LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
A biblioteca Collection em java.util
• Arquitectura unificada para estruturas de dados
mais comuns
–
–
–
–
listas, pilhas, filas, conjuntos, tabelas
Interfaces para descrever funcionalidade
Implementações “de uso geral”
Algoritmos típicos para cada estrutura
• genéricos (polimórficos)
• Aparece no jdk 1.2
– organiza e sistematiza estruturas de dados já oferecidas
nas API anteriores, ex. Vector, Hashtable.
Collection - 1
Colecções
• Agrupam objectos designados elementos
• Nas interfaces estão previstas variantes
– ex: estrutura pode ser não mutável, ou de tamanho fixo
– alguns métodos designados opcionais
– prevista excepção UnsupportedOperationException para
operações que não tenham significado na variante
• Normalização das estruturas
– Dispensa a programação de estruturas usuais
– Permite desenvolver programas independentes da implementação
das estruturas
– Facilita a interoperabilidade entre API’s
• normaliza a forma de tratar colecções de objectos
– Facilita o desenvolvimento de novas API’s
– Favorece reutilização de software
Collection - 2
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-1
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
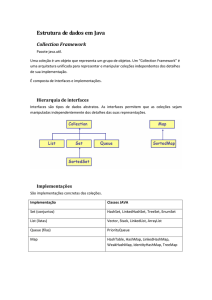
Collection, List, Set, Map
• Collection
– usada para transferir genericamente colecções de elementos
– não é fornecida implementação de referência
• Set
– Collection que não tem duplicados
– representação para a abstracção matemática “conjunto”
– implementações: AbstractSet, HashSet, TreeSet
• List
– Collection que tem ordem; admite duplicados
– acesso indexado
– implementações: AbstractList, LinkedList, ArrayList
• Map
– Mapeamento de chaves em valores
– Chaves únicas, cada chave mapeia em 1 valor no máximo
– Implementações: AbstractMap, HashMap, TreeMap
Collection - 3
Iteração sobre estruturas
• Solução directa: ciclo controlado por variável
for( int i = 0; i < v.length; i ++)
{...}
• Problema: requer conhecer a estrutura da colecção
• Alternativa: abstrair operações
for( itr = v.first(); itr.isValid();
itr.advance())
{...}
Collection - 4
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-2
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Estrutura com iterador-1
public class MyContainer
{
Object [ ] items;
int size;
public Object get( int idx ) {...}
public boolean add( Object x ) {...}
public MyContainerIterator iterator( )
{ return new MyContainerIterator(this);}
}
public class MyContainerIterator
{
private int current = 0;
private MyContainer container;
MyContainerIterator(MyContainer c)
{container = c;}
public boolean hasNext( )
{return current < container.size;}
public Object next( )
{ return container.items[ current++ ];}
}
Collection - 5
Estrutura com iterador-2
public class MyContainer
{
private Object [ ] items = new Object[ 5 ];
private int size = 0;
public Iterator iterator( )
{ return new MyContainerIterator(this); … }
public interface Iterator
{ boolean hasNext();
Object next(); }
class MyContainerIterator implements Iterator
{
private int current = 0;
private MyContainer container;
MyContainerIterator(MyContainer c)
{container = c;}
public boolean hasNext( )
{return current < container.size;}
public Object next( )
{ return container.items[ current++ ];}
}
Collection - 6
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-3
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Estrutura com iterador-3
package weiss.ds;
public class MyContainer
{
private Object [ ] items = new Object[ 5 ];
private int size = 0;
// ...
public Iterator iterator( )
{ return new LocalIterator(this);}
private static class LocalIterator implements Iterator
{
private int current = 0;
private MyContainer container;
private LocalIterator( MyContainer c)
{container = c;}
public boolean hasNext( )
{return current < container.size;}
public Object next( )
{ return container.items[ current++ ];}
}}
Collection - 7
Estrutura com iterador-4
package weiss.ds;
public class MyContainer
{
private Object [ ] items = new Object[ 5 ];
private int size = 0;
public Object get( int idx ) {...}
public boolean add( Object x ) {...}
public Iterator iterator( )
{ return new LocalIterator( );}
private class LocalIterator implements Iterator
{
private int current = 0;
public boolean hasNext( )
{return current < size;}
public Object next( )
{ return items[ current++ ];}
}
}
Collection - 8
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-4
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Iteradores
•
Solução 1
–
–
–
–
•
Classes públicas para iterador e contentor
Referência do iterador no contentor
Iterador partilha dados do contentor
Utilizador do contentor tem de definir iterador adequado
Solução 2
– Contentor devolve iterador genérico, programador usa interface Iterator
– iterator() é fábrica que produz iterador cujo tipo fica escondido do
utilizador
•
Solução 3
– Classe do iterador é nested class no contentor
– Evita partilha de dados no package
– Iterador é objecto independente construído com referência ao contentor
•
Solução 4
– Classe do iterador é inner class do contentor
– Iterador está implicitamente associado ao contentor, e refere directamente os
seus membros
Collection - 9
Hierarquia para listas em Collection
Collection
Iterator
AbstractCollection
List
ListIterator
AbstractList
AbstractSequentialList
LinkedList
ArrayList
Vector
Stack
Collection - 10
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-5
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
A interface Enumeration
• public interface Enumeration
– Objectos que a implementam geram séries de
elementos, um de cada vez
• Exemplo: imprimir elementos de um vector v
for (Enumeration e = v.elements(); e.hasMoreElements() ;)
{ System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
• Métodos
• boolean hasMoreElements()
–
Tests if this enumeration contains more elements.
• Object nextElement()
– Returns the next element of this enumeration if this
enumeration object has at least one more element to provide.
Collection - 11
A interface Iterator
• public interface Iterator
– Substitui Enumeration na biblioteca Collection
– Permite remover objectos da Collection
• Métodos
• boolean hasNext()
–
Returns true if the iteration has more elements.
• Object next()
– Returns the next element of the iteration.
• void remove()
– Removes from the underlying collection the last element
returned by the iterator (optional operation).
Collection - 12
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-6
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
A interface Collection
• Construtores nas classes que a implementam
– construtor sem argumentos
– construtor com argumento que é uma colecção
• Métodos obrigatórios:
boolean add(Object o)
void clear()
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean isEmpty()
Iterator iterator()
boolean
remove(Object o)
int size()
Object[] toArray()
Collection - 13
A interface Collection
• Genérica
– A biblioteca só fornece implementações para as suas
subinterfaces (ex: List, Map, Set)
boolean add(Object o)
boolean isEmpty()
boolean addAll(Collection c)
Iterator iterator()
void clear()
boolean
remove(Object o)
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean
removeAll(Collection c)
boolean
boolean retainAll(Collection c)
containsAll(Collection c)
boolean equals(Object o)
int size()
int
Object[] toArray()
hashCode()
Object[] toArray(Object[] a)
Collection - 14
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-7
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Iterador para Collection
public interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
void remove();
// Optional
}
hasNext()
e
• remove()
next()
usados para controlar ciclos
só pode ser chamado uma vez por cada
next()
• Exemplo: filtro sobre uma colecção:
static void filter(Collection c) {
for (Iterator i = c.iterator(); i.hasNext(); )
if (!cond(i.next()))
i.remove(); }
Collection - 15
Comparação
• Estão disponíveis 2 interfaces para normalizar as
comparações
• Comparable: “ordem natural” de uma classe
– impõe ordem total nos elementos de uma classe
– quem implementa: Character, File, Long,
ObjectStreamField, Short, String, Float, Integer, Byte,
Double, BigInteger, BigDecimal, Date, CollationKey
• Comparator: fornece função de comparação
– constrói-se “objecto funcional” que sabe comparar
• pode ser passado a métodos (ex: ordenação)
• permite usar ordenações diversas sobre objectos do mesmo
tipo
Collection - 16
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-8
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
A interface Comparable
em java.lang
• Impõe uma ordem total nos objectos das classes
que a implementam
– Ordem natural da classe
public int compareTo(Object o)
Compares this object with the specified object for
order. Returns a negative integer, zero, or a positive
integer as this object is less than, equal to, or
greater than the specified object.
The implementor must ensure sgn(x.compareTo(y)) == sgn(y.compareTo(x)) for all x and y.
The implementor must also ensure that the relation is
transitive: (x.compareTo(y)>0 &&
y.compareTo(z)>0) implies x.compareTo(z)>0.
Collection - 17
Interface Comparator
package weiss.util;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Comparator function object interface.
*/
public interface Comparator extends Serializable
{
/**
* Return the result of comparing lhs and rhs.
* @param lhs first object.
* @param rhs second object.
* @return < 0 if lhs is less than rhs,
*
0 if lhs is equal to rhs,
*
> 0 if lhs is greater than rhs.
* @throws ClassCastException if objects cannot be compared.
*/
int compare( Object lhs, Object rhs ) throws
ClassCastException;
}
Collection - 18
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-9
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Classe Collections em java.util
• Apenas métodos estáticos que operam em ou
retornam colecções
– Variáveis
static List EMPTY_LIST
static Map EMPTY_MAP
static Set EMPTY_SET
– Métodos
• cópia
• ordenações
static void sort(List list)
Sorts the specified list into ascending order, according to
the natural ordering of its elements.
static void sort(List list, Comparator c)
Sorts the specified list according to the order induced by
the specified comparator.
• mínimo, máximo
Collection - 19
A classe Collections
• Métodos de classe para trabalhar com colecções
static
static
static
static
int binarySearch(List list, Object key)
void copy(List dest, List src)
Object max(Collection coll)
Object max(Collection coll, Comparator comp)
static Comparator reverseOrder()
• Algoritmos polimórficos
static
static
static
static
void shuffle(List list)
Set singleton(Object o)
Collection unmodifiableCollection(Collection c)
Map unmodifiableMap(Map m)
Collection - 20
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-10
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Classe Collections
em weiss.util
package weiss.util;
/**
* Instanceless class contains static methods that operate on
collections.
*/
public class Collections
{
private Collections( ){}
/*
* Returns a comparator that imposes the reverse of the
* default ordering on a collection of objects that
* implement the Comparable interface.
* @return the comparator.
*/
public static Comparator reverseOrder( )
{
return new ReverseComparator( );
}
static final Comparator DEFAULT_COMPARATOR = new
DefaultComparator( );
(…)
Collection - 21
Classe Collections
em weiss.util
private static class ReverseComparator implements Comparator
{
public int compare( Object lhs, Object rhs )
{
return -( (Comparable) lhs ).compareTo( rhs );
}
}
static class DefaultComparator implements Comparator
{
public int compare( Object lhs, Object rhs )
{
return ( (Comparable) lhs ).compareTo( rhs );
}
}
(…)
Collection - 22
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-11
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Classe Collections
em weiss.util
public static Object max( Collection coll )
{
return max( coll, DEFAULT_COMPARATOR );
}
public static Object max( Collection coll, Comparator cmp )
{
if( coll.size( ) == 0 )
throw new NoSuchElementException( );
Iterator itr = coll.iterator( );
Object maxValue = itr.next( );
while( itr.hasNext( ) )
{
Object current = itr.next( );
if( cmp.compare( current, maxValue ) > 0 )
maxValue = current;
}
return maxValue;
}
}
Collection - 23
Interface de List
public interface List extends Collection {
// Positional Access
Object get(int index);
Object set(int index, Object element);
// Optional
void add(int index, Object element);
// Optional
Object remove(int index);
// Optional
abstract boolean addAll(int index, Collection c);// Optional
// Search
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
// Iteration
ListIterator listIterator();
ListIterator listIterator(int index);
// Range-view
List subList(int from, int to);
}
Collection - 24
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-12
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Iterador de List
public interface ListIterator extends Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
boolean hasPrevious();
Object previous();
int nextIndex();
int previousIndex();
void remove();
void set(Object o);
void add(Object o);
// Optional
// Optional
// Optional
}
… usando para iterar para trás numa lista:
for (ListIterator i=l.listIterator(l.size()); i.hasPrevious(); ) {
Foo f = (Foo) i.previous();
…
}
Collection - 25
Interface de List
em weiss.util
package weiss.util;
/**
* List interface.
* The version in java.util places the
* union of sensible LinkedList and ArrayList methods in
* this interface. We place the useful intersection here
* instead, which is arguably empty.
*/
public interface List extends Collection
{
/**
* Returns the item at position idx.
* @param idx the index to search in.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if index is out of
range.
*/
Object get( int idx );
(…)
Collection - 26
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-13
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Interface de List
em weiss.util
/**
* Changes the item at position idx.
* @param idx the index to change.
* @param newVal the new value.
* @return the old value.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if index is out of range.
*/
Object set( int idx, Object newVal );
/**
* Obtains a ListIterator object used to traverse the collection
bidirectionally.
* @return an iterator positioned prior to the requested element.
* @param idx the index to start the iterator. Use size() to do
complete
* reverse traversal. Use 0 to do complete forward traversal.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if idx is not between 0 and
size(), inclusive.
*/
ListIterator listIterator( int pos );
}
Collection - 27
Interface de ListIterator
em weiss.util
package weiss.util;
/**
* ListIterator interface for List interface.
*/
public interface ListIterator extends Iterator
{
/**
* Tests if there are more items in the collection
* when iterating in reverse.
* @return true if there are more items in the collection
* when traversing in reverse.
*/
boolean hasPrevious( );
/**
* Obtains the previous item in the collection.
* @return the previous (as yet unseen) item in the
collection
* when traversing in reverse.
*/
Object previous( );
}
/**
* Remove the last item returned by next or previous.
* Can only be called once after next or previous.
*/
void remove( );
Collection - 28
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-14
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
List e ListIterator
em java.util
• Implementações da interface List
– ArrayList
• apropriado quando inserções são no fim da list
• acesso indexado rápido
– LinkedList
• inserção com mesmo custo em qualquer ponto
• acesso indexado lento- é preciso percorrer a lista
– Vector
• anterior à biblioteca de colecções
• implementação com array
• Remoção com iterador ListIterator
• remove o elemento mais recentemente visto com next() ou
previous()
• só se pode chamar 1 vez entre chamadas de next() e previous()
Collection - 29
Classe LinkedList
em java.util
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Cloneable, Serializable
Linked list implementation of the List interface. Implements
all optional list operations, and permits all elements
(including null). In addition to implementing the List
interface, the LinkedList class provides uniformly named
methods to get, remove and insert an element at the beginning
and end of the list. These operations allow linked
lists to be used as a stack, queue, or double-ended queue
(deque).
void addFirst(Object o)
void addLast(Object o)
Object getFirst()
Object getLast()
Object removeFirst()
Object removeLast()
Collection - 30
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-15
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Exemplo: List com ArrayList
import java.util.*;
public class TestList{
public static void main( String [ ] args )
{
List
lista = new ArrayList();
List
lista2 = new ArrayList();
ListIterator itr = lista.listIterator();
ListIterator itr2 = lista2.listIterator();
// inserir 10 elementos
for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
itr2.add( new Integer( i ) );
itr2 = lista2.listIterator(0);
lista.addAll(lista2);
// Reset ao itr2
//copiar todos,método de Collection
System.out.print( "Mostrar primeira:" );
for( itr= lista.listIterator( ); itr.hasNext(); )
System.out.print( " " + itr.next() );
System.out.println( " fim." );
System.out.print( "Mostrar segunda:" );
for( itr2= lista.listIterator(); itr2.hasNext(); )
System.out.print( " " + itr2.next() );
System.out.println( " fim." );
}}
Collection - 31
Exemplo de List
import java.util.*;
// testar Interface List em Collections
// Array pode ser visto como lista (sem ser copiado)
public class TestList2
{
public static void replace(List l, Object val, Object newVal)
{
for (ListIterator i = l.listIterator(); i.hasNext(); )
if (val==null ? i.next()==null : val.equals(i.next()))
i.set(newVal);
}
public static void main( String [ ] args )
{
List lista = Arrays.asList(args);
Collections.shuffle(lista);
System.out.println(lista);
replace(lista, "1", "100");
System.out.println(lista);
}}
Collection - 32
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-16
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Stack em weiss.util
package weiss.util;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Stack class. Unlike java.util.Stack, this is not
* extended from Vector. This is the minimum respectable
* set of operations.
*/
public class Stack implements Serializable
{
private ArrayList items;
/**
* Constructs an empty stack.
*/
public Stack( )
{
items = new ArrayList( );
}
Collection - 33
Stack em weiss.util
/**
* Adds an item to the top of the stack.
* @param x the item to add.
* @return the item added.
*/
public Object push( Object x )
{
items.add( x );
return x;
}
/**
* Removes and returns item from the top of the stack.
* @return the former top item.
* @throws EmptyStackException if stack is empty.
*/
public Object pop( )
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
throw new EmptyStackException( );
return items.remove( items.size( ) - 1 );
}
Collection - 34
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-17
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Stack em weiss.util
/**
* Returns item from the top of the stack.
* @return the top item.
* @throws EmptyStackException if stack is empty.
*/
public Object peek( )
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
throw new EmptyStackException( );
return items.get( items.size( ) - 1 );
}
/**
* Tests if stack is empty.
* @return true if the stack is empty; false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isEmpty( )
{
return size( ) == 0;
}
Collection - 35
Stack em weiss.util
/**
* Returns
* @return
*/
public int
{
return
}
the size of the stack.
the size of the stack.
size( )
items.size( );
public void clear( )
{
items.clear( );
}
public String toString( )
{
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer( );
for( int i = size( ) - 1; i >= 0; i-- )
result.append( items.get( i ) );
return result.toString( );
}
}
Collection - 36
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-18
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Stack em java.util
• Class Stack- subclasse de Vector
boolean empty()
Tests if this stack is empty.
Object peek()
Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it from the stack.
Object pop()
Removes the object at the top of this stack and
returns that object as the value of this function.
Object push(Object item)
Pushes an item onto the top of this stack.
int search(Object o)
Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack.
• Alternativa: usar List e restringir operações
Collection - 37
Queue em weiss.nonstandard
package weiss.nonstandard;
// Queue interface
// ******************PUBLIC OPERATIONS*********************
// void enqueue( x )
--> Insert x
// Object getFront( )
--> Return least recently inserted item
// Object dequeue( )
--> Return and remove least recent item
// boolean isEmpty( )
--> Return true if empty; else false
// void makeEmpty( )
--> Remove all items
// ******************ERRORS********************************
// getFront or dequeue on empty queue
public interface Queue
{
/**
* Insert a new item into the queue.
* @param x the item to insert.
*/
void enqueue( Object x );
Collection - 38
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-19
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Queue em weiss.nonstandard
/**
* Get the least recently inserted item in the queue.
* Does not alter the queue.
* @return the least recently inserted item in the queue.
* @exception UnderflowException if the queue is empty.
*/
Object getFront( );
/**
* Return and remove the least recently inserted item
* from the queue.
* @return the least recently inserted item in the queue.
* @exception UnderflowException if the queue is empty.
*/
Object dequeue( );
/**
* Test if the queue is logically empty.
* @return true if empty, false otherwise.
*/
boolean isEmpty( );
}
/**
* Make the queue logically empty.
*/
void makeEmpty( );
Collection - 39
Queue em java.util
• Biblioteca não tem classe para queue
– Pode usar-se List restringindo operações
void addLast(Object o)
Appends the given element to the end of this list.
Object getFirst()
Returns the first element in this list.
Object removeFirst()
Removes and returns the first element from this list.
Collection - 40
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-20
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Hierarquia de Set e Map em Collection
Collection
AbstractCollection
Set
Map
SortedSet
AbstractSet
TreeSet
HashSet
AbstractMap
HashMap
SortedMap
TreeMap
Collection - 41
Interface de Set
public interface Set {
// Basic Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object element);
boolean add(Object element);
// Optional
boolean remove(Object element); // Optional
Iterator iterator();
// Bulk Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection c);
boolean addAll(Collection c);
//
boolean removeAll(Collection c); //
boolean retainAll(Collection c); //
void clear();
//
Optional
Optional
Optional
Optional
// Array Operations
Object[] toArray();
Object[] toArray(Object a[]);
}
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection - 42
Collection-21
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Map e SortedMap
• Mapeiam chaves em valores
– não admitem duplicados
– cada chave mapeia em 1 valor no máximo
• Map
– implementações: AbstractMap, HashMap,
Hashtable, RenderingHints, WeakHashMap,
Attributes
• SortedMap
– mantém as chaves em ordem crescente de chaves
– uso: dicionários e listas telefónicas
– implementações: TreeMap
Collection - 43
Interface de Map
public interface Map {
// Basic Operations
Object put(Object key, Object value);
Object get(Object key);
Object remove(Object key);
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
// Bulk Operations
void putAll(Map t);
void clear();
// Collection Views
public Set keySet();
public Collection values();
public Set entrySet();
Cristina Ribeiro
(…)
Collection - 44
Collection-22
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Interface de Map
public interface Map {
(…)
// Interface for entrySet elements
public interface Entry {
Object getKey();
Object getValue();
Object setValue(Object value);
}
}
Vistas como colecções: permitem iterar
for (Iterator i=m.keySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); )
System.out.println(i.next());
• vista de colecção permite remover
• vista de colecção não permite inserir
Collection - 45
Interfaces SortedSet e SortedMap
public interface SortedSet extends Set {
// Range-view
SortedSet subSet(Object fromElement, Object toElement);
SortedSet headSet(Object toElement);
SortedSet tailSet(Object fromElement);
// Endpoints
Object first();
Object last();
// Comparator access
Comparator comparator();
}
public interface SortedMap extends Map {
Comparator comparator();
SortedMap subMap(Object fromKey, Object toKey);
SortedMap headMap(Object toKey);
SortedMap tailMap(Object fromKey);
Object first();
Object last();
Cristina Ribeiro
}
Collection - 46
Collection-23
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Exemplo de Set
import java.util.*;
public class FindDups {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Set uniques = new HashSet();
Set dups = new HashSet();
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++)
if (!uniques.add(args[i]))
dups.add(args[i]);
uniques.removeAll(dups);
// Destructive
// set-difference
System.out.println("Unique words:
" + uniques);
System.out.println("Duplicate words: " + dups);
}
}
Collection - 47
Exemplo de Map
import java.util.*;
public class Freq {
private static final Integer ONE = new Integer(1);
public static void main(String args[]) {
Map m = new HashMap();
// Initialize frequency table from command line
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++) {
Integer freq = (Integer) m.get(args[i]);
m.put(args[i], (freq==null ? ONE :
new Integer(freq.intValue()
+ 1)));
}
System.out.println(m.size()+
" distinct words detected:");
System.out.println(m);
}
Collection - 48
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-24
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Conversão entre colecção e array
• Métodos toArray permitem traduzir Collection
para vector para uso em métodos que o exijam
Object[] a = c.toArray();
– cria novo vector da dimensão da colecção e copia
String[] a = (String[]) c.toArray(new
String[0]);
– cria novo vector usando o tipo do argumento e com a
dimensão da colecção e copia
Collection - 49
Classe Arrays
• Métodos para manipular arrays e para os tratar como listas
– Tratar array como lista
static List asList(Object[] a)
Returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array.
– 1 método para cada tipo primitivo e um para Object
• Pesquisa binária
static int binarySearch(byte[] a, byte key)
• Igualdade
static boolean equals(double[] a, double[] a2)
• Preencher array
static void fill(boolean[] a, boolean val)
• Ordenar
static void sort(float[] a)
• Ordenar com comparador
static void sort(Object[] a, Comparator c)
Collection - 50
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-25
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Testar iteradores sobre colecções
import
import
import
import
import
import
import
import
import
import
java.util.Comparator;
java.util.Collection;
java.util.Collections;
java.util.Iterator;
java.util.List;
java.util.Set;
java.util.ArrayList;
java.util.LinkedList;
java.util.TreeSet;
java.util.HashSet;
/**
* Illustrates use of Comparator for ignoring case distinctions.
*/
class IgnoreCase implements Comparator
{
public int compare( Object obj1, Object obj2 )
{
String s1 = (String) obj1;
String s2 = (String) obj2;
return s1.compareToIgnoreCase( s2 );
}
}
Collection - 51
Testar iteradores sobre colecções 2
/**
* Test program for lots of collections.
*/
class IteratorTest
{
/**
* Print any collection.
*/
public static void printCollection( Collection c )
{
Iterator itr = c.iterator( );
}
while( itr.hasNext( ) )
System.out.print( itr.next( ) + " " );
System.out.println( );
public static void main( String [ ] args )
{
List l1 = new ArrayList( );
l1.add( "Jack" );
l1.add( "Jill" );
l1.add( "Bill" );
List
Set
Set
Set
Set
l2
s1
s2
s3
s4
=
=
=
=
=
new
new
new
new
new
LinkedList( l1 );
TreeSet( l1 );
HashSet( l1 );
TreeSet( Collections.reverseOrder( ) );
TreeSet( new IgnoreCase( ) );
Collection - 52
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-26
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Testar iteradores sobre colecções 3
s3.add( "joe" );
s3.add( "bob" );
s3.add( "hal" );
s4.add( "Jeb!" );
s4.add( "jill" );
s4.add( "jack" );
printCollection(
printCollection(
printCollection(
printCollection(
printCollection(
printCollection(
List stud1
stud1.add(
stud1.add(
stud1.add(
l1
l2
s1
s2
s3
s4
);
);
);
);
);
);
//
//
//
//
//
//
Jack Jill Bill
Jack Jill Bill
Bill Jack Jill
Some unspecified order
joe hal bob
jack Jeb! jill
= new ArrayList( );
new SimpleStudent( "Bob", 0 ) );
new SimpleStudent( "Joe", 1 ) );
new SimpleStudent( "Bob", 2 ) ); // duplicate
Set
Set
}}
stud2 = new TreeSet( stud1 );
// will only have 2 items
stud3 = new HashSet( stud1 );
// will only have 2 items, if hashCode is
// implemented. Otherwise will have 3
// because duplicate will not be detected.
printCollection( stud1 ); // Bob Joe Bob
printCollection( stud2 ); // Bob Joe
printCollection( stud3 ); // Two items in unspecified order
Collection - 53
Testar iteradores sobre colecções 4
class SimpleStudent implements Comparable
{
String name;
int id;
public SimpleStudent( String n, int i )
{
name = n;
id = i;}
public String toString( )
{
return name + " " + id;}
public boolean equals( Object rhs )
{
if( rhs == null || getClass( ) != rhs.getClass( ) )
return false;
}
SimpleStudent other = (SimpleStudent) rhs;
return name.equals( other.name );
public int compareTo( Object other )
{
return name.compareTo( ((SimpleStudent)other).name );}
public int hashCode( )
{
return name.hashCode( );}}
Collection - 54
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-27
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Testar Map
import
import
import
import
import
weiss.util.Map;
weiss.util.TreeMap;
weiss.util.Set;
weiss.util.Iterator;
weiss.util.Comparator;
public class MapDemo
{
public static void printMap( String msg, Map m )
{
System.out.println( msg + ":" );
Set entries = m.entrySet( );
Iterator itr = entries.iterator( );
while( itr.hasNext( ) )
{
Map.Entry thisPair = (Map.Entry) itr.next( );
System.out.print( thisPair.getKey( ) + ": " );
System.out.println( thisPair.getValue( ) );
}
}
Collection - 55
Testar Map 2
// Do some inserts and printing (done in printMap).
public static void main( String [ ] args )
{
Map phone1 = new TreeMap( );
phone1.put( "John Doe", "212-555-1212" );
phone1.put( "Jane Doe", "312-555-1212" );
phone1.put( "Holly Doe", "213-555-1212" );
System.out.println( "phone1.get(\"Jane Doe\"): " +
phone1.get( "Jane Doe" ) );
System.out.println( );
printMap( "phone1", phone1 );
}
}
Collection - 56
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-28
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Fila de Prioridade
package weiss.nonstandard;
// PriorityQueue interface
//
// ******************PUBLIC OPERATIONS*********************
// Position insert( x )
--> Insert x
// Comparable deleteMin( )--> Return and remove smallest item
// Comparable findMin( )
--> Return smallest item
// boolean isEmpty( )
--> Return true if empty; else false
// void makeEmpty( )
--> Remove all items
// int size( )
--> Return size
// void decreaseKey( p, v)--> Decrease value in p to v
// ******************ERRORS********************************
// Throws UnderflowException for findMin and deleteMin when empty
Collection - 57
Interface de fila de prioridade
/**
* PriorityQueue interface.
* Some priority queues may support a decreaseKey operation,
* but this is considered an advanced operation. If so,
* a Position is returned by insert.
* Note that all "matching" is based on the compareTo method.
* @author Mark Allen Weiss
*/
public interface PriorityQueue
{
/**
* The Position interface represents a type that can
* be used for the decreaseKey operation.
*/
public interface Position
{
/**
* Returns the value stored at this position.
* @return the value stored at this position.
*/
Comparable getValue( );}
Collection - 58
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-29
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Interface de fila de prioridade 2
/**
* Insert into the priority queue, maintaining heap order.
* Duplicates are allowed.
* @param x the item to insert.
* @return may return a Position useful for decreaseKey.
*/
Position insert( Comparable x );
/**
* Find the smallest item in the priority queue.
* @return the smallest item.
* @throws UnderflowException if empty.
*/
Comparable findMin( );
/**
* Remove the smallest item from the priority queue.
* @return the smallest item.
* @throws UnderflowException if empty.
*/
Comparable deleteMin( );
Collection - 59
Interface de fila de prioridade 3
/**
* Test if the priority queue is logically empty.
* @return true if empty, false otherwise.
*/
boolean isEmpty( );
/**
* Make the priority queue logically empty.
*/
void makeEmpty( );
/**
* Returns the size.
* @return current size.
*/
int size( );
/**
* Change the value of the item stored in the pairing heap.
*/
void decreaseKey( Position p, Comparable newVal );}
Collection - 60
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-30
LEIC-FEUP 2001/2002
Algoritmos e Estruturas de Dados 1
Testar Fila de Prioridade
import weiss.nonstandard.PriorityQueue;
import weiss.nonstandard.BinaryHeap;
public class PriorityQueueDemo
{
public static void dumpPQ( String msg, PriorityQueue pq )
{
System.out.println( msg + ":" );
while( !pq.isEmpty( ) )
System.out.println( pq.deleteMin( ) );}
// Do some inserts and removes (done in dumpPQ).
public static void main( String [ ] args )
{
PriorityQueue minPQ = new BinaryHeap( );
minPQ.insert( new Integer( 4 ) );
minPQ.insert( new Integer( 3 ) );
minPQ.insert( new Integer( 5 ) );
dumpPQ( "minPQ", minPQ );
}}
Collection - 61
Cristina Ribeiro
Collection-31