REVISÃO DO PRESENTE SIMPLES (Present Simple or Simple Present Tense)
Empregamos o presente simples para descrever uma ação habitual, que ocorre em
nosso cotidiano, e que por vezes, ocorre rotineiramente (com freqüência).
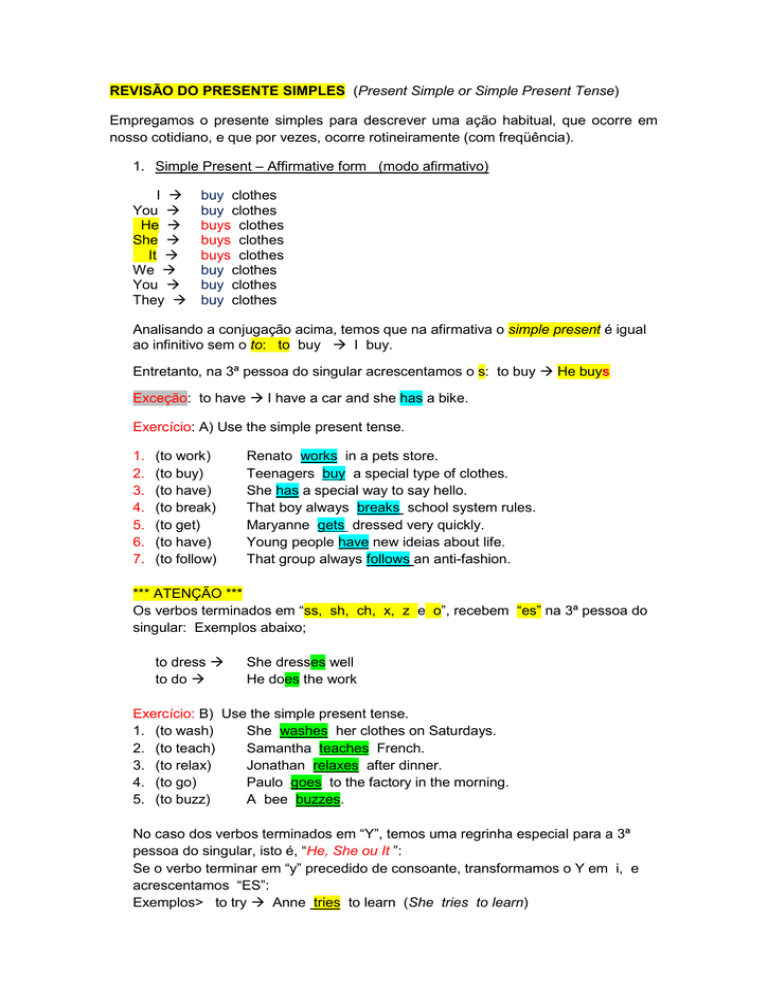
1. Simple Present – Affirmative form (modo afirmativo)
I
You
He
She
It
We
You
They
buy clothes
buy clothes
buys clothes
buys clothes
buys clothes
buy clothes
buy clothes
buy clothes
Analisando a conjugação acima, temos que na afirmativa o simple present é igual
ao infinitivo sem o to: to buy I buy.
Entretanto, na 3ª pessoa do singular acrescentamos o s: to buy He buys
Exceção: to have I have a car and she has a bike.
Exercício: A) Use the simple present tense.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
(to work)
(to buy)
(to have)
(to break)
(to get)
(to have)
(to follow)
Renato works in a pets store.
Teenagers buy a special type of clothes.
She has a special way to say hello.
That boy always breaks school system rules.
Maryanne gets dressed very quickly.
Young people have new ideias about life.
That group always follows an anti-fashion.
*** ATENÇÃO ***
Os verbos terminados em “ss, sh, ch, x, z e o”, recebem “es” na 3ª pessoa do
singular: Exemplos abaixo;
to dress
to do
She dresses well
He does the work
Exercício: B) Use the simple present tense.
1. (to wash)
She washes her clothes on Saturdays.
2. (to teach)
Samantha teaches French.
3. (to relax)
Jonathan relaxes after dinner.
4. (to go)
Paulo goes to the factory in the morning.
5. (to buzz)
A bee buzzes.
No caso dos verbos terminados em “Y”, temos uma regrinha especial para a 3ª
pessoa do singular, isto é, “He, She ou It ”:
Se o verbo terminar em “y” precedido de consoante, transformamos o Y em i, e
acrescentamos “ES”:
Exemplos> to try Anne tries to learn (She tries to learn)
Exercício: C) Use the simple present tense:
1. (to cry)
Flávia always cries like a baby!
2. (to study)
Fernando studies mathematics.
3. (to fly)
A jet plane flies long distances.
4.
(to play)
Daniel plays the guitar very well. ****
*** Vale lembrar que o verbo “to play” não segue a regra anterior, pois no caso do
‘play’, o ‘y’ está precedido de uma vogal, portanto a 3ª pessoa segue a regra geral,
que diz somente para acrescentar o ‘s’.
Simple Present – Negative and Interrogative forms
Negative
I
You
He
She
It
We
You
They
Interrogative
do not dance
do not dance
does not dance
does not dance
does not dance
do not dance
do not dance
do not dance
DO
DO
DOES
DOES
DOES
DO
DO
Do
I
dance ?
You
dance ?
He
dance?
She dance?
It
dance?
WE
dance?
You
dance?
They dance?
1.) Na negative usamos: o auxiliary do + not + verbo principal (no infinitivo, sem
‘to’). Apenas na penas na 3ª pessoa do singular substituímos ‘do’ por ‘does’.
2.) Na interrogativa o auxiliar (do / does) antecede o sujeito.
3.) Contrações : do + not = don’t I don’t dance
does + not = doen’t She doesn’t dance.
Exemplos:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
Roberto studies at home every day.(+) / Roberto doesn’t study at home every day. (-)
Luciano explains every new word. (+) / Luciano doesn’t explain every new word. (-)
Joana relaxes after lunch. (+) / Joana doesn’t relaxe after lunch.
Do I know how to drive?
Do You know how to answer the question?
Do they know how to swim?
Does he know how to play cards?
Does she know how to play the guitar?
Does It know how to come here?