Programme of Study
MYP 2
2016_2017
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
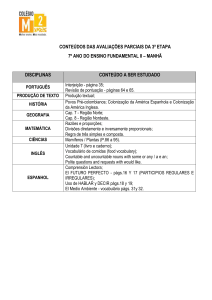
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Language & Literature English
Language & Literature Portuguese
Language & Literature Spanish
Language & Literature Japanese
Language & Literature Korean
Language Acquisition French
Language Acquisition Spanish
Language Acquisition Portuguese
Mathematics
Sciences
Humanities
História & Geografia
Visual Art
Drama
Music
Design
Physical & Health Education
2
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
LANGUAGE & LITERATURE ENGLISH
The MYP 1 English curriculum aims to develop the skills of reading, writing,
speaking, listening and viewing using an integrated approach. The literary
text constitutes the core of each unit’s activities and assessment. The works
chosen will be from different parts of the world and will include male and
female authors. Texts used will explore and challenge stereotypical gender
and cultural roles. Student selected independent reading is expected and
integral to developing vocabulary, writing skills, and improving grammar.
Unit One: Biographies
Genre: Biography
● Identify features of a Biography
● View and Identify aspects of visual language
● Prepare an inquiry to gather information to write and present a
Biography
● Write a biography
● Use media technology to tell a story
Unit Two: Poetry
●
●
●
●
●
●
Learn about different forms of poetry
Learn poetic terms such as simile, metaphor and personification
Write rhyming poetry
Write poetry using simile, metaphor and personification
begin to learn the basics of analysing literature (PEE)
Read poetry for pleasure
Unit Three: Feather Boy
●
●
●
●
●
●
Genre: Novel
Read and respond to the novel in discussions and writing
Role play situations and characters
Write a text response essay based on the novel
Create a poster about a theme from the text
Create a film trailer
Learn new vocabulary and maintain a glossary
Unit Four: Introduction to Drama Genre: Drama
●
●
●
●
●
●
Read and respond to the play in discussions and writing
Learn technical terms
Learn production roles
Perform a section of the play for the rest of the class
Learn features of script writing
Write, prepare and present the ending of a play
3
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
LANGUAGE & LITERATURE PORTUGUESE
1.
Estudo da Língua – Língua e Discurso
a.
Diferentes gêneros textuais com foco nos atos de contar e relatar:
mitos, lendas, notícia, reportagem (inclusive em mídias digitais),
biografia, poesia e conto. (todas as Units)
b. Competências - Aspectos de leitura e interpretação:
· Apreensão de sentidos explícitos e fluência de leitura;(U1/2)
· Seleção e reorganização de informações; (U 1)
· Sentidos da linguagem: a denotação e conotação; (U3)
· Elementos simples de Coesão e coerência nos textos: conectivos
básicos (conjunções e os efeitos de sentido provocados por elas)(U
1)
·
Construção do texto narrativo – estrutura (paragrafação,
emprego de maiúsculas, sinais de pontuação) (U1/2/4)
·
Reconhecimento de técnicas de composição: tipos de discurso
(sinais de pontuação, verbos e locuções verbais); relação entre fala
e escrita; construção de sequências narrativas simples. (conflito,
clímax, desfecho) (U 2/4)
c. Elementos de estilo:
·
Figuras de linguagem: figuras de som (ou de harmonia):
aliteração, assonância, paronomásia, onomatopeia;(U 3)
·
Introdução (vivência) ao texto poético.(U 3)
2. Estudo da Língua – Gramática – Morfossintaxe
a. Domínio linguístico:
·
Aplicação das classes de gramaticais: ((U1) – substantivo,
adjetivo, conjunção),(U2) – advérbio, pronome; (U3) artigo,
preposição, numeral, interjeição; (U4) verbos – modos e formas
nominais; conjugações verbais)
·
Sintaxe - Tipos de frase: Declarativa, exclamativa, interrogativa;
(U 1)
·
Sinais de pontuação; (U 1)
·
A ordem das palavras na oração: diferença entre direta e indireta;
(U 1)
·
Acentuação gráfica (U 2)
·
Estudo ortográfico (todas as units)
3. Produção textual
a.
Produção de textos com base nos gêneros textuais trabalhados em
sala de aula (literários e não literários):
· gêneros literários: poesia, contos e romances;
· gêneros não literários: notícia, reportagem, bilhetes, diário
(inclusive em mídias digitais);
4. Leitura: U 1,U2,U3 e U4
·
Ilíada (adapt.) U1
·
Odisseia (adapt.) U1
·
Coletânea de lendas e histórias do folclore brasileiro U1
·
Minhas memórias de Lobato, Luciana Sandroni. U1/2
·
O diário de Zlata. Zlata Filipovic. (leitura independente U2)
4
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
·
·
·
·
O meu pé de laranja lima. José Mauro de Vasconcelos.U2
Coletânea de poesias variadas e adequadas à faixa etária U3
Contos brasileiros 2 – Para gostar de ler vol. 9 U4
“Gaetaninho”, Alcântara Machado; “Baleia”, Graciliano Ramos; Será o
Benedito!, Mário de Andrade. U4
LANGUAGE & LITERATURE SPANISH
Unidad 1: De monstruos, dioses y héroes...
Género literario: el mito
Género no literario: la nota de enciclopedia
● Leer, apreciar y comentar relatos mitológicos de diferentes culturas de la
América prehispánica y analizar en ellos el tema de lo mítico.
● Descubrir las características del relato mítico.
● Identificar las características de la nota de enciclopedia.
● Valorizar las ventajas y desventajas de las enciclopedias digitales.
● Reconocer los componentes del circuito de la comunicación. Identificar los
elementos que componen la situación comunicativa.
● Identificar y aplicar las reglas generales de acentuación y los usos de B y V
● Aplicar los recursos verbales propios del relato mítico a la escritura de textos
propios.
● Crear un diccionario de monstruos.
Unidad 2: De tigres, espejos y emperadores… Género literario: la leyenda
Género no literario: el artículo periodístico
● Leer, apreciar y comentar leyendas pertenecientes a diferentes culturas
(hispanohablantes y no hispanohablantes)
● Descubrir las características de la leyenda: origen, lugar, tiempo, personajes.
● Establecer las relaciones entre la leyenda y el mito.
● Leer artículos periodísticos, identificar sus características y valorizar su
contenido.
● Clasificar los textos según sus funciones: apelativa, emotiva, referencial,
poética, fática y metalingüística.
● Identificar y aplicar las reglas especiales de acentuación y los usos de C, S, Z
● Redactar una leyenda.
Unidad 3: De detectives, crímenes e investigaciones… Género literario: el
cuento policial
Género no literario: la noticia
● Leer, apreciar y comentar relatos policiales
5
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
● Identificar las características del cuento policial: el delito, el enigma, el
detective y la víctima. Detectives clásicos en la historia de la literatura.
● Leer diferentes tipos de noticias, clasificarlas según su contenido e identificar
su estructura.
● Reconocer las unidades de la lengua: la oración y el enunciado, el párrafo y el
texto
● Identificar las características de las clases de palabras: el verbo y sus modos.
● Reconocer y aplicar los conceptos de sinonimia, antonimia y paráfrasis. Los
usos de G -J
● Argumentar y defender un punto de vista en un debate.
● Redactar una noticia policial.
Unidad 4: De versos, estrofas y metáforas...
Género no literario: el decálogo
Género literario: la poesía
● Leer, apreciar y comentar poemas de diferentes autores españoles e
hispanoamericanos.
● Identificar las características del texto poético: rima, versificación y figuras
retóricas (las imágenes sensoriales, la personificación, la comparación, la
metáfora, el paralelismo, el oxímoron y la aliteración).
● Leer algunos decálogos, clasificarlos e identificar sus características como
textos instructivos.
● Reconocer la heterogeneidad en la lengua: el concepto de variación lingüística.
● Identificar las características de las clases de palabras: el sustantivo, el
adjetivo.
● Reconocer y aplicar los conceptos de diptongo y hiato. Los usos de H.
● Redactar un decálogo.
LANGUAGE & LITERATURE JAPANESE
1. Literature – Short stories by various authors
● Appreciation of Japanese literature in modern era and in our time
● New idioms, expressions and Chinese characters
● Writing exercise
2. Poetry by various authors
● Appreciation of poetry
● Learning of rhetoric
● Writing poetry
3. Writing
● Basic of writing – organize what you want to write
● Write your favourite things
6
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
LANGUAGE & LITERATURE KOREAN
Unit One: 글자
• 한글 자.모음의 생성과 원리
• 단어와 낱말과의 관계
• 문장과 문장의 연결성
• 낱말의 의미
Unit Two: 듣기, 말하기, 읽기, 쓰기
• 읽기 => 상상의 세계 (시, 동화와 희곡의 특성과 개념)
• 듣기, 말하기, 쓰기 => 드라마(소나기, 점프…..
• 각 장르와의 비교
• 글을 읽고 발표하기
Unit Three: 정보와 이해
• 관점에 대해 알기 è 헬렌 켈러의 얘기, 진정한 금메달,종이책의 미래
• 고유어 이름
• 토의와 토론
• 다양한 주장: 많이 웃자
Unit Four: 나누는 즐거움
• 인사말: 상황과 사회적 관계, 중요성
7
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
• 식탁위의 작은 변화 => <참여를 바라는 글> 식사습관
• 글짓기: 편지글, 독후감, 기행문
Unit Five : 우리말과 외국어
• 외래어와 외국어, 소중히 가꾸어야 할 우리 말
• 낱말 카드, 십자말 풀이 •이어 주는 말
LANGUAGE ACQUISITION FRENCH
Tout à mon sujet
Genre: Blog.
● Meet, greet and say goodbye
● Objects from classroom
● Say where you live and ask other people where they live
● Talk about things in the classroom
● Find out about the main towns in France
● Read, understand and write the first page of a blog.
Une Journée Scolaire
Genre: email
● Talk about your family and your home
● Talk about other people's homes and families
● Say where things are and who they belong to
● Talk about your routine and the days of the week
● Ask what the time is
● Understand and tell the time in French
● Discuss when something is happening
● Talk about a typical day, school subjects and what you think about them.
● Describe the school and find out about others schools in the world.
Les Animaux
Genre: poster
● Talk about animals and pets
● Describe animals and other things (colour and size)
● Talk about your likes, dislikes and preferences.
● Read and understand campaigns against animal abuse and abandon.
● Create a campaign.
● Read, understand and reproduce little poems about nature.
8
9
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
Action
Genre: brochure
● Talk about sport and leisure activities
● Talk about what you do at weekends and in bad weather
● Talk about how we benefit doing sports
● Find out and talk about the Olympics Games and the France Tour.
● Write a travel diary.
LANGUAGE ACQUISITION SPANISH
Unidad 1: Nuestra identidad
formulario y los documentos de identidad
Géneros textuales: El
● Saludar y despedirse.
● Presentarse a uno mismo y presentar a alguien.
● Comprender presentaciones breves, identificar las ideas principales y
realizar actividades relacionadas.
● Intercambiar de forma oral o escrita información básica sobre el origen, la
edad, la fecha de cumpleaños, el número de teléfono, la dirección, el curso,
etc. deletreándola cuando sea necesario.
● Leer, comprender y completar formularios con datos personales.
● Identificar diversos documentos de identidad y el sentido de pertenencia
a las diferentes comunidades.
Unidad 2: Mi familia, mi casa, mi rutina
electrónico y el anuncio
Géneros textuales: el correo
● Escuchar, comprender e identificar las ideas principales de videos bre las
relaciones sociales y familiares básicas.
● Interactuar en situaciones comunicativas en las que haya que pedir y dar
información sobre actividades escolares propias y de otras personas,
horarios y frecuencia.
● Intercambiar información básica sobre actividades de ocio (aficiones,
viajes, deportes, etc.).
● Escribir correos electrónicos básicos hablando sobre la rutina y textos
descriptivos breves sobre la propia familia.
● Obtener y proporcionar información básica sobre las características de
una vivienda.
● Elaborar una presentación oral y escrita acerca de las características de la
vivienda propia localizando objetos en el espacio y expresando existencia.
● Leer, comprender y analizar anuncios sobre alquiler y compra de
viviendas.
● Elaborar un anuncio de venta de “la casa ideal”.
10
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
Unidad 4: Animales amigos
campaña
Género
textual:
la
● Leer, comprender fábulas y responder preguntas relacionadas.
● Describir personas y animales proporcionando información sobre los
rasgos físicos y de carácter y ser capaz de obtener de otros esa
información en conversaciones informales.
● Escuchar, comprender e identificar las ideas principales de vídeos sobre
los derechos de los animales.
● Realizar comparaciones.
● Hacer recomendaciones o dar consejos.
● Comprender, analizar y elaborar una campaña de adopción.
Unidad 5: Deportes y tiempo libre
Género textual: la entrevista
● Escuchar, comprender e identificar información básica en entrevistas y
realizar actividades relacionadas.
● Intercambiar en conversaciones informales información básica sobre
actividades de ocio y deportes.
● Obtener y proporcionar información sobre gustos y preferencias siendo
capaz de expresar acuerdo y desacuerdo.
● Expresar necesidad.
● Leer, comprender Identificar las ideas principales de campañas
gubernamentales para fomentar la inclusión social a través del deporte.
● Hablar brevemente de una experiencia pasada.
● Realizar una entrevista y presentar oralmente las respuestas obtenidas.
LANGUAGE ACQUISITION PORTUGUESE
O curso visa atender às necessidades emergentes do aluno que acaba de entrar
em contato com uma nova língua e uma nova cultura. Objetivamos:
● Desenvolver habilidades para que o aluno que está entrando em contato pela
primeira vez com a língua portuguesa possa utilizá-la de maneira satisfatória
em diferentes contextos sociais.
● Explorar as competências linguísticas intermediárias, avançando no
conteúdo e na gramática da língua, fazendo com que o aluno caminhe para
ser inserido em ambientes acadêmicos onde a língua portuguesa é o
instrumento de estudo.
O curso é dividido em fases.
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
Fase 1
Unidade 1 - Fazendo apresentações
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Expressões de sobrevivência em sala de aula (com material escolar)
Cumprimentos e despedidas formais e informais
Pronomes pessoais do caso reto
Pronomes de tratamento você, o senhor, a senhora
Alfabeto
Verbo “ser” no presente do indicativo
Pronomes possessivos: meu(s), minha(s), seu(s), sua(s), nosso(s), nossa(s),
dele(s), dela(s)
Profissões no masculino/feminino/singular/plural: escritor, professor,
aluno, secretária, engenheiro, dentista, motorista, advogado
Nacionalidades no masculino/feminino/singular/plural: francês, argentino,
brasileiro, chinês, japonês, espanhol, coreano.
Países
Pronomes demonstrativos: este(s) como sinônimo de esse(s), esta(s) como
sinônimo de essa(s), isto como sinônimo de isso, aquele(s), aquela(s) e
aquilo.
Números (0 – 1000)
Verbos regulares terminados em “ar” (gostar, precisar, ligar, telefonar,
conectar, morar) “er”, “ir” no presente do indicativo
Preposição em, na e no com o verbo “morar”
Vocabulário de família: pai, mãe, marido, esposa/mulher, filho, filha, irmão,
irmã, avó, avô.
Vocabulário: amigo, amiga, colega, namorado, namorada.
Perguntas pessoais
Rotinas diárias
Verbo “poder”, “querer” no presente do indicativo.
Cores
Horas
Parlenda “1, 2 feijão com arroz”
Comidas básicas (leite, pão, refrigerante, suco, arroz, carne, peixe, frango,
água, macarrão, ovo, salada)
Matérias da escola
Esportes
Unidade 2- Conversando nos locais que frequento
● Vários locais e o que fazer em cada um deles (academia – fazer ginástica,
parque – andar, correr, cinema – assistir filme, teatro – assistir peça, ponto
de ônibus – esperar o ônibus)
● Comprar remédio na farmácia.
● Conversa ao telefone (pegar recado)
● Conversa no taxi
● Pedir e dar sugestão de comidas em restaurantes.
● Vocabulário básico de utensílios de mesa (prato, copo, garfo, etc)
● Convidar para ir ao restaurante
● Tipos de restaurante (buffet, à la carte)
11
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
● Comidas favoritas
● Expressões: estar com/ ter fome, sede, calor, sono, frio, medo; estar com/ ter
vontade de
● Conjunção nem....nem
● Saber usar a moeda brasileira
● Verbo querer no sentido de oferecer (quer um taxi?) e achar que para
expressar opinião
● Situações no trabalho
● Adjetivos cansado, atrasado
● Revisão: dias da semana, advérbios de tempo: hoje, ontem, anteontem,
amanhã, depois de amanhã, meses do ano
● Verbos: achar, comprar, telefonar, conectar, precisar, saber, poder, ter, ter
que e ir no presente do indicativo
● Rotina com detalhes (hora e dia) Ex. Eu pratico ____ às ___ horas.
● Advérbios de frequência (uma vez, duas vezes, com que frequência?, --- por
mês/ano/sempre/nunca/às vezes)
● Onde? De onde? Qual? O quê? Quando? Quem? Cadê?
● Relações familiares: expandir (tio, tia, avô, avó, prima, primo, sobrinho)
● Meios de transportes + adjetivos: seguro, confortável, perigoso, rápido,
devagar, caro, barato
● Verbos TER e VIR
● Estar + adjetivo (simpático, antipático, complicado, inteligente, estressado,
atarefado, cansado, feliz, descansado, relaxado)
● Sugestão: Por que vc não...?
● Verbo saber como habilidade vs conhecer (pessoas e lugares), tocar, nadar
● Verbo preferir (Vc conhece....? Vc prefere.....? Vc sabe onde é....?)
Unidade 3 Passeando no tempo
● Presente do indicativo – revisão dos verbos regulares e do verbo ser e
estudo de alguns verbos irregulares
● Pretérito perfeito ( advérbios de tempo, verbos regulares ar/er/ir e alguns
irregulares: usar jornal, biografias)
● Futuro Composto ( planos para as férias, transporte, resoluções de ano novo,
turismo, folhetos turísticos para descrever lugares)
● Partes do corpo
● doenças e tratamentos associados às viagens + sugestões( precisar + verbo)
● Ter/ precisar + comprar/ estar com / ficar com - dor de cabeça, dor de
garganta, etc)
● Verbos ir e vir
● Estar + adjetivo (simpático, antipático, complicado, inteligente, estressado,
atarefado, cansado, feliz, descansado, relaxado)
● Sugestão: por que você não...?
● Verbo saber como habilidade (tocar, nadar) + contraste com conhecer
pessoas e lugares
12
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
Fase 2
Unidade 1 - A casa ideal
Partes da casa
Gostaria de comprar x gosto de ...
Veja – expressão fixa (Veja estas fotos)
Ficar – localização – Onde fica....?
Advérbios de lugar – em frente a, atrás, entre, ao lado do , na esquina , na rua
Mobília – eletrodoméstico
Presente contínuo com partes da casa ( está lendo na sala, esta cozinhando
etc)
● Pronomes indefinidos – algum, alguma, nenhum, nenhuma, ligado a bairro.
No seu bairro tem algum....
Comparativo de igualdade, superioridade, inferioridade.
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Unidade 2 - A Vida Antigamente
●
●
●
●
●
●
Descrição física e psicológica – adjetivos generoso, cruel
Pretérito imperfeito regular e irregular (ir, por, ser, ver, vir)
Revisão das cores
Vestuário social associado às situações
Vestuário esportivo e íntimo às situações
Adjetivo roupas – curto – apertado
Unidade 3 - A Importância do Passado
● Pretérito perfeito e pretérito mais que perfeito composto
● Pretérito perfeito regular e irregular (estar)
● Comparação entre o pretérito perfeito e imperfeito
Fase 3
Unidade 1
● Desinências nominais – derivação prefixal, sufixal prefixal e sufixal,
parassintética
● Desinência de superlativo sintético
● Superlativo relativo de superioridade e inferioridade – regular e irregular
● Desinência de particípio passado – ado-ido com verbo principal no presente
ou passado (é casado – era usado
● Futuro composto & futuro do presente (desinência de futuro do presente)
● Futuro do pretérito (desinência de futuro do pretérito)
● Retomar outras desinências – o pretérito imperfeito – do presente do
indicativo, do pretérito perfeitoUnidade 2
● Pronomes oblíquos – me, o, a, os, as, os, no, na, nos, nas, lhe, lhes, nos,
comigo, com ele, com ela, com ele, com eles, com elas, com você, com vocês,
com a gente, conosco.
● Linguagem informal – encontrar ele, convidar ela
● Saber como deixar recado ao telefone.
● Falar ao telefone na situação de trabalho
13
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
● Expressões relativas ao telefone – ocupado, caiu a ligação, acabou a bateria.
● Tipos de telefone – fixo, celular
● Discurso direto e indireto
Unidade 3
Regência verbal – pensar em, andar de, gostar de, ir a ,ser do tipo
Futuro do subjuntivo
Planos para férias + vocabulário de hotel – reserva
Problemas no hotel + roupa de banho e cama
Verbos relacionados a viagem e hospedagem- avisar, conseguir, aproveitar,
combinar, reparar+ verbos reflexivos (vestir-se, lembrar-se, queixar-se,
sentar-se, levantar-se, lavar-se, cortar-se, enxugar-se) conectados a
hospedar-se
● Tipos de souvenir com materiais – criar texto sobre algo típico do Brasil +
haver no sentido de existir Ex: Em São Paulo há muitos prédios.
●
●
●
●
●
Fase 4
Unidade 1
Regência verbal – pensar em, andar de, gostar de, ir a ,ser do tipo
Futuro do subjuntivo
Planos para férias + vocabulário de hotel – reserva
Problemas no hotel + roupa de banho e cama
Verbos relacionados a viagem e hospedagem- avisar, conseguir, aproveitar,
combinar, reparar+ verbos reflexivos (vestir-se, lembrar-se, queixar-se,
sentar-se, levantar-se, lavar-se, cortar-se, enxugar-se) conectados a
hospedar-se
● Tipos de souvenir com materiais – criar texto sobre algo típico do Brasil +
haver no sentido de existir Ex: Em São Paulo há muitos prédios.
● Imperfeito do subjuntivo
● Presente do subjuntivo
● Vocabulário sobre partes do carro
● Vocabulário sobre desastres naturais
● Vocabulário sobre casamento. (noivo, noiva, madrinha, lista de presentes,
alianças etc)
Unidade 2
●
●
●
●
●
Voz ativa e voz passiva
Sujeito indeterminado
Imperativo
Revisão e ampliação das partes do corpo (U1 Avenida Brasil)
Órgãos mais importantes
Verbos relativos aos problemas de saúde (quebrar, torcer, engessar)
Revisão e ampliação dos diálogos: ligar para mandar consulta + imperativo
com direções
● Revisão e ampliação dos diálogos: conversa com o médico + imperativo com
recomendações (durma, coma, não fume)
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
14
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
Unidade 3
●
●
●
●
●
Discurso direto
Discurso indireto
Pontuação (aspas, travessão, dois pontos)
Recontar contos e histórias em quadrinhos
Projeto: histórias em quadrinhos
Unidade 4
● Verbos irregulares no presente (mentir, sentir, valer, caber, pentear, passear,
construir, distribuir e odiar)
● Rever os verbos reflexivos (+ suicidar-se, arrepender-se)
● Revisão do verbo haver com diversos significados
● Revisão do verbo ficar com diversos significados
● Futuro do Pretérito composto do Indicativo (teria dito)
● Pretérito mais que Perfeito Composto do Subjuntivo (tivesse tido)
● Expressões: ser o braço direito, estar de olho em, estar com dor de cotovelo,
ter olho gordo, ser todo ouvidos, estar com a pulga atrás da orelha, entrar
com o pé esquerdo, quebrar o galho
● Aprofundar o vocabulário de animais domésticos, da fazenda, aquáticos,
selvagens, aves, insetos
● Aprofundar o vocabulário sobre a família: enteado, ex marido, madrinha,
meio irmão, etc.
● Aprofundar o vocabulário sobre profissões
● Ampliar o vocabulário com o sufixo Eiro e atividades da casa (lavar roupas,
passa, etc)
● Rever e ampliar vocabulário de roupas, acessórios, roupas de cama, massa e
banho
● Aprofundar o vocabulário sobre comidas
● Uso formal e informal do pronome oblíquo (lhe)
● Leitura de textos literários relativos ao assunto
1. “A Falta Que Ela Me Faz”, Fernando Sabino
2. “Apelo”, Dalton Trevisan
3. “O Homem Nu”, Fernando Sabino
4. “A Sogra”, Sebastião Nery
5. “Elas Mandam, O Mercado Obedece”, Veja
6. “O Lixo”, Luís Fernando Veríssimo
7. “O Defunto Vivo”, Antonio Henrique Weitel
8. “A Chuva”, Gabriel Garcia Edson
9. “Quadrilha”, Carlos Drummond de Andrade
10. “Havia uma Pedra no Meio do Caminho”, Carlos Drummond de
Andrade
11. “Irene no Céu”, Manoel Bandeira
12. Entrevista com Will Smith
13. Quadrinhos
14. Fábula “O Leão e o Ratinho”
15. Textos jornalísticos atuais
16. Carta do Leitor
15
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
16
17. Comerciais Atuais
18. Literatura Fantástica “O Homem que Devia Entregar a Carta”,
Ignácio De Loyola Brandão
19. “177 Bilhetinhos de Desculpas”
20. “As Meninas São Mais Discretas”, texto sobre bullying
21. “Como ser Ruim no Futebol”, Marcelo Coelho
22. Provérbios
MATHEMATICS
Unit 1 : Essential Skills
Multiplication Facts / Place Value
Rounding / Ordering /
Fractions of Amounts, Converting fractions. Factors & Multiples.
Unit 2 : Percentages, Fractions & Decimals Equivalence.
Shading fractions, equivalent fractions, fractions of quantities.
Comparing & improper fractions.
Percentages, converting to fractions & decimals.
Unit 3 : Percentage, Fractions & Decimals Calculation
Four rules of fractions.
Four Rules of Decimals.
% of quantity, % increase & decrease.
Unit 4 : Lines , Angles & Properties of Shapes.
Measuring, Naming & drawing Angles. Rules of angles on lines, in triangles, quadrilaterals,
parallel lines. Solve problems. Properties of Triangles & Quadrilaterals. Constructions.
Unit 5 : Number Sequences
Multiples, Square & Triangle numbers. Generating sequences. Recognizing term to term and
position to term rules. Function machines & mappings. Investigations.
Unit 6 : Ratio & Proportion
Write ratios, simplify ratios, divide in a given ratio. Direct proportion, scales, simple problems.
Similar shapes.
Unit 7 : Statistics
Collect data, frequency tables, tally marks. Bar Charts & Pie Charts. Calculate averages,
use % and fractions as informal probability.
Unit 8 : Area & Perimeter
Area & Perimeter definition. Metric Conversions for length, mm, cm, m, Km. Area and
Perimeter of basic shapes: Rectangle, Triangle, Parallelogram, Trapezium, Circle.
Areas of Composite Shapes
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
SCIENCES
Science in MYP 1 consists of an integrated science curriculum. The goal of the
program is to give our students the skills required for Secondary Science; they
will learn the names specific laboratory equipment and how to use it, they will
learn how to conduct an experiment correctly, analyse results, draw conclusions
and suggest improvements to different methods. This program also provides the
opportunity to learn some of the fundamental concepts of Science, such as force,
food chain, adaptation and chemical changes. Our aim is to inspire students so
that they understand that Science is a very dynamic subject which will provide
interesting challenges and rewarding learning experiences.
Unit 1 - How do we do Science?
● Laboratory Safety
● Laboratory Equipment
● Measurements
● Laboratory Reports: research question, hypothesis, variables, fair test
● Collecting and processing data
Unit 2 - How do living things interact with the environment?
● Characteristics of living things
● Introduction to cells
● Classification of living things
● Adaptation and evolution
● Food chains and ecosystems
Unit 3 - Why do objects move?
● Distance, displacement and position
● Speed
● Position-time graphs
● Introduction to Forces
Unit 4 - What is the nature of matter?
● The particle model
● States of matter and energy
● Density
● Physical and chemical changes
● Elements and atoms
17
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
HUMANITIES
Term 1
Fluvial Civilizations and the forces that shaped them.
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Mapping - Rivers, continents, countries, etc.
Spacial awareness - latitude and longitude
Water processes
Channel shape
Erosion, transportation and deposition
Causes/effects of floods
Functions of rivers
Surplus
Ancient Civilizations that developed around rivers, mentioning some of
their cultural, political and economic characteristics
○ Ancient Egypt
○ Ancient Mesopotamia
The Growth and Movement of the Human Race
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
How do we measure population?
What is a population pyramid?
How do you read a population pyramid?
Can we predict the future of human population?
What are demographics?
What is human migration?
What is the difference between an immigrant and a refugee?
What is the Demographic Transition Model
Term 2
Food production and the Green Revolution
●
●
●
●
●
Global food trade- the systems that govern it
Carrying Capacity, world population, and agricultural land
The green revolution
Food production systems in the world
Why are people hungry and starving in the world?
Industrial Systems
● What is industry?
18
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
●
●
●
●
What are the different kinds of industry?
What are the causes and effects of industrialization?
What factors influence the development of an industrial sector?
How does industrialization affect my life?
HISTÓRIA E GEOGRAFIA
Term 1
○ Conceitos iniciais de História.
○ Tipos de fontes - escrita, oral, material, imaterial
● Povoamento do continente americano - teorias
● Povos pré-colombianos
○ O que é civilização?
● Características sociais, culturais, econômicas, políticas e cosmologias
das seguintes civilizações pré-colombianas:
○ Esquimós
○ Tupi-Guarani
○ Astecas
○ Maias
○ Incas
● Formação do povo brasileiro
○ As diferentes civilizações que formam o povo brasileiro
○ Processos de miscigenação e imigração
○ Povoamento do território ao longo da história do Brasil
○ Tendências e perspectivas demográficas para o futuro.
Term 2
● Os ciclos econômicos ao longo da História do Brasil
○ A importância das atividades econômicas para um país
○ Exploração de recursos naturais no território brasileiro e sua
relevância dentro do contexto histórico específico.:
■ Pau-brasil
■ Cana de açúcar
■ Ouro
■ Café
○ A escravidão e o seu papel dentro das atividades econômicas
no Brasil
○ Exploração e expansão do território brasileiro
○ Início da industrialização
VISUAL ARTS
Drawing
● Right side of the brain exercises
● Process Journal - Design Process
● Introduction to Elements of Art & Principles of Design
19
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
● Tone / Texture / Shape
● Mark- making techniques
Paint
● Colour Wheel – Primary and Secondary colours – Paint handling
● Texture / Line
● Creating mood and expression
Perspective
● Space - simple colour modulation
● Abstraction and Emotion in art
Graphic Design
● Notan - Positive and Negative Space cut outs.
Monoprinting
● Simple linear prints
3 Dimensional Studies
● Papier-mâché
● Mask construction techniques
Textiles
●
Carnival Costume creations
DRAMA
Improvisation
● What is improvisation?
● What tools do we have to help us improvise?
● Is improvised performing more difficult than planned / scripted work for a
performer?
● In real life, do you improvise or follow a script?
Musicals
● What are the key aspects of a Musical?
● What makes a Musical successful?
● Are Musicals predominantly an American phenomenon?
● Does an audience need to be familiar with the Musical genre to appreciate a
Musical performance?
20
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
The Performer’s Tools
● What are the tools (which an audience can see and are) available to you as a
performer?
● Which of the performer´s tools have greatest impact on an audience, and why?
● Should performers play to their strengths to develop an effective performance?
Mask
● What are the tools (which an audience can see and are) available to you as a
performer?
● Which of the performer´s tools have greatest impact on an audience, and why?
● Should performers play to their strengths to develop an effective performance?
MUSIC
Students are involved in two lessons per week and work on three key skills listening and analysis, composing and performing. During the weekly
instrumental lessons, students will develop their performance skills. The other
music lesson will focus more on listening and analysis and composing (music
theoretical knowledge).
The studied units will include:
MUSICALS
Students will analyse, learn and appreciate key aspects of musicals and their
different forms, and perform a key piece from a musical.
FORRÓ
Students will learn about this common form of Brazilian music and analyse and
reflect in detail on some key pieces.
POPULAR MUSIC
Students will be involved in listening, creating and understanding key musical
aspects of Popular music.
21
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
DESIGN
Design in MYP 1 is taught using the Design Cycle as its main focus for the process
of its learning. Students will work through and complete a total of six units of
work structured around the Design Cycle. These units of work will give students
opportunities to develop and improve their design and making skills on a more
constructive plain. Students will reflect on their learning and development
throughout the programme and will be tested towards the end of the year to give
an overall indication of their Design skills, knowledge and understanding.
MYP Focus:
Throughout their time at St. Francis students will follow a progression of foci
that give them the skills and competencies needed to be a designer and develop
their individual design philosophy.
MYP 1: Designers that shape our world
MYP 2: Function
MYP 3: Form
MYP 4: Branding/Messaging
MYP 5: Design Philosophy
Course Schedule:
MYP across Design at St. Francis is composed of 4 units. These units are
sequential and take us through the whole year. These units are the same every
year however foci, individual tasks and assessment vary at year level.
Unit 1: Designing Our Year - First Term
Unit 2: Digital Design - Second Term
Unit 3: Product Design - Third Term
Unit 4: Design of Student’s Choice - Fourth Term
Skills & Assessment:
Student are always assessed on 4 Criterion that enables students to go from idea
to creation;
Criterion A: Inquiring and Analyzing
Criterion B: Developing Ideas
Criterion C: Creating the Solution
Criterion D: Evaluating
PHYSICAL & HEALTH EDUCATION
General skills:
22
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
● demonstrate ways to improve and refine the functional and expressive
quality of locomotor skills to improve personal performance
● demonstrate locomotor skills by using elements of body and space
awareness, effort and relationships to improve personal performance
● demonstrate ways to improve and refine the functional and expressive
quality of nonlocomotor skills to improve personal performance
● demonstrate non-locomotor skills by using elements of body and space
awareness, effort and relationships, to improve personal performance
● demonstrate ways to receive, retain and send and object with varying speeds
and accuracy in skills specific to an activity
● demonstrate manipulative skills by using elements of space awareness,
effort and relationships, with and without objects, to improve performance
Dance:
● refine and present a variety of dance sequences; e.g., folk, square, social and
novelty, alone and with others
● choreograph and perform dance sequences, using the elements of movement
and basic dance steps and patterns
Games and Sports:
● demonstrate activity-specific basic skills in a variety of games
● demonstrate more challenging strategies and tactics that coordinate effort
with others; e.g., team/fair play, in order to achieve a common goal
Individual Activities:
● demonstrate activity-specific skills in a variety of individual pursuits
Functional fitness:
● analyse personal nutritional habits and how they relate to performance in
physical activity
● demonstrate and evaluate ways to achieve a personal functional level of
physical fitness
● explain the components of fitness; e.g., strength, endurance, flexibility, cardio
respiratory activity; analyze individual abilities and formulate an individual
plan for growth
Body Image:
● identify different body types and how all types can contribute to, or
participate positively in, physical activity
● discuss performance-enhancing substances as a part of the negative effect on
physical activity
Well-Being:
● identify and explain the effects of exercise on the body systems before,
during and after exercise
● interpret personal fitness changes as a result of physical activity
● understand the connection between physical activity, stress management
and relaxation
Communication:
23
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
● communicate thoughts and feelings in an appropriate respectful manner as
they relate to participation in physical activity
● identify positive active living role models
Fair Play:
● demonstrate etiquette and fair play
Leadership:
● identify and then take responsibility for various roles while participating in
physical activity; and, identify the leadership and followership skills used
while participating in physical education
Teamwork:
● select and apply practices that contribute to teamwork
● identify and demonstrate positive behaviours that show respect for self and
others
Effort:
● participate regularly in, and identify the benefits of, an active lifestyle
● identify and demonstrate strategies that encourage participation and
continued motivation
Safety:
● identify, describe and follow the rules, routines and procedures for safety in
a variety of activities in all dimensions
● explain the benefits of, and demonstrate safe, warm-up and cool-down
activities
● recommend safe movement experiences that promote an active, healthy
lifestyle; e.g., protective equipment for in-line skating, ball hockey
Goal Setting / Personal Challenge:
● record and analyse personal goals based on interests and abilities
● evaluate different ways to achieve an activity goal, and determine a personal
approach that is challenging
Active Living in the Community:
● identify local community programs that promote physically active lifestyles
● identify factors that affect choices of daily physical activity for life, and create
personal strategies to overcome barriers
24
St. Francis College | Programme of Study | MYP 2
Jardins
Rua Bélgica, 399 . Jardim Europa
São Paulo, SP . Brasil . 01448-030
Phone +55 11 3905-6200
Fax +55 11 3905-6211
Pinheiros
Rua Joaquim Antunes, 678 . Pinheiros
São Paulo, SP . Brasil . 05415-001
Phone +55 11 3728-8050
Fax +55 11 3728-8051
stfrancis.com.br
Layout revised by: Christina Karam | Date: September 2016
Content revised by: Fabrice Bidaury | Date: September 2016
Next revision due on: August 2017
25