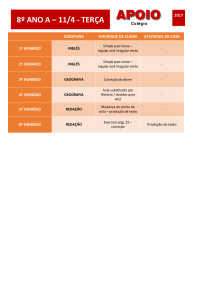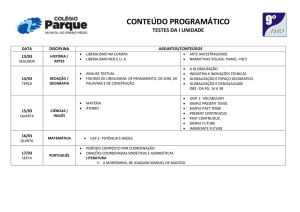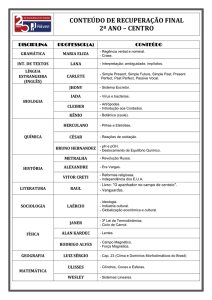
Verb TO BE
(O Verbo TO BE)
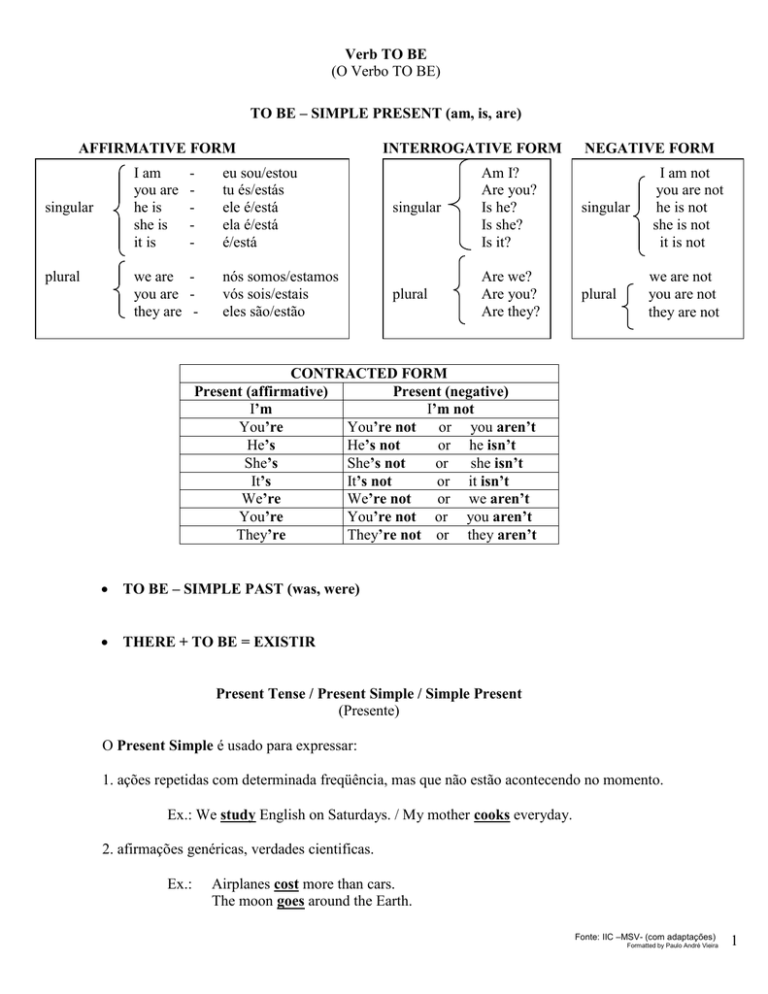
TO BE – SIMPLE PRESENT (am, is, are)
AFFIRMATIVE FORM
singular
plural
I am
you are
he is
she is
it is
-
we are you are they are -
eu sou/estou
tu és/estás
ele é/está
ela é/está
é/está
nós somos/estamos
vós sois/estais
eles são/estão
INTERROGATIVE FORM
NEGATIVE FORM
singular
Am I?
Are you?
Is he?
Is she?
Is it?
singular
plural
Are we?
Are you?
Are they?
plural
I am not
you are not
he is not
she is not
it is not
we are not
you are not
they are not
CONTRACTED FORM
Present (affirmative)
Present (negative)
I’m
I’m not
You’re
You’re not or you aren’t
He’s
He’s not
or he isn’t
She’s
She’s not
or she isn’t
It’s
It’s not
or it isn’t
We’re
We’re not
or we aren’t
You’re
You’re not or you aren’t
They’re
They’re not or they aren’t
TO BE – SIMPLE PAST (was, were)
THERE + TO BE = EXISTIR
Present Tense / Present Simple / Simple Present
(Presente)
O Present Simple é usado para expressar:
1. ações repetidas com determinada freqüência, mas que não estão acontecendo no momento.
Ex.: We study English on Saturdays. / My mother cooks everyday.
2. afirmações genéricas, verdades cientificas.
Ex.:
Airplanes cost more than cars.
The moon goes around the Earth.
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
1
CONJUGAÇÃO
TO WORK
singular
I work
You work
He works
She works
It works
plural
we work
you work
they work
***TERCEIRA PESSOA DO SINGULAR (He, She, It):
A terceira pessoa do singular é geralmente formada pelo acréscimo de um s ao verbo.
Ex.:
to like
to drink
-
he likes
she drinks
1. Os verbos terminados em ss, sh, ch, x, z e o, recebem a terminação es.
Ex.:
to wash
to go
to pass
to fix
to buzz
-
he washes
he goes
she passes
she fixes
it buzzes
2. Nos verbos terminados em y precedidos por consoante, troca-se o y pelo i e acrescenta-se es.
Ex.:
to try
-
he tries
Porém, se o y for precedido por vogal, segue-se a regra geral.
Ex.:
to play
-
he plays
INTERROGATIVE AND NEGATIVE FORMS - para a formação de orações interrogativas e negativas no
present simple é necessário o uso do verbo auxiliar do 1 (ou does – 3ª p. do singular), que, na língua
portuguesa, não tem nenhum significado já que sua única função é formar as frases interrogativas e negativas
no present simple.
PALAVRAS-CHAVE
Em geral, para expressar o present simple são usados advérbios de freqüência, ou expressões de tempo, nas
orações.
always – usually – often – rarely – never – generally – sometimes – seldom
every day - every night - every week - every Saturday - twice a day - two days a week
1
Observação: o verbo “to do” como verbo principal significa fazer.
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
2
Present Continuous Tense
(Presente Contínuo)
O Present Continuous descreve uma ação que está acontecendo agora.
PALAVRAS -CHAVE
now
- agora
//
at this moment - neste momento
FORMAÇÃO
PRESENT “TO BE” + MAIN VERB + “ING”
Outros usos:
1) Quando nos referimos a um fato que está acontecendo no período de tempo em que estamos
vivendo.
Ex.: I’m reading an interesting book.
2) Quando as ações se repetem com freqüência.***
Ex.: He is always arriving late.
3) Quando nos referimos a ações futuras planejadas.
Ex.: I am visiting Ruth tomorrow.
Existem verbos que, normalmente, não são usados no Present Continuous (verbos de percepção,
posse, opinião ou desejo). Neste caso, o seu uso é substituído pelo Simple Present.
STATIVE VERBS
Verbs of Inert Perception and Cognition*
abhor
adore
astonish
believe
desire
detest
dislike
doubt
feel
forgive
guess
hate
hear
imagine
impress
intend
know
like
love
mean
mind
perceive
please
prefer
presuppose
realize
recall
recognize
regard
remember
satisfy
see
smell
suppose
taste
think
understand
want
wish
Relational Verbs
be*
depend on involve possess
belong to
concern
consist of
contain
cost
deserve
equal
fit
have
include
lack
matter
need
owe
own
require
resemble
seem
sound
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
3
**Quando verbos são precedidos por preposição acrescenta-se ‘ING’.
Ex.:
John is interested in buying a new car.
Mary is afraid of seeing a ghost.
We are looking forward to seeing you soon.
**Used to do / be used to doing
Ex:
I used to study math at school.
They are used to getting up early everyday.
Simple Past Tense / Past Simple
(Passado)
O Simple Past descreve uma ação que aconteceu no passado, em um momento específico:
FORMAÇÃO
Dividimos os verbos em inglês em regulares e irregulares. Os verbos regulares formam o passado
pelo acréscimo de ED ao infinitivo, e os irregulares...apenas verificando a tabela!
Alguns verbos regulares:
to work
to like
to play
to study
to wait
to stop
-
worked
liked
played
studied
waited
stopped
→ atenção! (acrescentou-se somente o d)
→ atenção! (transformou-se o y em i)
→ atenção! (dobrou-se a ultima consoante)
Alguns verbos irregulares
to go – went
to see – saw
to run – ran
to read – read
to take – took
Formação da Interrogativa e Negativa: para a formação de orações interrogativas e negativas no
past simple é necessário o uso do verbo auxiliar do/does no passado (=DID).
Ex.:
I worked here last month. (affirmative) He went to the movies yesterday.
Did I work here last month? (interrogative)1 Did he go to the movies yesterday?1
I didn’t work here last month. (negative) He didn’t go to the movies yesterday.
PALAVRAS-CHAVE :
1
Observe que, com o uso do verbo auxiliar, o verbo principal volta para o infinitivo.
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
4
Yesterday
ago
last year
last week
last month
last Saturday
Past Continuous Tense
(Passado Contínuo)
FORMAÇÃO
PAST OF “TO BE”
+
MAIN VERB + “ING”
USOS
1. Para descrever uma ação em progresso no passado.
Ex.: It was still raining in Brasilia yesterday.
1. Para descrever uma ação que foi interrompida por uma outra ação também no passado. (A ação
que interrompeu fica no Simple Past)
I was having lunch when the telephone rang.
↓
↓
ação interrompida
ação que interrompeu
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Future Tense
(Futuro)
FORMAÇÃO
O futuro pode ser expresso por uma das formas a seguir:
1) WILL + verbo principal no infinitivo (- ‘to’)
Ex.:
You will do a test next Monday.
Will Mary go to her class on Saturday?
I will not (won’t) go to the bakery.
2) “TO BE GOING TO” + verbo principal no infinitivo
Ex.:
He is going to visit his father next weekend.
3) PRESENT CONTINUOUS / PRESENT SIMPLE
Ex:
We are playing tennis this weekend.
The concert starts at 7 o’clock tonight.
PALAVRAS-CHAVE
Soon
tomorrow
tonight
next week
next month
next Tuesday
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
5
Present Perfect Tense
(Presente Perfeito)
FORMAÇÃO
HAVE / HAS + PAST PARTICIPLE OF THE MAIN VERB
PALAVRAS-CHAVE
Already
Just
since
recently
lately
USOS
→ Para descrever uma ação ocorrida em uma época desconhecida no passado.
Ex.: I have traveled to New York.
Attention!
I traveled to New York last month. (SIMPLE PAST, porque o tempo foi definido)
→ Para descrever uma ação repetida várias vezes (no passado).
Ex.: I have been to New York many times.
→ Para descrever uma ação que começou no passado e que continua até hoje.
Ex.: I have lived in Brasilia since 1981.
→ Para descrever uma ação que acabou de acontecer.
Ex.: He has just arrived.
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
6
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
(Presente Perfeito Contínuo)
FORMAÇÃO
PRESENT PERFECT OF TO BE+ MAIN VERB + “ING”
Ex.: I have been studying English for more than 17 years.
USO
Para descrever uma ação iniciada no passado e que continua até hoje. É igual ao PRESENT
PERFECT, mas o uso do “Continuous” dá ênfase à oração.
Ex.:
I have been living in Brasilia since 1981.
We have been studying English for 6 weeks.
They haven’t been going there for a while.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Past Perfect Tense
(Passado Perfeito)
Descreve uma ação no passado que aconteceu antes de uma outra ação também passado.
HAD + PAST PARTICIPLE OF THE MAIN VERB
Ex.: When I arrived1 home yesterday, my children had already left.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Future Perfect Tense
(Futuro Perfeito)
USO
Descreve uma ação que terá acontecido em uma determinada situação no futuro.
FORMAÇÃO
WILL + HAVE + PAST PARTICIPLE OF THE MAIN VERB
Ex.: By the year 2050, the Earth will have suffered many changes.
The taxi will have arrived, by the time we get there.
1
A ação que aconteceu “depois” fica no Simple Past.
Fonte: IIC –MSV- (com adaptações)
Formatted by Paulo André Vieira
7