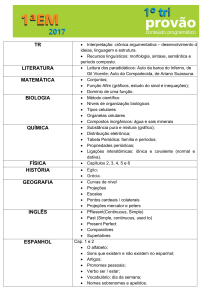
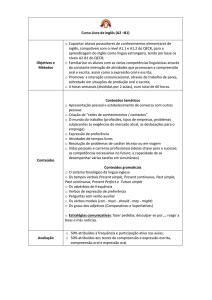
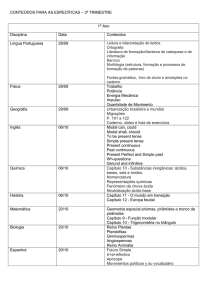
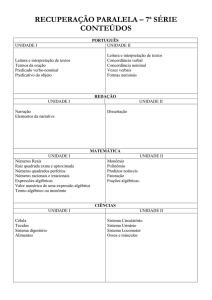
Present Continuous
Present Continuous
Formação:
No tempo progressivo ou contínuo utiliza-se o verbo
auxiliar to be a todas as pessoas junto com o
gerúndio -ing do verbo principal.
Ex.: The climate is getting warner. (get)
That child is growing bigger every day. (grow)
The Universe is expanding, and has been
since its beginning. (expand)
Present Continuous
Usos:
1) Utilizamos o present progressive/continuous para
expressar atividades que estão ocorrendo normalmente no
momento em que se fala.
Ex.: Please don’t make so much noise. I’m working.
“Where’s Margaret?” “She’s having a bath”.
Let’s go out now. It isn’t raining anymore.
I’m very tired. I’m going to bed now. Good night!
2) Usamos o progressive/continuous quando falamos sobre
coisas que estão acontecendo no período em que se fala,
não necessariamente no exato momento.
Ex.: John and Sarah are talking in a Café. John says:
– I’m reading an interesting book at the moment. I’ll
lend it to you when I’ve finished it.
(John isn’t reading the book at the time of speaking.)
Present Continuous
3) Para fazer referências a ações futuras planejadas ou
previstas.
Ex.: Next year, we are spending our vacation at
Nottingham.
Janice and Fred are leaving for Paris tomorrow.
4) É utilizado, ainda, para descrever ações que ocorrem
com freqüência ou que se repetem. É comum o uso do
advérbio always, que é posicionado entre o verbo
auxiliar e o verbo principal.
Ex.: I’m always doing something.
I’ve lost my key again. I’m always losing my things.
Ney is always telling the same jokes.
Present Continuous
Cuidado:
Os verbos a seguir não são usados no
tempo progressivo.
like, love, hate, want, prefer, believe, see,
know, realise, suppose, need, understand,
remember, taste, belong, contain, consist,
depend, seem, hear, smell
Present Continuous
Lembrando que na forma negativa basta
acrescentar o not junto ao verbo to be, ou
abreviá-lo.
Ex.: I am not working now
She is not (isn´t) playing baseball.
We are not (aren´t) eating pizza.
Present Continuous
Já na forma Interrogativa basta inverter a
ordem do sujeito com o verbo to be, e
acrescentar o ponto de interrogação no
final da pergunta.
Ex.: Is she studing English now ?
Are they going to Fred´s farm ?
Present Continuous
Thank you very much !!!