ENSINO FUNDAMENTAL II
Professor(a):Karla Rodrigues
Disciplina: Inglês
Data:
Aluno:
Série: 7º Ano
Turma:
Review
Lesson 2
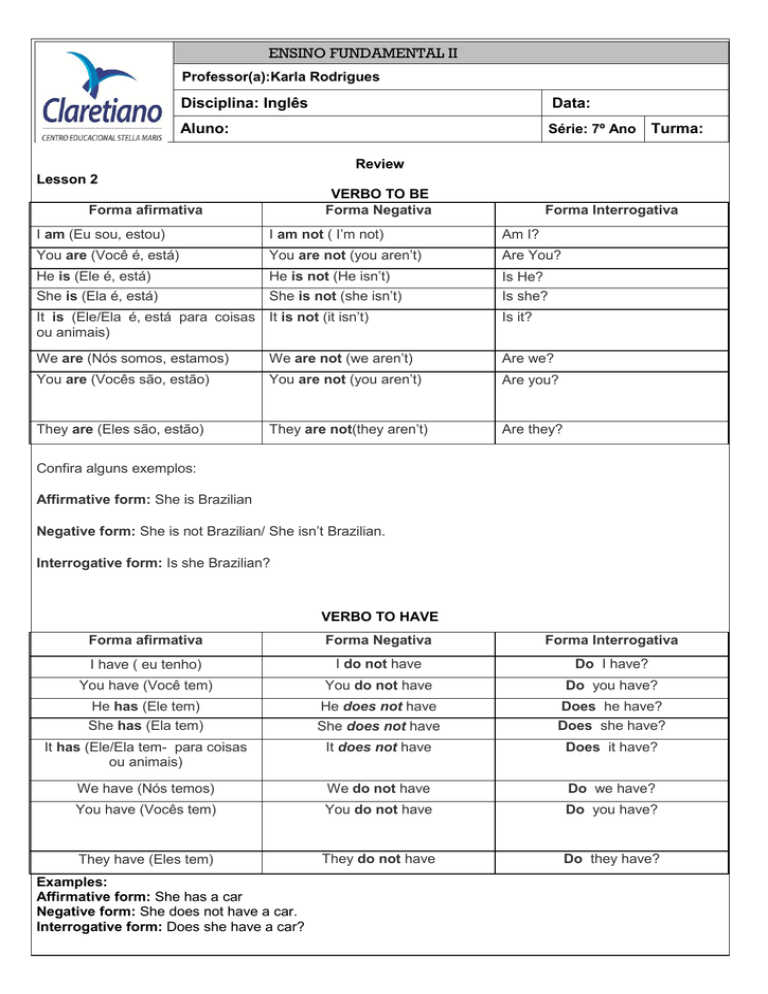
VERBO TO BE
Forma Negativa
Forma afirmativa
Forma Interrogativa
I am (Eu sou, estou)
I am not ( I’m not)
Am I?
You are (Você é, está)
You are not (you aren’t)
Are You?
He is (Ele é, está)
He is not (He isn’t)
Is He?
She is (Ela é, está)
She is not (she isn’t)
Is she?
It is (Ele/Ela é, está para coisas It is not (it isn’t)
ou animais)
Is it?
We are (Nós somos, estamos)
We are not (we aren’t)
Are we?
You are (Vocês são, estão)
You are not (you aren’t)
Are you?
They are (Eles são, estão)
They are not(they aren’t)
Are they?
Confira alguns exemplos:
Affirmative form: She is Brazilian
Negative form: She is not Brazilian/ She isn’t Brazilian.
Interrogative form: Is she Brazilian?
VERBO TO HAVE
Forma afirmativa
Forma Negativa
Forma Interrogativa
I have ( eu tenho)
I do not have
Do I have?
You have (Você tem)
You do not have
Do you have?
He has (Ele tem)
She has (Ela tem)
He does not have
She does not have
Does he have?
Does she have?
It has (Ele/Ela tem- para coisas
ou animais)
It does not have
Does it have?
We have (Nós temos)
We do not have
Do we have?
You have (Vocês tem)
You do not have
Do you have?
They have (Eles tem)
They do not have
Do they have?
Examples:
Affirmative form: She has a car
Negative form: She does not have a car.
Interrogative form: Does she have a car?
Lesson 3
INDEFINITE ARTICLES
A:um(a) – usado antes de som de consoante.
Example: a doctor
An:um(a)- usado antes de som de vogal.
Example: an architect
Observação: Os artigos indefinidos não são usados diante de substantivos no plural.
Example: X offices
Lesson 4
SOME/ANY
Some- usado em frases afirmativas.
Example: I have some friends.
Any- usado em frases negativas e interrogativas.
Examples: I do not (don’t) have any friends.
Do you have any friends?
Lesson 5
PLURAL OF NOUNS
Regra geral: acrescenta-se -s
Examples: car- cars/ pencil- pencils
Substantivos terminados em s,sh,ch, x e o recebem –es.
Examples: potato- potatoes/ Box- boxes/ address- addresses
Substantivos terminados em y precedido de consoante retira-se o y e acrescenta-se -ies.
Examples: city- cities/ family- families/ strawberry- strawberries
Irregular plural:
Child- children
Foot-feet
Man-men
Person-people
Tooth-teeth
Woman-women
Goose-geese
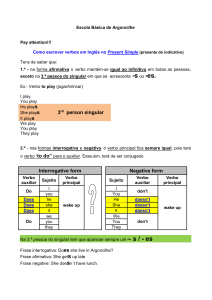
Lessons 8 to 10- SIMPLE PRESENT - PRESENTE SIMPLES
Sujeito Comum
Afirmativa: Sujeito + verbo (sem to)
Example: I study English
SIMPLE PRESENT 3RD PERSON OF SINGULAR- (PRESENTE SIMPLES- 3ª PESSOA DO SINGULAR)
FORMA AFIRMATIVA
Regra geral: verbo+ s. Example: He likes her.
Verbos terminados em s,sh,ch,x e o recebem –es. Example: She goes to school.
Verbos terminados em y precedido de consoante, retira-se o y e acrescenta-se –ies. Example:He studies
French.
SIMPLE PRESENT – INTERROGATIVE FORM
Na forma interrogativa do Simple Present usamos os verbos auxiliares do (quando o sujeito for I , You, We
ou They) e does (quando o sujeito for 3ª pessoa do singular- He, she, it) antes do sujeito na frase. Note que o
verbo fica na sua forma básica sem o to e sem as alterações que foram feitas na 3ª pessoa do singular.
Observe o exemplo: Do you like orange juice? (Você gosta de suco de laranja?)
RESUMO DO SIMPLE PRESENT
AFIRMATIVO
I work
You work
He works
She works
It works
We work
You work
They work
INTERROGATIVO
Do I work ...?
Do you work ...?
Does he work ...?
Does she work ...?
Does it work ...?
Do we work...?
Do you work ...?
Do they work ...?
Short answers:
QUESTION WORDS
Where- Onde?
Example: Where do you go? I go to the club.
When- Quando?
Example: When do you study? I study in the morning.
What- o quê? Qual?
Example: What do you usually do in the evenings? I usually watch TV.
How- Como?
Example: How do you go to school? I go to school by bus.
What time - A que horas?
Example: What time do you have lunch? I have lunch at 12 o’clock.
SIMPLE PRESENT-NEGATIVE FORM
Na forma negativa, usa-se o verbo auxiliar do / does junto com a partícula de negação not que é
posicionada antes do verbo principal ( na sua forma básica sem o to e sem as alterações que foram feitas na 3ª
pessoa do singular):
A forma contraída de do not é don’t e de does not é doesn’t.
AFIRMATIVO
I work
You work
He works
She works
It works
We work
You work
They work
NEGATIVO
I do not (don’t) work
You do not (don’t) work
He does not (doesn’t) work
She does not (doesn’t) work
It does not (doesn’t) work
We do not (don’t) work
You do not (don’t) work
They do not (don’t) work
FREQUENCY ADVERBS
Os advérbios de freqüência são posicionados normalmente antes do verbo principal da frase.
Always - Sempre
Usually -Usualmente/Geralmente
Often- Frequentemente
Sometimes- Às vezes
Rarely- Raramente
Never- Nunca
Example: I usually play computer games.
ADVERBIAL PHRASES OF FREQUENCY
As expressões de tempo são colocadas no final das frases.
Example: Bob studies English three times a week.
Every day
Todo dia
Every week
Toda semana
Every Saturday
Todo sábado
Every evening
Toda noite
Twice a day
Duas vezes ao dia
Three times a month
Três vezes por mês
In the morning
De manhã
In the afternoon
De tarde
On Mondays
Às segundas.
Once a week
uma vez por semana
Very rarely
muito raramente
Very often
muito frequentemente
How often? –Com que frequência?
Lesson 12
Personal Pronouns
Subject Pronouns
São usados como sujeito
I- Eu
You- você
He- ele
She-ela
It-ele/ela( animal ou “coisa”)
We (nós)
You( vocês)
They(eles/elas)
Bob likes Lisa
He likes her.
Lisa likes Bob
She likes him
Object Pronouns
São usados como objeto
Me
You
Him
Her
It
Us
You
Them