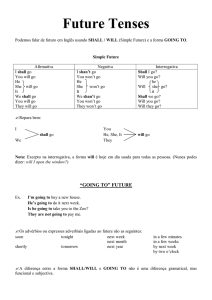
Utilizamos as formas imperativas quando queremos:
Dar ordens
Dar instruções
Oferecer algo
Convidar alguém
Dar
ordens:
Sit down!
IMPERATIVO AFIRMATIVO:
Stop speaking.
Make your bed.
Formado do verbo no infinitivo,
sem o “to”.
IMPERATIVO NEGATIVO:
Don’t + infinitivo sem o “to”
Don’t open the door.
Dar
instruções:
Mix all the ingredients and put them in the oven.
Oferecer
algo:
Please, have some coffee.
Convidar:
Let’s go to the movies tonight?
Convite:
Let’s + infinitivo sem o “to”
as
when
until
after
while
as soon as
since
before
When I finish my homework, I will go out
with my friends.
I will study while I am on the bus.
As he drives, I’ll talk to him
Em seguida, imediatamente depois, uma vez que
...
They will go to the beach as soon as they
have their breakfast.
As soon as I leave home, I will call you.
You will have to respect me, once I am the
teacher
Antes
Before he moves to São Paulo, he will spend
a week at his mother’s house.
I will tell her the truth, before I go out.
Depois
After her sister prepares dinner, they’ll invite
their friends.
My father will buy a new car after he saves
enough money.
Condição imposta por determinado momento. “Até que.”
I won’t travel to London until / till I have enough money.
You can go out. I will wait until she calls.
Observem que em todas as frases anteriores,
os verbos estão no presente e no futuro.
Observe:
My father will buy a new car after he saves
enough money.
A oração que acompanha a conjunção fica no presente.
A outra oração fica no futuro.