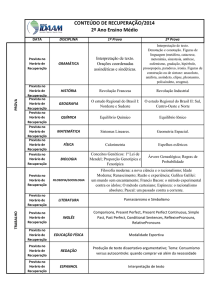
PRESENT PERFECT
UNIT. 9
Present Perfect é usado para ações que
aconteceram no passado em um tempo
indefinido.
Formamos o present perfect da seguinte maneira:
subject + have (s. pres. form) +verb (past participle form)
EX:
I have won the championship three times.
She has eaten there many times.
Contracted form:
I’ve won the championship three times.
She’s eaten there many times.
PRESENT PERFECT
Para sentenças negativas adicionamos not ao auxiliar have.
have not = haven’t
has not = hasn’t
EX:
I have not won the championship three times.
or
I haven’t won the championship three times.
She has not eaten there many times.
or
She hasn’t eaten there many times.
PRESENT PERFECT
Para sentenças interrogativas o auxiliar have precede
o sujeito.
EX:
Have you won the championship three times?
Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t. (short answers)
Has she eaten there many times?
Yes, she has. / No, she hasn’t. (short answers)
PRESENT PERFECT
PRESENT PERFECT x SIMPLE PAST
Usamos simple past para uma ação que aconteceu em
um passado definido.
Ex:
I went to the mall yesterday.
He won the championship last year.
Para sentenças negativas e interrogativas usamos o auxiliar “ did”.
Lembrando que ao usar o auxiliar o verbo fica na sua forma basica.
Ex:
What did you do last night?
I visited my sister.
She didn’t run the marathon last Sunday.
Os verbos regulares possuem a mesma forma para simple past e
past participle. Seguindo a mesma regra de acréscimo do –ed.
Os verbos regulares recebem a terminação -ed para formar o passado.
Ex: clean – cleaned
wash - washed
Alguns verbos, apesar de regulares, exigem mudanças antes de
receberem a terminação -ed.
Ex: live – lived
love - loved
Y - Verbos terminados em y, sendo esta letra precedida de uma
consoante, perderão o y para, então, ser acrescentada a terminação -ied.
Caso a letra y seja precedida de uma vogal, não há mudanças.
Ex: study – studied
play - played
try - tried
destroy - destroyed
Os verbos, cuja última sílaba seja formada por uma consoante, uma vogal
e uma consoante, sendo esta a sílaba tônica, terão sua última consoante
dobrada para então ser acrescentada a terminação -ed. Esta regra é a
mesma ao acrescentarmos todos os sufixos que se iniciam por vogal,
como ed e o ing.
Ex: step - stepped
develop – developed
prefer - preferred
offer - offered
Algumas exceções: open – opened; listen- listened
PRESENT PERFECT
Os verbos irregulares possuem forma própria para o
simple past e para o past participle, portanto, não
seguem nenhuma regra.
Há uma lista com sua forma basica, sua forma simple
past e sua forma past participle.
Ex:
base
Simple past
Past participle
Translation
(Portuguese)
be
was/were
been
ser, estar
begin
began
begun
começar
build
built
built
construir
eat
ate
eaten
comer
grow
grew
grown
crescer
lose
lost
lost
perder
wear
wore
worn
vestir
PRESENT PERFECT
PRESENT PERFECT 2
UNIT. 10
Apesar de sabermos que o Present Perfect é
usado para ações que aconteceram no
passado em um tempo indefinido. É comum
usarmos palavras que sinalizem essa
indefinição de tempo. Sugerindo um passado
mais recente ou o fato de que a ação
aconteceu desde o nascimento do sujeito até
hoje.
Ex: ever, never, before, yet, already, recently,
lately
PRESENT PERFECT 2
Ever, before, never são usadas para falar de experiências de vida.
Para dizer que nunca na vida...
She has never traveled abroad.
Para perguntar se alguma vez na vida...
Have you ever eaten cow tongue?
O uso do before tem o mesmo sentido do ever mas
entende-se que o sujeito ta vivendo a experiência naquele
momento
Have you been to this restaurant before?
She has never surfed before.
A posição da palavra também muda.
yet, already, recently, lately
PRESENT PERFECT 2
yet, already, recently, lately são usadas para falar de
experiências recentes.
Para dizer que recentemente...
She has practiced a lot of sports recently/lately.
Para dizer que algo já aconteceu...
I have already finished my homework.
Para dizer que algo ainda não aconteceu...
I haven’t finished my homework yet.
Have you finished your homework yet?
Geralmente yet é usado em negativa e interrogativa e already
em afirmativa
PRESENT PERFECT 2
Podemos usar o present perfect para falar de uma ação
que começou no passado e continua até hoje.
I have taught English for 11 years.
She has lived in London since 2005.
For – indica por quanto tempo essa ação vem acontecendo.
Since – indica um ponto no passado quando a ação começou.
Podemos usar outras palavras para indicar quanto tempo,
quantas vezes...
Always – sempre, still- ainda;
He has always wanted to be na actor.
I still haven’t found what I’m looking for.
PRESENT PERFECT 2