MODAL VERBS
PROF.ª DANIELLE CACERES DA SILVA
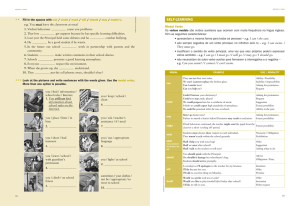
O que são “modal verbs”?
São verbos diferentes dos outros pois possuem características
próprias.
São um tipo especial de verbos auxiliares que alteram ou
completam o sentido do verbo principal. De um modo
geral, estes verbos expressam ideias como capacidade,
possibilidade, obrigação, permissão, proibição,
dedução, suposição, pedido, vontade, desejo ou, ainda,
indicam o tom da conversa (formal / informal). Os verbos
modais (modal verbs) podem ser chamados também de
modal auxiliaries ou apenas modals.
• Não precisam de auxiliares (‘did’, ‘do’, ‘does’, etc.).
• Não sofrem alterações nas terceiras pessoas do
singular no presente, ou seja, eles nunca recebem “s”,
“es”, “ies”.
• Sempre após os modais o verbo deve vir no infinitivo
sem o “to”.
• não têm passado nem futuro (com exceção do can que
tem passado e condicional).
Quais são os“modal verbs”?
Can
Ought to
Could
Used to
Should
Have to
Must
Shall
May
Will
Might
Would
CAN - CAN’T
Pode ser usado para expressar HABILIDADE, PERMISSÃO.
- I can play piano.
- We can wait for you.
- Liz and Mary can run for a long time.
Affirmative
- Tom can use the computer for 2 hours.
- They can’t eat all desert.
- Sarah can’t stop to do it.
Negative (can + not = can’t)
- Can I use your cell phone
- Can we show these picture for you?
Interrogative
SHOULD - SHOULDN’T
É usado para expressar um CONSELHO , uma SUGESTÃO.
• You should obey the rules.
• You should go to the doctor.
Affirmative
• We should come back to home.
• We shouldn’t bring the cell phone to the class.
• Linda shouldn’t go to the party.
Negative
• You shouldn’t drink soda.
• Should you tell her about me?
• Should we go out?
Interrogative
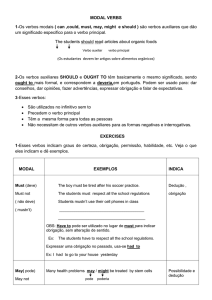
MUST = HAVE TO
São usados para expressão OBRIGAÇÃO.
(estudaremos no sentido de algo preocupante, com consequências.
Geralmente casos de estudo e saúde (unit 4))
•
•
•
•
You must go to school. = You have to go to school.
She must study more. = She has to study more.
Para HE / SHE/ IT
I must go. = I have to go.
They must leave early. = They have to leave early.
• You must take some time off and get some rest. =
You have to take some time off and get some rest.
• You must take some medicine for that cough. =
You have to take some medicine for that cough.
MUST NOT or MUSTN’T
Indica uma PROIBIÇÃO.
• Passengers must not use their cell phones on board airplane.
• You mustn’t smoke here.
• She mustn’t go.
• Tom mustn’t stay on the internet all day.
• You mustn’t smoke.
• They mustn’t destroy other’s property.
• You mustn’t interrupt the teacher
• You mustn’t discuss with your sister.
• Liz mustn’t stay up late.
DON’T HAVE TO
Indica AUSÊNCIA DE OBRIGAÇÃO, ou seja a “não obrigação”.
• You don’t have to go out.
• She doesn’t have to study today.
Para HE / SHE/ IT
• Fred don’t have to go to the party.
• Megg and Brian don’t have to come back.
• They don’t have to stand up all time.
• I don’t have to do this.
• I don’t have to sell my car.
• We don’t have to tell her about this.
• You don’t have to stay here.
REVIEW
OBRIGAÇÃO
PROIBIÇÃO
(OBLIGATION) (PROHIBITION)
MUST
HAVE TO
MUST NOT
MUSTN’T
SUGESTÃO /
CONSELHO
(SUGGESTION /
ADIVICE)
AUSÊNCIA DE
OBRIGAÇÃO
(ABSENCE OF
OBLIGATION)
HABILIDADE /
PERMISSÃO
(ABILITY
/PERMISSION)
SHOULD
DON’T HAVE
TO
CAN