NEUROQUÍMICA DAS
COMORBIDADES EM PSIQUIATRIA
RODRIGO MACHADO VIEIRA
PROGRAMA DE PESQUISA EM TRANSTORNOS DO HUMOR- LIM27
PROFESSOR ORIENTADOR DO PROGRAMA DE PÓS-GRADUAÇÃO
EM PSIQUIATRIA-UNIVERSIDADE DE SÃO PAULO
Edited by: Michael R. Von Korff, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, 2009
Modelos de Comorbidades em Psiquiatria
Comorbidade Diagnóstica – dois ou mais transtornos cujos critérios
diagnósticos se baseiam em sintomas não específicos
Comorbidade Prognóstica – quando a combinação de 2 transtornos
facilita o aparecimento de um terceiro, como por exemplo, a maior chance
de que um paciente com diagnóstico de depressão e ansiedade venha a
apresentar o abuso ou dependência de álcool e drogas
Comorbidade Patogênica – quando um determinado
distúrbio pode levar ao aparecimento de outro, e
ambos podem ser etiologicamente relacionados
Comorbidades nos Transtornos
Psiquiátricos
Transtornos de Humor e
Psicoses
Manji et al 2000
Comorbidades mais comuns em Psiquiatria
Depressão e Enxaqueca
Alcoolismo e Transtorno Bipolar (também
Dependência a Drogas)
Alcoolismo e Depressão
Depressão e Doença Cardiovascular
Depressão e Transtornos de Ansiedade
Depressão e Dor
TDAH e Transtornos de Humor
NIH, 2002
Comorbidades em Eixo I no Transtorno Bipolar
(Stanley Bipolar Treatment Network)
Abuso de Substância
Abuso de Alcool
Abuso de Maconha
Abuso Estimulantes
Abuso Cocaina
Abuso de Sedativos
Abuso de Opióides
T. De Ansiedade
Pânico/Agorafobia
Fobia Social
Fobia Simples
TOC
TEPT
TAG
Transtorno Alimentar
Bulimia Nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa
0
10
20
30
40
50
Mcal
Elroy
et al Goodwin
2001, Goodwin
Jamison 2007
Mc Elroy et
2001,
andand
Jamison
2007
Segundos-Mensageiros e
Comorbidades em Psiquiatria
**
canais iônicos
PLC-b
adenil ciclase
Múltiplos processos
fisiológicos
**
**
Depressão
T. Bipolar
Esquizofrenia
**
adenil ciclases
Inibição AMPc
canais iônicos
fosfodiesterases
fosfolipases
PLC-b
DAG
Ca2+
PKC
Adenil
ciclases
Ca2+
**** Tratamento das comorbidades
**** Eventos adversos
From Gutkind
Cascatas de Plasticidade Intracelular:
Relevância nas Comorbidades em Psiquiatria
Responsável
pelas
“comorbidades?”
Monoaminas
Glutamato
GABA
Neuropeptídeos
Cascatas de
Plasticidade
Intracelular
Perda &
Atrofia Celular
Perda da Resiliência
Celular
Principal alvo
para T4, CORT
Alvos para os
tratamentos
tradicionais
eficazes
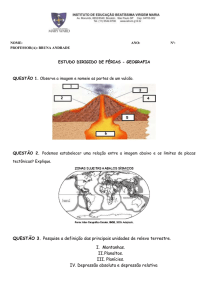
Neurobiologia das Comorbidades em Psiquiatria
-DEPRESSÃO E TRANSTORNOS DE ANSIEDADE
-DEPRESSÃO E DOENÇA CARDIOVASCULAR
-TRANSTORNO BIPOLAR E GOTA
Comorbidade entre Depressão e Ansiedade:
Neurobiologia Compartilhada ?
Kessler et al 1999, Roy-Birne et al 2000
Primeira Linha no Tratmento dos Transtornos
Ansiosos são Antidepressivos
O Sistema Serotonérgico na Comorbidade Depressão
e Transtornos Ansiosos
Psicofarmacologia na Comorbidade Depressão e Ansiedade:
Papel Chave dos Sistemas Serotonérgico e Noradrenérgico
Russell JM et al 2001, Silverstone et al 2002, Stahl et al 2007
Neurobiologia das Comorbidades em Psiquiatria
-DEPRESSÃO E DOENÇA CARDIOVASCULAR
Depressão e Doença Cardiovascular:
Lidando com o Problema
Integration of Evidence Article
Abnormal Function of MAO-A in Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder
and Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic
Implications
Rodrigo Machado-Vieira, Carlos A Zarate Jr, Ellen Frank, Michael Thase, Alan Mallinger
Abstract
The association between Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and cardiovascular disease (CVD)
is among the best described medical comorbidities. The presence of MDD increases the risk for
cardiac admissions and death and increases healthcare costs in patients with CVD, and likewise, CVD
affects the course and outcome of MDD. The potential shared biological mechanisms involved in
these comorbid conditions are not well known. However, the enzyme monoamine oxidase-A (MAOA), which has a key role in the degradation of catecholamines, has been associated with the
pathophysiology and therapeutics of both MDD and CVD. Increased MAO-A activity results in the
dysregulation of downstream targets of this enzyme, and thus affects the pathophysiology of both
diseases. These deleterious effects include altered noradrenaline turnover, with a direct elevation in
oxidative stress parameters as well as increased platelet activity and cytokine levels. These effects
were shown to be reversed by MAO inhibitors. Here, a model describing a key role for the MAO-A in
comorbid MDD and CVD is proposed, with focus on the shared pathophysiological mechanisms and
the potential therapeutic relevance of agents targeting this enzyme.
Biol Psychiatry, submitted
Comorbidade entre Depressão e Doença
Cardiovascular: Papel Chave da MAO-A
MAO-A
CÉREBRO
Estresse Oxidativo
Turnover Noradrenalina
Depleção de Monoaminas
CORAÇÃO
Estresse Oxidativo
Aumento NA
(disfunção endotelial)
(aumento cortisol)
(aumento citocinas)
Dano mitocondrial
Turnover Noradrenalina
Depleção de Monoaminas
Agregação Plaquetária
Agregação Plaquetária
Disfunção HPA
Inflamação
Efeitos dos Inibidores da
MAO-A
Disfunção HPA
Inflamação
Disfunção/Dano Celular
Depressão
Doença Cardiovascular
Depressão e Doença Cardiovascular:
MAO-A no Cérebro e Periferia
IMAO-A
Distribuição MAO-A
Cascatas de Plasticidade Intracelular: Monoaminas
na Depressão e Doença Cardiovascular
Responsável
pelas
“comorbidades?”
Monoaminas
Glutamato
GABA
Neuropeptídeos
Cascatas de
Plasticidade
Intracelular
Perda &
Atrofia Celular
Perda da Resiliência
Celular
Principal alvo
para T4, CORT
Alvos para os
tratamentos
tradicionais
eficazes
Neurobiologia das Comorbidades em Psiquiatria
-TRANSTORNO BIPOLAR E GOTA (HIPERURICEMIA)
Therapeutic Efficacy of Allopurinol in Mania Associated
With Hyperuricemia
A 43-year-old white man was admitted for treatment of his first manic episode. He had previous major
depressive episodes that started when he was 25 years old and had a strong family history of bipolar disorder.
Initial treatment included daily dosages of lithium 900 mg (level = 0,8 mEq/L) and haloperidol 15 mg for two weeks,
without improvement, despite adequate compliance. Increase in lithium dosage was limited by side effects and
divalproex sodium 500 mg three times daily was added gradually to the treatment (level = 92 mcg/mL). After three
weeks with this treatment regimen, symptoms did not improve and he was still hyperactive, irritated, and
presenting insomnia, pressure of speech, and grandiose ideas (Young Mania Rating Scale [YMRS] score = 36).
Physical and laboratory investigations performed were normal, except for hyperuricemia (level = 9.9 mg/100 ml).
At this stage, risperidone 2 mg twice daily was included in the treatment, without improvement after two weeks
(YMRS score = 35). Serum lithium and uric acid presented no changes compared to the first screening.
Subsequently, adjunctive treatment with allopurinol 300 mg daily was initiated. Three days later, the patient
presented important remission of insomnia and within two weeks he became calmer and presented remission of
agitation, aggressive behavior, and flight of ideas (YMRS score = 11). Uric acid declined to normal levels (6.9
mg/100 ml).
A 42-year-old woman was admitted with treatment-refractory mania taking daily dosages of lithium 1200 mg
(level = 1,0 mEq/L), divalproex sodium 2250 mg (level = 92 mcg/mL), and haloperidol 15 mg for at least one month
before admission. She reported feeling euphoric, powerful, with less need for sleep, pressure of speech,
hyperactive, and hypersexual (YMRS score = 36). Similar episodes had occurred since the age of 32 and symptoms
had been worsening even with adequate compliance with medications. No medication had been used for
hyperuricemia (level = 10,2 mg/100 ml) presented at baseline. Given our previous successful experience in the case
above, allopurinol 300 mg daily was added. During the next five days, symptoms did not improve (YMRS score = 33)
and hyperuricemia was still present (level = 9,7 mg/100 ml). Symptoms then started to diminish gradually and after
three weeks with allopurinol; she was calmer and her sleep improved (YMRS = 17), but she still described herself
feeling happy. Uricemia decreased to normal levels (7,7 mg/100 ml), along with a slight increase in the hepatic
function tests (glucose oxidase test and glutamyl transpeptidase). The only reported side effect was mild memory
worsening.
Machado-Vieira et al, J Clin Psychopharmacol 2001
Disfunção Purinérgica no Transtorno Bipolar
1859- Lítio demonstrou dissolver pedras de urato
Século 19: diátese do ácido úrico, predisposição a reumatismo, doença
cardiovascular e transtornos mentais
1896 Carl Lange- depressão e excitação periódica‘’ e sais de lítio
John Cade em 1949 injetou lítio (urato) e observou que guinea pigs “acalmavam”
Remissão dos sintomas maníacos associados com maior excreção de ácido úrico
(Anumonye et al 1968)
Dados genéticos sugerem disfunção purinérgica no THB (Barden et al 2006; Lucae et al
2006)
Lesh-Nyhan Syndrome é uma doença rara do metabolismo purinérgico (ausência da
enzima HPRT); distonia, disartia, retardo mental, e auto-agressão
• Purinas exercem um papel chave no
metabolismo energético e na
regulação de neurotransmissão (ATP
+ adenosina)
• Adenosina é um neuromodulador
amplamente distribuído, atuando
pelos receptores Adenosina-A1 e A2
• Agonistas da adenosina apresentam
efeitos:
– sedativos
– anticonvulsivante
– anti-agressividade
– antipsicótico
Vias do Sistema Purinérgico
AMP
IMP
deaminase
deaminase
Inosine
Adenosine
GMP
Guanosine
Purine nucleotide
phosphorylase
Xanthine
Hypoxanthine
deaminase
deaminase
Xanthosine
Purine nucleotide
phosphorylase
Adenine
deaminase
XMP
Xanthine Oxidase
deaminase
Xanthine Oxidase
Uric Acid
Guanine
Alopurinol e Dipiridamol
•
Dois fármacos comercialmente disponíveis
Alopurinol (Zyloprim, Progout): xanthine oxidase inhibitor for
gout
• decreases production of uric acid, superoxide, &
hydroxide peroxide
Dipiridamol (Persantin): adenosine reuptake inhibitor (inhibits
platelet aggregation)
• increases extracellular concentrations of both
endogenous and exogenous adenosine
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled 4-week
study on the efficacy and safety of the purinergic agents
allopurinol and dipyridamole in acute bipolar mania
Inclusion Criteria
-Dx of bipolar disorder
-Current episode manic
with or without psychotic
features (YMRS 22)
Exclusion Criteria
-Rapid cycling in past 12
months
-Current mixed episode
-History of nonresponse
to to lithium
-Current axis I psychiatric
disorder other than BD
Drug Free Period
7 days
Allopurinol (600 mg/day)
+
Lithium 600-900 mg/
N=45
Dipyridamole (200 mg/day)
+
Lithium 600-900 mg/d
N=50
Placebo
+
Lithium 600-900 mg/d
N=46
Double Blind Phase
4 weeks
Machado-Vieira et al. J Clin Psychiatry 2008
YMRS scores during the four
week follow-up period
40
Lithium +
Allopurinol
W
Dipyridamole
30
Placebo
W
20
W
W
W
W
10
W
*
W
*
0
0
1
2
3
4
Week
Machado-Vieira et al. J Clin Psychiatry 2008
Mudanças na Sintomatologia Maníaca e
Associação com Níveis de Ácido Úrico
Allopurinol
Allopurinol
20
Dipyridamole
A
A
A
0
A
A
-20
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
A A
A
A
A
-40
A
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
AA
A A A
A A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
(r=.39, p=.01)
A A
A
A AA
A
A
A
AA
A
AA
A
A
AA
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
-60
Placebo
20
A
A
0
A
A
A
A
-20
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
AA A
A A
A
A
A
AA A
A
A
AA
A
A A
A
AA
-40
A
-60
-6.0
-4.0
-2.0
0.0
2.0
4.0
Uric Acid Change
Machado-Vieira et al. 2008
Aumento nos Níveis de Ácido Úrico durante
Episódios Maníacos
(F = 28.12, df = 42, p < 0.001)
Salvadore et al, Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacol and BiolPsychiatry, 2010
Perspectivas
Pesquisas Biológicas avaliando Comorbidades
Critérios Diagnósticos (DSM-V...)
Pesquisa Clínica em Comorbidades
Base Genética (Co-Transmissão?) dos Transtornos Mentais Comórbidos
Diagnóstico e Biologia das Comorbidades Psiquiátricas e Médicas Gerais
Novos Alvos Terapêuticos
Obrigado
[email protected]