____________________ in the shower. (sing)
l) ___________ he ______________________ the guitar? (play)
4
02. Put the sentences in the interrogative and negative form.
a) They play hockey at school.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
b) She writes e-mails.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
c) Tom works in an office.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
d) She helps the kids in the neighborhood.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
e) Cats like milk.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
f) Tina lives in a house.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
g) They cook dinner every day.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
h) You love music.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
i) My friends speak English.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
j) Tom and Mark play chess once a week.
Int: ______________________________________________________________________
Neg: _____________________________________________________________________
5
03. Fill in the gaps with the appropriate word from the box.
likes
is
walks
drive
works
like
helps
live
Tom _________________ at a bank. He _________________ the manager. He starts work every day
at 8:00 am. He finishes work every day at 6:00 pm. He lives very close to the bank. He __________________
to work every day. His brother and sister also work at the bank.
But, they do not _________________ close to the bank. They _________________ cars to work. They
start work at 9:00 am. In the bank, Tom is the boss. He ____________________ all the workers and tells
them what to do.
He likes his job. He is also very good at his job. Many customers ____________________ Tom, and
they say hello to him when they come to the bank. Tom _____________________ to talk to the customers
and make them feel happy. Tom really likes his job.
Tópico 2. Simple Past
O tempo verbal Simple Past corresponde ao Passado Simples em português. Nós o utilizamos para expressar
hábitos passados ou para expressar ações que se iniciaram no passado e também foram finalizadas no passado,
podendo ter o tempo determinado. Neste caso costumamos acompanhar o verbo com advérbios ou expressões de
frequência que dão maior especificidade à ideia da frase, tais como:
yesterday (ontem)
last ... (na última...)
ago (atrás)
in.... (em...), e etc.
I worked all day yesterday. (Eu trabalhei ontem o dia todo.)
I studied Spanish two years ago. (Estudei espanhol três anos atrás.)
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS AFIRMATIVAS PARA VERBOS REGULARES
O verbo é regular quando para conjugá-lo não há alteração em seu radical. Logo, para colocar esse verbo
no Simple Past basta deixar o verbo no infinitivo, sem a partícula to, e acrescentar a terminação -ed. Essa é a
forma para todas as pessoas. Observe:
TO WORK (trabalhar)
I
You
He
She
It
We
You
They
worked
6
CASOS ESPECIAIS
1º caso especial: verbos terminados em Y. Eles têm 2 possibilidades:
Y precedido de VOGAL: acrescenta-se -ED
play (jogar)
playED
Y precedido de CONSOANTE: retira-se o -Y acrescenta-se -IED
try (tentar)
tried
O 2º caso é o dos verbos terminados em -E, neles nós simplesmente acrescentamos o -D:
love – loved
O 3º caso especial é o dos verbos terminados em consoante+vogal+consoante, cuja sílaba tônica é a
última, dobra a consoante antes de acrescentar o -ed:
Occur: occurred
Nos demais casos, acrescenta-se simplesmente -ed:
Work: worked
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS AFIRMATIVAS PARA VERBOS IRREGULARES
O verbo é irregular quando, ao ser conjugado, por exemplo, ele muda toda a sua estrutura. Nesse caso,
para ele ficar no passado, temos que consultar uma lista de verbos para, depois, através do uso, ir memorizando.
Alguns verbos irregulares com os respectivos passados:
INFINITIVO
PASSADO
TO AWAKE
AWOKE
TO BUY
BOUGHT
TO FORGET
FORGOT
TO LAY
LAID
TO SEE
SAW
TO RING
RANG
TO UNDERSTAND
UNDERSTOOD
Exemplos:
I forgot my keys. (Eu esqueci as chaves.)
I saw you yesterday at the bus station. (Eu te vi ontem no ponto de ônibus.)
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS NEGATIVAS DOS VERBOS REGULARES E IRREGULARES
Para escrever uma sentença negativa no Simple Past utiliza-se o verbo auxiliar did + not – mais utilizado na
escrita, pois é formal – ou sua forma contracta didn’t – mais utilizada na fala, pois é informal – antes da forma
básica do verbo sem o to, exemplo:
1- I did not buy the piano yesterday. (Eu não toquei piano ontem.)
2- My parents didn’t travel to Porto Seguro last year. (Meus pais não viajaram para Porto Seguro no ano
passado.)
7
Ao colocar a sentença na negativa, é interessante observar que como o verbo auxiliar na negativa, o didn’t,
já está no passado (pois é o passado de do), o verbo principal não tem a terminação –ed.
ESTRUTURA DAS SENTENÇAS INTERROGATIVAS DOS VERBOS REGULARES E IRREGULARES
Na forma interrogativa do Simple Past utiliza-se o verbo auxiliar did antes do sujeito na frase. Note que o
verbo principal fica na sua forma básica sem o to e sem -ed, pois o verbo auxiliar já se encontra no passado.
Observe o exemplo:
1- Did you run yesterday? (Você correu ontem?)
2- Did Mariah watch Harry Potter last week? (A Mariah assistiu Harry Potter semana passada?)
RESUMO DO SIMPLE PAST
AFIRMATIVO
NEGATIVO
INTERROGATIVO
I worked
I didn’t work
Did I work ...?
You worked
You didn’t work
Did you work ...?
He worked
He didn’t work
Did he work ...?
She worked
She didn’t work
Did she work ...?
It worked
It didn’t work
Did it work ...?
We worked
We didn’t work
Did we work...?
You worked
You didn’t work
Did you work ...?
They worked
They didn’t work
Did they work ...?
EXERCISE
01. Complete the sentences with the simple past.
a) _________ she________________ the dishes? (wash)
b) _________ he _________________ a good holiday? (have)
c) I ___________________________ the soccer game last night. (enjoy)
d) They ____________________________ abroad. (not-travel)
e) They _________________________ the composition. (not-write)
f) Mary ___________________________ in Japan. (live)
g) ____________ you _____________________ to the park? (go)
h) Kim __________________________ smoking. (stop)
i) We ___________________________ a party for our friend. (plan)
j) The teacher ___________________________ to the students. (talk)
k) My mother _____________________________ the dishes. (not-wash)
l) Sam ___________________________ a new car. (buy)
8
02. Classify the verbs as regular or irregular.
see
dance
work
eat
bring
Regular
play
drink
wash
do
make
buy
play
think
visit
stay
Irregular
03. Change the sentences to the simple past.
a) I have a dream:_________________________________________________
b) She drives a car:_______________________________________________
c) They cook dinner:_______________________________________________
d) He rides his bike: _______________________________________________
e) We listen to music:______________________________________________
f) They don’t play the guitar. ________________________________________
g) My sister makes a delicious sandwich. ______________________________
h) I understand the problem.________________________________________
i) I go to school by bus. ____________________________________________
j) They see horror films. ____________________________________________
k) The girls play volleyball. _________________________________________
l) Ana doesn’t sleep early. _________________________________________
29/11/2016
plan