03/06/2015
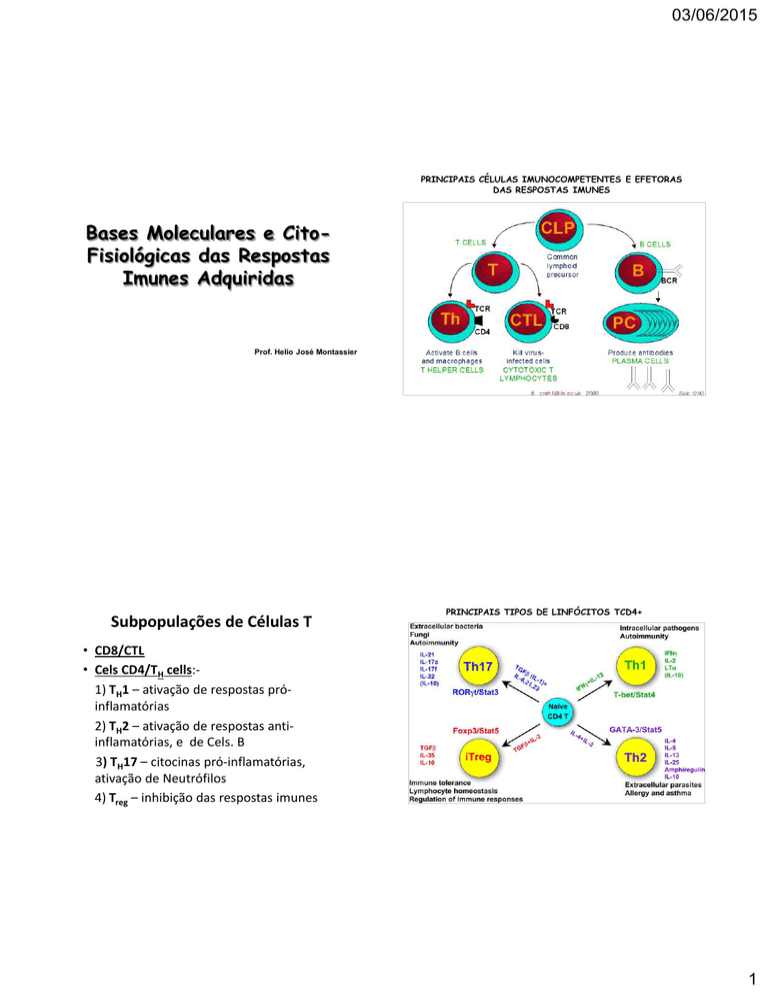
PRINCIPAIS CÉLULAS IMUNOCOMPETENTES E EFETORAS
DAS RESPOSTAS IMUNES
Bases Moleculares e CitoFisiológicas das Respostas
Imunes Adquiridas
Prof. Helio José Montassier
Subpopulações de Células T
PRINCIPAIS TIPOS DE LINFÓCITOS TCD4+
• CD8/CTL
• Cels CD4/TH cells:1) TH1 – ativação de respostas próinflamatórias
2) TH2 – ativação de respostas antiinflamatórias, e de Cels. B
3) TH17 – citocinas pró-inflamatórias,
ativação de Neutrófilos
4) Treg – inhibição das respostas imunes
1
03/06/2015
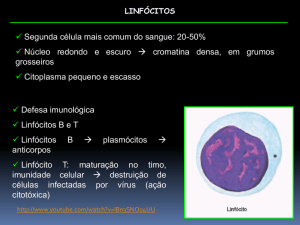
Linfócitos T
Como as Células T interagem,
reconhecem e respondem aos
Antígenos ???
Necessidade de 3 Sinais para a
MHC-II + Ag + TCR
2
03/06/2015
Moléculas co-estimuladoras na
apresentação de Ag para LT
Inibição da Ativação das células T CD4+ / TCD8+
pela interação da molécula CTLA-4 com a B7
As formas de atuação de atuação das CITOCINAS (Cytokines)
Entendendo melhor o
3º SINAL e a forma de
atuação das Cels. TH
Cytokines
Cytokines
As citocinas servem de
mensageiros / carreadores
de sinais (+) ou (-) entre as
Cels. TH e as demais Cels.
Do SI como Cels. B, Tc,
Macrófagos, etc.
Cytokines
3
03/06/2015
Possíveis Efeitos das Citocinas nas Células do Sistema Imune
Principais Fases das Respostas Imunes
4
03/06/2015
Fases da Ativação dos Linfócitos TCD4
Principais Fases das RIs Mediadas por
Linfócitos T
5
03/06/2015
Principais Fases das RIs Mediadas por
Linfócitos B
Respostas Imunes Mediadas por
Linfócitos B para a Produção de
Anticorpos
Linfócitos B
6
03/06/2015
Ag
Funções dos Linfócitos TH na Mudança de
Isótipo de Ac Produzido pelos Linfócitos B
A ação de Diferentes Citocinas sobre as Mudanças no Isótipo dos Anticorpos
Produzidos pelos Linfócitos B contra Antígenos T-dependentes
7
03/06/2015
A ação de Diferentes Citocinas sobre as Mudanças no
Isótipo dos Anticorpos Produzidos pelos Linfócitos B
contra Antígenos T-dependentes
Respostas Imunes Mediadas por
Linfócitos T citotóxicos CD8+
Principais Fases das RIs Mediadas por Linfócitos Tc – CD8+
Ativação das células T
CD8+
• Ligação do Linf. TCD8 naive à APC
– TCR + peptídeo-MHC classe I
– Co-estimuladores
• A ativação completa das células T CD8 naive
pode exigir a participação dos LT CD4
• Expansão clonal – IL-12, IL-15, IL-7
8
03/06/2015
Mecanismos efetores da imunidade
mediada por células
Células T CD4 efetoras
• Subconjunto Th1 e Th2 das células T CD4
– Células TCD4 podem se diferenciar em
subconjuntos de células efetoras que produzam
conjuntos diferentes de citocinas e, portanto,
desempenham funções efetoras distintas
Células TCD4+
Diferenciação
em Th1 e Th2
• Th1 - reconhecem Ag microbianos e ativam
fagócitos a destruir os microrganismos
ingeridos
• Th2 - resposta imune a parasitas e alérgenos
9
03/06/2015
Th1 e Th2
Th1
Células
Th1/Th2
Infecções mediadas por fagócitos, especialmente
por microrganismos intracelulares
• Estimula a atividade microbicida dos fagócitos
– Ativação mediada por contato (interação CD40L-CD40)
e por IFN-γ
– MØ – espécies reativas do Oxigênio, oxido nítrico e
enzimas lisossômicas
– MØ – estimula a inflamação – citocinas (TNF e IL-1),
prostaglandinas e leucotrienos
– MØ – formação de tecido de reparo – síntese de fatores
de crescimento
• Produção de Ac IgG opsonizantes e fixadores do
complemento – fagocitose de microrganismos
10
03/06/2015
Figure 13-7 Effector functions of TH1 cells. CD4+ T cells that differentiate into TH1 cells
secrete IFN-γ, lymphotoxin (LT) and TNF, and IL-2. IFN-γ acts on
macrophages to increase phagocytosis and killing of microbes in phagolysosomes and on B
lymphocytes to stimulate production of IgG antibodies that opsonize microbes for phagocytosis.
LT and TNF activate neutrophils and stimulate inflammation. IL-2 is the autocrine growth factor
made by this subset of T cells (not shown). APC, antigen-presenting cell.
Figure 13-13 Effector functions of TH2 cells. CD4++ T cells that differentiate into TH2 cells
secrete IL-4 and IL-5. IL-4 acts on B cells to stimulate production of antibodies that bind to
mast cells, such as IgE. IL-4 is also an autocrine growth and differentiation cytokine for TH2
cells. IL-5 activates eosinophils, a response that is important for defense against helminthic
infections. Cytokines from TH2 cells also inhibit macrophage activation and TH1-mediated
reactions. APC, antigen-presenting cell.
Antagonismos entre as Cels. Th1 e Th2 nas
respostas imunes
11
03/06/2015
Funções Efetoras das Cels. Th17
Atividades das Cels. TH17
Respostas Imunes Adaptativas
Mediadas por Linfócitos Tc
12
03/06/2015
LT CD8+
Citotoxicidade por Tc – CD8+
• A morte celular por
CTLs é específica para
o Ag e dependente de
contato
Célula
TCD8
Célula-alvo
(infectada)
Figure 13-14 Steps in CTL-mediated lysis of target cells. A CTL recognizes the antigen-expressing target cell and
is activated. Activation results in the release of granule contents from the CTL, which delivers a lethal hit to the
target. The CTL may detach and kill another target cell while the first target goes on to die. Note that formation
of conjugates between a CTL and its target and activation of the CTL also require interactions between accessory
molecules (LFA-1, CD8) on the CTL and their specific ligands on the target cell; these are not shown.
Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 12 September 2008 02:01 AM)
© 2005 Elsevier
Mecanismos efetores das Respostas
Mediadas por células TReg
Figure 13-16 Mechanisms of CTL-mediated lysis of target cells. CTLs kill target cells by two main
mechanisms. A. Complexes of perforin and granzymes are released from the CTL by granule
exocytosis and enter target cells. The granzymes are delivered into the cytoplasm of the target
cells by a perforin-dependent mechanism, and they induce apoptosis. B. FasL is expressed on
activated CTLs, engages Fas on the surface of target cells, and induces apoptosis.
13
03/06/2015
Regulação das RIs por Linfócitos TReg
Mecanismos Inibitórios (Negativos)
das Respostas Imunes Adquiridas
3 – LINFÓCITOS T reguladores (T reg)
C
H
14