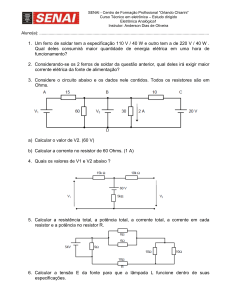
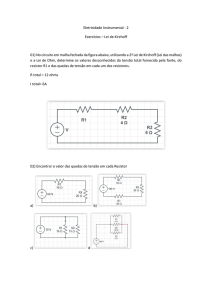
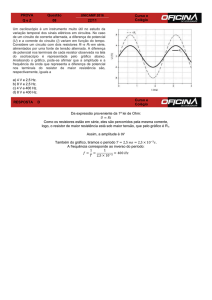
Física Geral - Laboratório
(2014/1)
Propagação de erros e medida de resistores em
série e em paralelo
1
Medidas indiretas - Propagação de erros
Propagação de erros
u = f (x, y)
Estimativa da grandeza
associada (medida indireta)
Medidas de duas grandezas x e y:
{(x1 , y1 ) , (x2 , y2 ) , . . . , (xN , yN )}
2
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Medidas indiretas - Propagação de erros
Propagação de erros
u = f (x, y)
Estimativa da grandeza
associada (medida indireta)
Medidas de duas grandezas x e y:
{(x1 , y1 ) , (x2 , y2 ) , . . . , (xN , yN )}
Queremos obter:
ū ±
2
ū
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Medidas indiretas - Propagação de erros
u = f(x)
x
3
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Medidas indiretas - Propagação de erros
u = f(x)
u + Δu
u
x
x + Δx
3
x
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Medidas indiretas - Propagação de erros
u = f(x)
u
u + Δu
df
=
dx
x
u
x
x + Δx
3
x
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Propagação de erros
u = f (x, y)
Em geral:
2
ū
=
✓
@f
@x
◆2
2
x̄
(x̄,ȳ)
+
✓
@f
@y
◆2
2
+
N
2
ȳ
(x̄,ȳ)
ū = f (x̄, ȳ)
i)
ii)
u=x±y
u = xy
ou
u = x/y
ū
ū
|ū|
=
4
s
⇣
=
x̄
x̄
✓
⌘2
q
+
✓
@f
@x
2
x̄
ȳ
ȳ
◆✓
+
◆2
2
ȳ
@f
@y
◆
xy
(x̄,ȳ)
± 2r
± 2r
⇣
x̄
x̄
x̄ ȳ
⌘✓
ȳ
ȳ
◆
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Propagação de erros
u = ↵x )
↵
u= )
x
ū
ū
= |↵|
|↵|
= 2
x̄
x̄
x̄
Exercícios:
i)
u=x
2
v)
ii) u = (x · y) / (x + y)
iii)
u=x+y+z
iv) u = xy + z
5
p = kl
vi) I = V /R
vii) v =
p
2gh
s
l
viii) T = 2⇡
g
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Montagem experimental
“Protoboard”
6
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
eplace
the bulb
thewith
bulba with a
em
paralelo:
purpose
r the Resistores
purpose
of calculating
of calculating
the current.
the current.
A
A
I
I
V 1/R1 + 1/R2
+
+ and IandV 1/R
P =
I
R
R
1
2
R
R
V
V
R
R
R
=
(R
–
–
P
1 . R2)/(R1 + R2) = “R1 // R2”
Resistores em série e paralelo
A
Resistores em série:
B
B
R1
B
R2
discrete
discrete
resistor
resistor
In EE, we
In EE,
do things
we do things
the easy
the
way…
easy way…
B
In
EE,
R represents the only property
the
Like with point-mass: replace o
a
with
their mass
to find
R represents
themonly
property
the
for the purpose of calculating t
Replace theAbulb with a
discrete Iresistor
for the purpose+of calculating
t
I
and
R
V
A –
I
B + R
and I
V
In EE,
–
The Easy
The Easy
Way…Way…
7
6.002 Fall 2000
Lecture 1
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and Ele
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Do
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and Ele
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Do
Like with point-mass: replace o
a
with
their
mass
m
to
find
6.002 Fall 2000
Lecture 1
RS = R 1 + R 2
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
eplace
the bulb
Replace
thewith
bulb
the
a with
bulbawith a
Resistores
em
paralelo:
purpose
r the
for
purpose
the
of calculating
purpose
of calculating
ofthe
calculating
current.
the current.
the current.
A
A
A
I
I
I
+
+ and+ IandV IandV I VRP= (R1 // R2) // R3
R
V1 R RV2 RRV3 R R
R
R
–
–
–
for the purpose of calculating t
Replace theAbulb with a
B
discrete Iresistor
for the purpose+of calculating
t
I
and
R a
Replace theAbulb
V with
–
discrete Iresistor
for the purpose
t
B +of calculating
I
and
R
V
In EE,
A –
I
the
B + R
and I
V
In
EE,
–
R represents the only property
the
Like with point-mass:
replace o
B
In
EE,
a
with
their mass
to find
R represents
themonly
property
the
Resistores em série e paralelo
Resistores em série:
B
A
A
B
B
R1
B
R2
B
R3
RS = R 1 + R 2 + R 3
discrete
discrete
resistor
discrete
resistor
resistor
In EE, we
In EE,
do things
In
we EE,
do things
we do things
the easy
the
way…
easy
theway…
easy way…
8
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and Ele
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Do
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and Ele
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Do
Like with point-mass: replace o
a
with
their
mass
m
to
find
6.002 Fall 2000
Lecture 1
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and Ele
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Do
Like with point-mass: replace o
a
with
their
mass
m
to
find
R
represents
the
only
property
6.002 Fall 2000
Lecture 1
The Easy
The Easy
Way…
The Easy
Way…Way…
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Montagem experimental
iscrete
discrete
resistor
resistor
discrete resistor
The
Easy
Way…
A
Replace
Replace
the bulb
thewith
bulba with a
discrete
discrete
resistor
resistor
the the
easyeasy
way…
way… the
B
ose
urpose
offor
calculating
ofthe
calculating
the the
current.
current. t
purpose
of
calculating
Replace
the
bulb
with
a
A
A
I I discrete resistor
I
V
V
+
+
+
for the
purpose
of
calculating
the
I
I
and
and
I
and
R
R
R
V V
V
R
R
A
– –
–I
+
B
B
I
and
R
V
In EE,
In
EE,do
wethings
do things
In E
– we
TheThe
Easy
Easy
Way…
Way…
The Easy Way…
B
In EE, we
In EE,
do things
we do things
theResistores
easy
the
way…
easy
way…
em paralelo:
B
B
B
1 2 3 4 ...
B
the
bulbbulb
with
with
a athe bulb with a
Replace
B
for thefor
purpose
the purpose
of calculating
of calculating
the
current.
the em
current.
Resistores
série:
A
A
1 2 3 4 ...
R1
I
I
V
V
+
+
R1
R2 and
Iand I
R2
R
R
V
V
R
R
–
–
R1
A
R represents
R represents
the only
the
property
only property
of interest!
of interest!
Like with
Likepoint-mass:
with point-mass:
replacereplace
objects
objects
F
F
with their
withmass
their m
mass
to find
m toafind a
m R2 m
Cite as: Anant Agarwal
Cite as: and
Anant
Jeffrey
Agarwal
Lang,
and
course
Jeffrey
materials
Lang, course
for 6.002
materials
Circuits
forand
6.002
Electronics,
Circuits and
Spring
Electronics,
2007. MIT
Spring 2007. MIT
OpenCourseWare
OpenCourseWare
(http://ocw.mit.edu/),
(http://ocw.mit.edu/),
Massachusetts Institute
Massachusetts
of Technology.
Institute Downloaded
of Technology.
on Downloaded
[DD Month YYYY].
on [DD Month YYYY].
9
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
A discrete resistor
ete
iscrete
resistor
resistor
discrete
resistor
for the purpose of calculating
bulb
with
a
pose
ofReplace
calculating
of calculating
the
current.
the
current.
purpose
ofthe
calculating
the
current.
B A
I
A A
discrete resistor
I
I
I
+
for
the
purpose
of
calculating
the
and
V
V
V
+ + Replace
R
+ and and
the
bulb
with
a
V
I and
I – I
A
R
R
R
V V V
I
R
R
R
discrete
resistor
– – –
+
for the purpose
of
calculating
B
I
and
R
V
B B
A–
In E
Iwethings
In EE,
In we
EE,
do
we
things
do
In
EE,
do things
the
the easy
the easy
way…
way…way…
the
easy
+
B
and
R
V
In EE, w
–
R represents the only propert
the
ea
nts
he
only
the only
property
property
of interest!
of interest!
esents
the
only
property
of interest
Like with point-mass:
replace
B
-mass:
oint-mass:
replace
replace
objects
objects
ith
point-mass:
replace
objects In E
ao
R represents
theFonly
property
with theirFmass
mF to
find the
ato find
a a
smass
m mass
tomfind
tomfind
eir
m m mreplace obj
Like with point-mass:
F
a
with
their
mass
m
to
find
R
represents
the
only
propert
6.002 Fall 2000
Lecture 1
m
1
1
1
00
Lecture
Lecture
all
2000
Lecture
Like with point-mass: replace
a
with
their
mass
m
to
find
6.002 Fall 2000
Lecture 1
Resistores em série:
R1
R3
R2
Resistores em paralelo:
R1
R2
R3
10
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
course
reyand
Lang,
materials
course
for
materials
6.002 Circuits
for
6.002
and
Circuits
and
Electronics,
Spring
Spring
MIT2007.
MIT2007. MIT
al
Jeffrey
Lang,
course
materials
forElectronics,
6.002
Circuits
and2007.
Electronics,
Spring
Massachusetts
it.edu/), Massachusetts
Institute
ofInstitute
Technology.
ofInstitute
Technology.
Downloaded
Downloaded
on [DD Downloaded
Month
on [DD
YYYY].
Month
YYYY].
tp://ocw.mit.edu/),
Massachusetts
of Technology.
on [DD
Month YYY
Montagem experimental
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Cite as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey Lang, course materials for 6.002 Circuits and Electro
OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu/), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Downlo
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
B
In
EE,
we
do
th
represents the only property
of
inter
the easy way
the easy way
the purpose of calculating the curre
lace theAbulb with a
discrete Iresistor
V
+
the purpose of calculating
the
curre
I
and
R
V
R
A –
I
V
+
B
I
and
V R
R
In
EE,
we
do th
–
Atividade de aula
The Easy
The Easy
Way…Way…
The Easy Way…
The Easy Way…
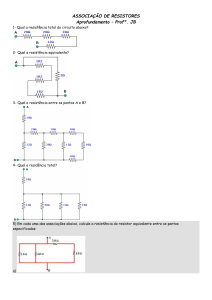
1- Determinar os valores de dois resistores a partir da medição com um
multímetro digital → Obter R1 ± σR1 e R2 ± σR2
discrete resistor
A
- Utilize a escala de maior precisão
A
- Compute a incerteza (Tipo B) a partir das especificações do multímetro
B
B
lace the bulb with a
B
2 - Montar um circuito com os dois resistores em série e medir a resistência
equivalente → Obter RS ± σRS
R1
R2
Replace
Replace
the bulb
thewith
bulba with a
discrete
discrete
resistor
resistor
B
A
A
forosthe
for
purpose
the purpose
of paralelo
calculating
of ecalculating
the
3 - Montar um circuito com
dois
resistores
em
medirthe
a curren
resistência equivalente → Obter RP ± σRP
A
A
11
I
+
R
V1
–
B
I
+ and
R RV2 R
–
B
V
Iand I
R
V
In EE, we
In EE,
do th
w
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Atividade de aula
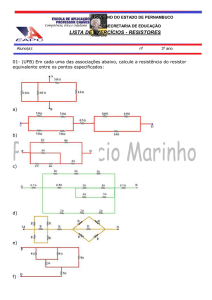
4 - A partir das medidas de resistência dos dois resistores
independentemente: R1 ± σR1 e R2 ± σR2
- Calcular a resistência equivalente dos resistores em série
(RS = R1 + R2)
- Calcular a resistência equivalente dos resistores em paralelo
(1/RP = 1/R1 + 1/R2)
5 - Analisar a compatibilidade entre a medida direta (2 e 3) e indireta (4) da
resistência equivalente dos resistores em série e paralelo
Trabalho em forma de relatório:
- Introdução, objetivo e descrição da experiência
- Cálculos e análise dos resultados
- Conclusão
12
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Multímetro digital
Display digital de “3
1/2” dígitos:
d1/2 d3 d2 d1
Número de
“contagens”: 0 - 1999
Funções:
Medição de tensão contínua (DC - V)
Medição de tensão alternada (AC - V)
Medição de corrente contínua (DC - A)
Medição de resistência (Ω)
Possivelmente: Teste de continuidade,
testes de diodos e transistores,...
13
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
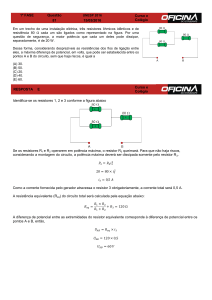
Multímetro digital: Incerteza da medida
Um multímetro digital possue especificações fornecidas pelo
fabricante que determinam o limite de erro (L) para uma
medida, da forma:
L = a% (leitura) + b dı́gito
B
L
=
2
Mais uma vez podemos considerar o limite de erro
correspondendo a um nível de confiança de ~95% (σ = L/2)
14
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Multímetro digital: Incerteza da medida
Especificações para medição de resistência (limites de erro):
Escala
Resolução
Precisão (Limite de erro)
200 Ω
0,1 Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 4 dígitos)
2 kΩ
1Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
20 kΩ
0,01 kΩ = 10 Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
200 kΩ
0,1 k Ω = 100 Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
20 MΩ
10 kΩ
± (3,0% leitura + 3 dígitos)
Minipa ET-1100
15
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Multímetro digital: Incerteza da medida
Especificações para medição de resistência (limites de erro):
Escala
Resolução
200 Ω
2000 Ω
20 kΩ
200 kΩ
2000 kΩ
0,1 Ω
1Ω
0,01 kΩ = 10 Ω
0,1 k Ω = 100 Ω
1kΩ
Precisão (Limite de erro)
± (0,8% leitura + 5 dígitos)
± (0,8% leitura + 5 dígitos)
± (0,8% leitura + 5 dígitos)
± (0,8% leitura + 5 dígitos)
± (0,8% leitura + 5 dígitos)
20 MΩ
0,01 MΩ = 10 kΩ
± (1,0% leitura + 5 dígitos)
Minipa ET-1110A
16
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
Multímetro digital: Incerteza da medida
Especificações para medição de resistência (limites de erro):
Escala
Resolução
Precisão (Limite de erro)
200 Ω
100 mΩ
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
2000 Ω
1Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
20 kΩ
10 Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
200 kΩ
100 Ω
± (0,8% leitura + 2 dígitos)
2000 kΩ 1 kΩ
± (1% leitura + 2 dígitos)
Multitoc DT830B
17
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7
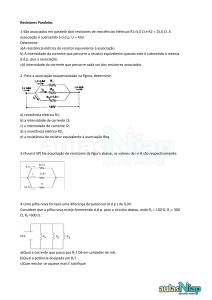
Como ler o código de cores de um resistor
Precisão
18
Cor
Código
Preto
0
Castanho
1
Vermelho
2
Laranja
3
Amarelo
4
Verde
5
Azul
6
Violeta
7
Cinza
8
Branco
9
Castanho
± 1%
Vermelho
± 2%
Dourado
± 5%
Prata
± 10%
Física Geral - 2014/1 - Aula 7