Algoritmia e Programação
APROG
Matrizes
Algoritmia e Java
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
1/28
Sumário
Matrizes
Enquadramento
Noção
Interesse
Uso
Exemplos
Soma
Global
Cada Linha
Cada Coluna
Declaração
Java: Matriz é um Array de Arrays
Manipulação de Elementos
Transferência entre Módulos/Métodos
Passagem de Parâmetros
Diagonal Principal
Maior
Global
Cada Linha
Cada Coluna
Matriz
Retorno da Função
Transposta
Exemplo
Ordenada
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
2/28
Enquadramento
Matrizes
Tipos de Arrays
Vetor
// array uni-dimensional
Matriz
// array bi-dimensional
Vector
Estrutura de dados complexa
Armazena múltiplos valores ao mesmo tempo
Valores
Todos do mesmo tipo
Organizados de forma linear
Dimensão
Fixa
Não pode ser alterada em tempo de execução (run-time)
elemento 2
valor 10
elementos
12
15
10
18
...
13
14
índices
0
1
2
3
...
n-2
n-1
comprimento (ou dimensão) n
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
3/28
Noção de Matriz
Matrizes
Estrutura de dados complexa
Armazena múltiplos valores ao mesmo tempo
Valores
Todos do mesmo tipo
Organizados em linhas e colunas
Dimensão
Fixa
Não pode ser alterada em tempo de execução (run-time)
0
1
...
m-1
0
11
24
...
27
1
5
56
...
18
...
...
...
...
...
1
8
...
34
dimensão n x m
índice de linha
(comprimento n)
n-1
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
índice de coluna (comprimento m)
elemento (1,m-1)
valor 18
4/28
Interesse
Matrizes
Armazenar
Tabelas bidimensionais
Valores
Todos do mesmo tipo
Organizados em linhas e colunas
Exemplos
Tabela de notas de alunos
// conjunto de números inteiros organizados em linhas e colunas
Nº Aluno
Português
Inglês
Matemática
1138
12
15
19
1249
18
17
12
1544
15
12
14
Tabela de disciplinas de um curso // conjunto de Strings organizadas em linhas e colunas
Ano
Disciplinas
1º
APROG
LAPR1
PRCMP
PPROG
ESOFT
LAPR2
2º
ARQCP
BDDAD
ESINF
EAPLI
LAPR3
LAPR4
3º
ASIST
ALGAV
ARQSI
SGRAI
LAPR5
PESTI
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
5/28
Matrizes
Uso
Preciso Saber
Declarar uma matriz
Java
Matriz é um Array de Arrays
Manipular elementos de uma matriz
Transferir uma matriz entre módulos/métodos
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
6/28
Declaração
Matrizes
Algoritmia
1/4
Java
Declaração 1: dimensão definida na declaração
Sintaxe: tipo nomeMatriz[Linhas][Colunas]
Ex: INTEIRO notas[20][10]
RAM
notas[0,0]
Matriz é um objeto (array de arrays)
Nome da matriz é referência para objeto
tipo nomeMat[ ][ ] = new tipo [Linhas][Colunas];
int notas[ ][ ] = new int[20][10];
ou
tipo[ ][ ] nomeMat = new tipo [Linhas][Colunas];
int[ ][ ] notas = new int[20][10];
notas[0,1]
notas[0,2]
...
notas[19,9]
Inicializações automáticas:
Tipo primitivo
Numérico: 0
Booleano: false
Tipo referência: null (Ex: String)
Declaração 2: dimensão definida depois da declaracão
Sintaxe: tipo nomeMatriz[ ][ ]
...
criar nomeMatriz[Linhas][Colunas]
Ex: INTEIRO notas[ ][ ]
criar notas[20][10]
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
tipo nomeMatriz[ ][ ];
...
nomeMat= new tipo [Linhas][Colunas];
int notas[ ][ ];
notas = new int[20][10];
7/28
Declaração
Matrizes
2/4
Exemplos
// Algoritmia
ED
INTEIRO numLin, numCol, notas[20][10], mat[][]
INÍCIO
...
numLin lerNumero("Linhas")
// lerNumero é função do programa
numCol lerNumero("Colunas")
criar mat[numLin][numCol]
...
FIM
...
// Java
public class Exemplo_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int
...
int
int
int
...
notas[][] = new int[20][10];
// matriz criada; elementos inicializados a 0
numLin = lerNumero("Linhas");
// lerNumero é função do programa
numCol = lerNumero("Colunas");
mat[][] = new int[numLim][numCol];
}
...
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
8/28
Declaração
Matrizes
3/4
Exemplos
// Algoritmia
ED
REAL mat1[][]
INTEIRO[][] mat2
INÍCIO
...
criar mat1[10][30]
...
criar mat2[5][10]
FIM
// Java
public class Exemplo_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
double mat1[][];
...
mat1 = new double[10][30];
// declarada variável mat1 para representar matriz
// matriz criada e atribuída a mat1
// elementos inicializados a zero
...
int[][] mat2 = new int[5][10];
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
9/28
Declaração
Matrizes
4/4
Exemplos
// Algoritmia
ED
INTEIRO matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{10,12,15},{19,9,18} }
...
FIM
linha 0
linha 1
// criada e inicializada uma matriz 2x3
10
12
15
19
9
18
// Java
public class Exemplo_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{10,12,15},{19,9,18}};
...
// criada e inicializada uma matriz 2x3
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
10/28
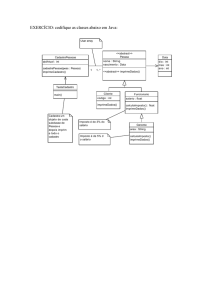
Java : Matriz é um Array de Arrays
Matrizes
Nome da Matriz
Referência de um array
Guarda referências de outros arrays
Representam linhas da matriz
Constituem os elementos da matriz
Exemplo
// referência = endereço
// podem ter dimensões diferentes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
mat[0][0]
mat[0][1]
mat[0][2]
1
2
3
mat[1][0]
mat[1][1]
mat[1][2]
mat[1] referência
4
5
6
ARRAY
mat[2] referência
mat[2][0]
7
mat[2][1]
8
mat[2][2]
9
ARRAY
int[][] mat = new int[3] [3];
Representação RAM
mat referência
mat[0]
mat.length
referência
ARRAY
ARRAYS
ARRAY
mat[x].length (x=0, 1 ou 2)
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
11/28
Matrizes
Manipulação de Elementos
Elemento
Pode ser manipulado individualmente
RAM
Funciona como variável simples
notas[0,0]
Identificado
notas[0,1]
Nome da matriz
Índices de linha e coluna respetivos
notas[0,2]
...
notas[19,9]
Indicar um elemento
Algoritmia
Java
Sintaxe: nomeMatriz [índiceLinha] [índiceColuna] nomeMatriz [índiceLinha] [índiceColuna];
Ex: notas[0][2]
notas[0][2]
Manipulação de Elementos
Um elemento
Todos os elementos
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
12/28
Manipulação de um Elemento
Matrizes
Algoritmia
Java
Atribuir um valor a um elemento
Ex:
guardar ou actualizar um elemento
Sintaxe: nomeMatriz[índice Linha][índice Coluna] valor
Ex: notas[0][2]18
nomeMatriz[í. Linha][í. Coluna] = valor;
notas[0][2] = 18;
Atribuir o valor de um elemento a uma variável
Sintaxe: variável nomeMatriz[índice Linha][indice Coluna] variável=nomeMatriz[í. Linha][í.Coluna];
Ex: x notas[0][2]
// x do tipo INTEIRO
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
x = notas[0][2];
// x do tipo int
13/28
Manipulação de todos os Elementos
Matrizes
Algoritmia
Java
Indicar todos os elementos (matriz n x m)
PARA (i0 ATÉ n-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
PARA (j0 ATÉ m-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
nomeMatriz.length (nº linhas)
nomeMatriz[i].length (nº cols linha i)
for(i=0; i< nomeMatriz.length; i++){
for(j=0; j< nomeMatriz[i].length; j++){
... nomeMatriz[i][j] ...
... nomeMatriz[i][j] ...
FPARA
FPARA
}
}
Exemplo
Preencher toda a matriz notas (n x m) com valores lidos do teclado
PARA (i0 ATÉ n-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
PARA (j0 ATÉ m-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
for(i=0; i<notas.length; i++){
for(j=0; j<notas[i].length; j++){
LER( notas[i][j] )
notas[i][j]=ler.nextInt();
FPARA
FPARA
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
14/28
Transferência entre Módulos/Métodos
Matrizes
1/5
Em Java
Matriz é objeto basta transferir referência desse objeto indicar nome da matriz
Exemplo
int[ ][ ] mat = new int[3][3];
nome da matriz (objeto)
mat referência
mat[0][0]
mat[0][1]
mat[0][2]
1
2
3
mat[1][0]
mat[1][1]
mat[1][2]
mat[1] referência
4
5
6
ARRAY
mat[2] referência
mat[2][0]
7
mat[2][1]
8
mat[2][2]
9
ARRAY
mat[0]
mat.length
referência
ARRAY
(objeto)
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
ARRAY
ARRAYS
(objetos)
mat[2].length
15/28
Matrizes
Transferência entre Módulos/Métodos
2/5
Formas de Transferir uma Matriz
Passagem de parâmetros
Retorno da função
DEFINIR nome (..., tipo nomeMatriz [ ][ ], ...)
ED
// variáveis e constantes locais
INÍCIO
// corpo do procedimento
FDEF
Procedimento
DEFINIR tipo_retornado nome (..., tipo[ ][ ] nomeMatriz, ...)
ED
// variáveis e constantes locais
INÍCIO
// corpo da função
RETORNAR expressão_tipo_retornado
FDEF
Função
DEFINIR tipo[ ][ ] nome (...)
ED tipo[ ][ ] nomeMatriz
INÍCIO
// corpo da função
RETORNAR nomeMatriz
FDEF
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
Função
16/28
Transferência entre Módulos/Métodos
Matrizes
3/5
Passagem de Parâmetros
Passada cópia da referência da matriz
DEFINIR tipo nome(..., tipo nomeMatriz [ ][ ], ...)
Módulo acede à matriz original Pode modificar a matriz original
Parâmetro formal funciona como parâmetro de entrada e de saída
Declaração de um parâmetro formal
Para receber a referência da matriz
Algoritmia
Java
Sintaxe: tipo nomeMatriz[][]
tipo nomeMatriz[][];
ou
tipo[][] nomeMatriz
Ex: DEFINIR ler( INTEIRO matriz[ ][ ] , ...) ...
ou
tipo[][] nomeMatriz
public static void ler( int matriz[ ][ ], ...){...}
Chamada de um módulo
Passar referência da matriz (i.e., nome da matriz)
Algoritmia
Sintaxe: nomeMatriz
Ex: ler(notas, ...)
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
Java
nomeMatriz
ler(notas, ...);
17/28
Transferência entre Módulos/Métodos
Matrizes
4/5
Retorno da Função
Retornada referência da matriz
DEFINIR tipo[ ][ ] nome(...)
ED tipo[ ][ ] nomeMatriz
INÍCIO
Declaração do tipo_retornado da função
Tipo matriz
// corpo da função
Algoritmia
•
Sintaxe: DEFINIR tipo[ ][ ] nomeFunção ( ...) ...
RETORNAR nomeMatriz
FDEF
Ex: DEFINIR INTEIRO[ ][ ] filtrar(...) ...
Java
public static tipo[ ][ ] nomeMétodo(...){...};
public static int[ ][ ] filtrar(...){...}
Retorno
Referência da matriz (i.e., nome da matriz)
Algoritmia
Sintaxe: RETORNAR nomeMatriz
Ex: RETORNAR notas
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
Java
return nomeMatriz;
return notas;
18/28
Matrizes
Transferência entre Módulos/Métodos
5/5
Exemplo
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Exemplo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numLin = lerNumero("linhas");
int numCol = lerNumero("colunas");
int[][] m1 = new int[numLin][numCol];
lerMatriz(m1);
int[][] m2 = clonar(m1);
mostrarMatriz(m1);
mostrarMatriz(m2);
}
private static void lerMatriz(int[][] mat) {
Scanner ler = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\nDigite nº inteiros:");
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print((i+1)+ "," +(j+1) +":");
mat[i][j] = ler.nextInt();
}
}
}
private static int[][] clonar(int[][] mat1){
int[][] mat2;
mat2 = new int[mat1.length][mat1[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < mat1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat1[i].length; j++)
mat2[i][j] = mat1[i][j];
return mat2;
}
private static int lerNumero(String s){
Scanner ler = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("\nInsira o nº de "+s+":");
int n = ler.nextInt();
while (n<=0) {
System.out.println("Valor Inválido!!" +
"Insira novo nº de "+s+":");
n = ler.nextInt();
}
return n;
}
}
private static void mostrarMatriz(int[][] mat){
System.out.println("\nMatriz:")
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < mat[i].length; j++)
System.out.printf("%6d",mat[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
19/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Soma Global
ED
Funções pré-definidas
INTEIRO soma, lin, col, matriz[][]
comprimentoLinhas
INÍCIO
comprimentoColunas
matriz {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}}
soma 0
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
PARA (col0 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,lin)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
soma soma + matriz[lin][col]
FPARA
FPARA
ESCREVER("A soma de todos os elementos é ", soma)
FIM
public class SomaGlobal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}};
int soma=0;
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
for (int col = 0; col < matriz[lin].length; col++) {
soma = soma + matriz[lin][col];
}
}
System.out.println("A soma de todos os elementos é " + soma);
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
20/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Soma de Cada Linha
ED
INTEIRO soma, lin, col, matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}}
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
soma 0
PARA (col0 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,lin)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
soma soma + matriz[lin][col]
FPARA
ESCREVER("A soma da linha ", lin, " é ", soma)
FPARA
FIM
public class SomaLinha {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}};
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
int soma=0;
for (int col = 0; col < matriz[lin].length; col++) {
soma = soma + matriz[lin][col];
}
System.out.println("A soma da linha " + lin + " é " + soma);
}
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
21/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Soma de Cada Coluna
ED
INTEIRO soma, lin, col, matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}}
PARA (col0 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,0)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
soma 0
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
soma soma + matriz[lin][col]
FPARA
ESCREVER("A soma da coluna ", col, " é ", soma)
FPARA
FIM
public class SomaColuna {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}};
for (int col = 0; col < matriz[0].length; col++) {
int soma=0;
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
soma = soma + matriz[lin][col];
}
System.out.println("A soma da coluna " + col + " é ", soma);
}
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
22/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Soma da Diagonal Principal
ED
INTEIRO soma, lin, matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}}
soma 0
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
soma soma + matriz[lin][lin]
FPARA
ESCREVER("A soma da diagonal principal é ", soma)
FIM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class SomaDiagonalPrincipal{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}};
int soma=0;
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
soma = soma + matriz[lin][lin];
}
System.out.println("A soma da diagonal principal é " + soma);
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
23/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Maior Global
ED
INTEIRO maior, lin, col, matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,18,3},{4,17,6},{7,28,9},{10,11,12}}
maior matriz[0][0]
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
PARA (col0 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,lin)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
SE ( matriz[lin][col] > maior ) ENTÃO
maior matriz[lin][col]
FSE
FPARA
FPARA
ESCREVER("O maior número global é ", maior)
FIM
public class MaiorGlobal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,18,3},{4,17,6},{7,28,9},{10,11,12}};
int maior = matriz[0][0];
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
for (int col = 0; col < matriz[lin].length; col++)
if( matriz[lin][col] > maior )
maior = matriz[lin][col];
}
System.out.println("O maior número global é ", maior);
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
24/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Maior de Cada Linha
ED
INTEIRO maior, lin, col, matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,18,3},{4,17,6},{7,28,9},{10,11,12}}
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
maior matriz[lin][0]
PARA (col1 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,lin)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
SE ( matriz[lin][col] > maior ) ENTÃO
maior matriz[lin][col]
FSE
FPARA
ESCREVER("O maior número da linha ", lin, " é ", maior)
FPARA
FIM
public class MaiorLinha {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,18,3},{4,17,6},{7,28,9},{10,11,12}};
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
int maior = matriz[lin][0];
for (int col = 1; col < matriz[lin].length; col++)
if( matriz[lin][col] > maior )
maior = matriz[lin][col];
System.out.println("O maior número da linha ", lin, " é ", maior);
}
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
25/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Maior de Cada Coluna
ED
INTEIRO maior, lin, col, matriz[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,18,3},{4,17,6},{7,28,9},{10,11,12}}
PARA (col0 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,0)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
maior matriz[0][col]
PARA (lin1 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
SE ( matriz[lin][col] > maior ) ENTÃO
maior matriz[lin][col]
FSE
FPARA
ESCREVER("O maior número da coluna ", col, " é ", maior)
FPARA
FIM
public class MaiorColuna {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,18,3},{4,17,6},{7,28,9},{10,11,12}};
for (int col = 0; col < matriz[0].length; col++) {
int maior = matriz[0][col];
for (int lin = 1; lin < matriz.length; lin++)
if( matriz[lin][col] > maior )
maior = matriz[lin][col];
System.out.println("O maior número da coluna ", col, " é ", maior);
}
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
26/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Matriz Transposta
ED
INTEIRO lin, col, matriz[][], transposta[][]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}}
criar transposta[comprimentoColunas(matriz,0)][comprimentoLinhas(matriz)]
PARA (lin0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
PARA (col0 ATÉ comprimentoColunas(matriz,lin)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
transposta[col][lin]matriz[lin][col]
FPARA
FPARA
FIM
public class MatrizTransposta {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9},{10,11,12}};
int transposta[][] = new int[matriz[0].length][matriz.length];
for (int lin = 0; lin < matriz.length; lin++) {
for (int col = 0; col < matriz[lin].length; col++) {
transposta[col][lin] = matriz[lin][col];
}
}
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
27/28
Matrizes
(Exemplos)
Matriz Ordenada
ED
INTEIRO i, j, matriz[][], tmp[]
INÍCIO
matriz {{1,2,3},{7,8,9},{10,11,12},{4,5,6}}
PARA (i0 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-2 PASSO 1) FAZER
PARA (ji+1 ATÉ comprimentoLinhas(matriz)-1 PASSO 1) FAZER
SE (matriz[j][0] > matriz[i][0]) ENTÃO
tmp matriz[i]
Linhas ordenadas por
matriz[i] matriz[j]
matriz[j] tmp
ordem decrescente dos
FSE
elementos da primeira
FPARA
coluna
FPARA
FIM
public class MatrizOrdenada {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int matriz[][] = {{1,2,3},{7,8,9},{10,11,12},{4,5,6}};
for (int i = 0; i < matriz.length-1; i++)
for (int j = i+1; j < matriz.length; j++)
if( matriz[j][0] > matriz[i][0]){
int[] tmp = matriz[i];
// matriz[i] é a linha i
matriz[i] = matriz[j];
matriz[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
Nelson Freire (ISEP–DEI-APROG 2012/13)
28/28