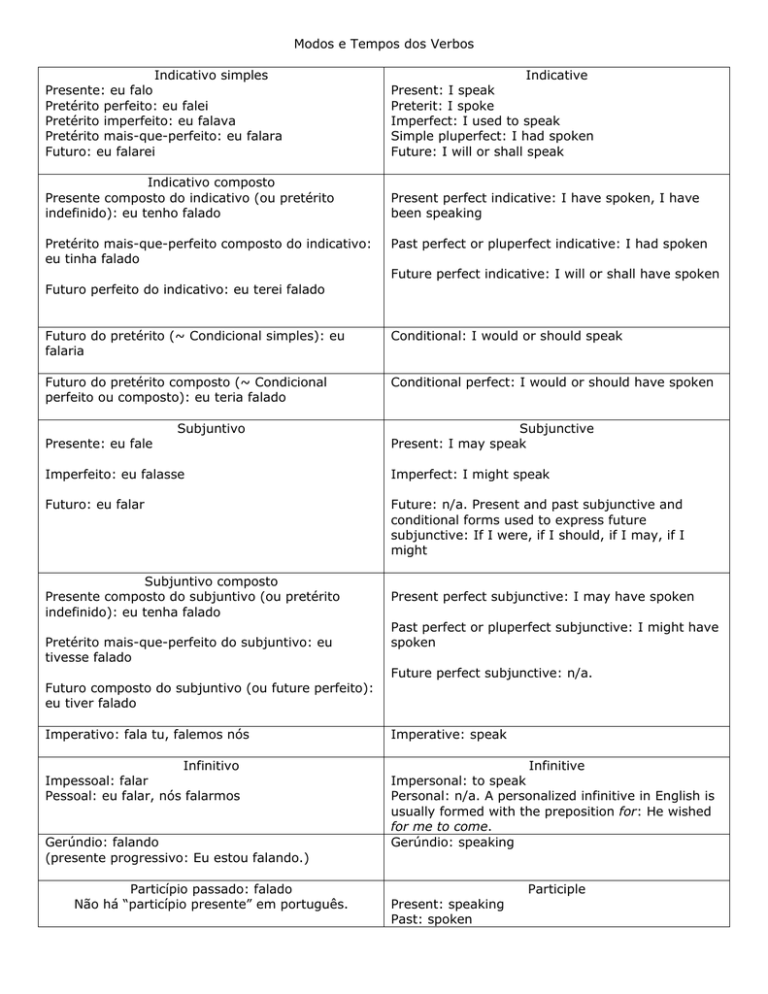
Modos e Tempos dos Verbos
Indicativo simples
Presente: eu falo
Pretérito perfeito: eu falei
Pretérito imperfeito: eu falava
Pretérito mais-que-perfeito: eu falara
Futuro: eu falarei
Indicative
Present: I speak
Preterit: I spoke
Imperfect: I used to speak
Simple pluperfect: I had spoken
Future: I will or shall speak
Indicativo composto
Presente composto do indicativo (ou pretérito
indefinido): eu tenho falado
Present perfect indicative: I have spoken, I have
been speaking
Pretérito mais-que-perfeito composto do indicativo:
eu tinha falado
Past perfect or pluperfect indicative: I had spoken
Future perfect indicative: I will or shall have spoken
Futuro perfeito do indicativo: eu terei falado
Futuro do pretérito (~ Condicional simples): eu
falaria
Conditional: I would or should speak
Futuro do pretérito composto (~ Condicional
perfeito ou composto): eu teria falado
Conditional perfect: I would or should have spoken
Presente: eu fale
Subjuntivo
Subjunctive
Present: I may speak
Imperfeito: eu falasse
Imperfect: I might speak
Futuro: eu falar
Future: n/a. Present and past subjunctive and
conditional forms used to express future
subjunctive: If I were, if I should, if I may, if I
might
Subjuntivo composto
Presente composto do subjuntivo (ou pretérito
indefinido): eu tenha falado
Pretérito mais-que-perfeito do subjuntivo: eu
tivesse falado
Futuro composto do subjuntivo (ou future perfeito):
eu tiver falado
Present perfect subjunctive: I may have spoken
Past perfect or pluperfect subjunctive: I might have
spoken
Future perfect subjunctive: n/a.
Imperativo: fala tu, falemos nós
Imperative: speak
Infinitivo
Impessoal: falar
Pessoal: eu falar, nós falarmos
Infinitive
Impersonal: to speak
Personal: n/a. A personalized infinitive in English is
usually formed with the preposition for: He wished
for me to come.
Gerúndio: speaking
Gerúndio: falando
(presente progressivo: Eu estou falando.)
Particípio passado: falado
Não há “particípio presente” em português.
Present: speaking
Past: spoken
Participle
