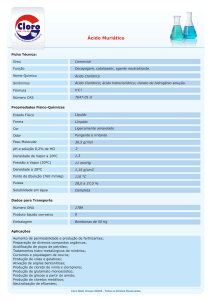
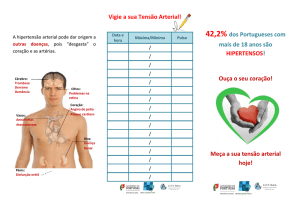
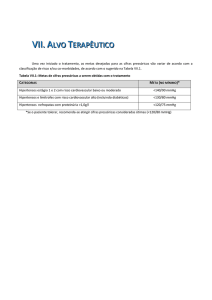
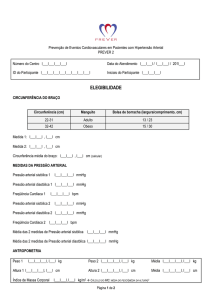
UNIFESP
A vasodilatação muscular em reações
de alerta e a
regulação da pressão arterial
Sergio L. Cravo
Disciplina de Fisiologia Cardiovascular e Respiratória
Universidade Federal de São Paulo - UNIFESP-EPM
Geração e modulação baroceptora da atividade simpática
Cardiovascular responses to eletrical stimulation
of the left sciatic nerve in a decerebrate rat.
250
PAP
mmHg
30
30
50
7
20
20
LHBF
1
7
RHBF
kHz
0
250
CVC (% of baseline)
kHz
10
10
00
-10
-10
MAP
mmHg
50
-20
-20
650
HR
bpm
-30
-30
300
00
10
10
20
20
30
30
TIME (s)
(s)
TIME
40
40
50
50
60
60
Role of RVLM in the cardiovascular adjustments to
sciatic nerve stimulation in anesthetized rats
200
PA
mmHg 0
200
MAP
mmHg 0
600
HR
bpm
360
4
HBF
kHz
0
30 s
Kainic
Before acid
kainic
(2nmol/100
acid into
nl)
RVLM
intocontralateral
contralateral
Within RVLM Pressor and vasodilatatory responses are
mediated by different neurotransmitters
Kynurenic
200
Before
After
Bicuculine
Before
After
PA
mmHg 0
200
MAP
mmHg 0
480
HR
bpm
360
2
HBF
kHz
0
30 s
Summary
RVLM mediates cardiovascular
responses to sciatic nerve
afferents stimulation, including
vasodilation of the stimulated
limb and vasoconstriction of the
contralateral hindlimb.
This redistribution of blood flow
is probably mediated through
differential adjustments in the
sympathetic
vasoconstrictor
drive to the limbs.
Aferentes nociceptivos mobilizam vias inibitórios capazes
de inibir seletivamente neurônios do RVL
A vasodilatação muscular provocada pela estimulação
elétrica do hipotálamo contém 3 componentes
CONT
CONT
150
150
ADREN+PHENT
ADREN+PHENT
HQVC (% of Baseline)
L-NAME
L-NAME
100
100
50
50
00
-50
-50
00
10
10
20
20
30
30
40
40
50
50
60
60
20
30
40
50
60
MVC (% of Baseline)
25
0
-25
-50
-75
-100
0
10
TIME (s)
A vasodilatação muscular é integrada por sinapses
glutamatérgicas na RVLM
200
HQVC (% of baseline)
Kynurenic acid
150
100
50
0
-50
M VC (% of baseline)
0
-25
-50
-75
0
30 s
10
20
30
Time (s)
40
50
60
Aferentes hipotalâmicos mobilizam vias inibitórios
capazes de inibir seletivamente neurônios do RVL
• Estudos anteriores demonstraram que a
estimulação de receptores glutamatérgicos
no NTS provoca vasodilatação quem no trem
posterior parece envolver liberação de NO.
O bloqueio glutamatérgico no NTS abole a vasodilatação muscular
induzida por estimulação hipotalâmica
Aferentes hipotalâmicos mobilizam vias inibitórios
(talvez a partir do NTS) capazes de inibir
seletivamente neurônios do RVL
O bloqueio glutamatérgico no RVL abole
a vasodilatação muscular induzida por
estimulação do NTS
A via NTS-RVL seria parte das vias dos
reflexos dos baroceptores?
O bloqueio glutamatérgico no RVL abole a
vasodilatação muscular induzida por
estimulação de aferentes baroceptores
2 vias para os reflexos baroceptores?
?
Colaboradores
•
•
•
•
Marcos Luiz Ferreira Neto
Olga S. Possas
Willian S. Korim
Gustavo R. Pedrino
Apoio Financeiro: FAPESP, CNPq, CAPES