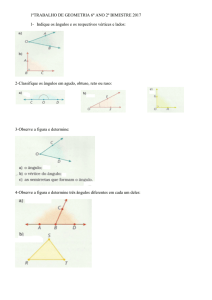
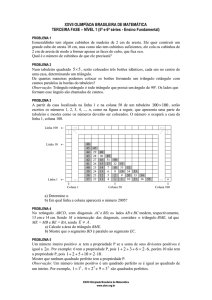
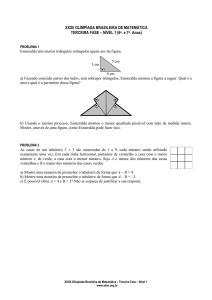
Busca em Arvore
Propaganda

Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
1
Pesquisas em Árvores
1. O que é?
Pesquisar em uma árvore é navegar em seus nós até que um específico nó seja
localizado.
Dos diversos algoritmos encontrados na literatura, pode-se destacar dois algoritmos
que são facilmente implementados com o conceito de lista. Esses dois algoritmos são muito
utilizados pela Inteligência Artificial na resolução de problemas e são conhecidos por
algoritmos de força bruta. Esses algoritmos são :
Busca em Amplitude
Busca em Profundidade
Além desses dois algoritmos, também destaca-se um terceiro algoritmo realizar
pesquisas, o Best-First Search. Esse algortimo é heurístico e diferencia-se pouco dos dois
anteriores. O Best-First Search faz uso de uma função heurística de avaliação para ordenar
as possíveis soluções em uma lista. Ordenadas essas soluções, seleciona-se a “melhor”
solução para ser analisada antes das demais.
Exemplo:
A Figura 1, exemplifica uma árvore binária.
Figura 1-Exemplo de Árvore Binária
2. Tipos de Busca:
A árvore da Figura 1 pode ser percorrida conforme ilustram as Figuras 2 e 3. Na
Figura 2, ela é percorrida com a Busca em Amplitude. Investiga-se todos os nós de uma
profundidade N antes de iniciar a busca na profundidade N+1.
Na Figura 3, ela é percorrida com a Busca em Profundidade. Nessa busca, investigase em seqüência cada ramo da árvore.
Tanto a pesquisa ou busca em Profundidade quanto em Amplitude permitem
navegar na árvore. Essas duas técnicas apresentam o inconveniente da explosão de nós, ou
seja, muitos nós são gerados enquanto a solução não é encontrada.
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
2
Figura 2-Busca em Amplitude
Figura 3- Busca em Profundidade
2.1 Algoritmos
Algoritmo de Busca em Amplitude (Breadth-First Search)
1) Criar uma lista e adicionar o primeiro nó. Esse nó representa o estado inicial da busca
ou o nó raiz da árvore.
2) Loop:
3)
Se a lista está vazia, então fim.
4)
Remover o primeiro elemento da lista. Esse elemento é chamado de SearchNode
5)
Se SearchNode contém o objetivo, então finalize com SearchNode como solução e
fim.
6)
Para cada filho do atual SearchNode, adicione esses elementos no final da lista.
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
3
Algoritmo de Busca em Profundidade (Depth-First Search)
1. Criar uma lista e adicionar o primeiro nó. Esse nó representa o estado incial da busca ou
o nó raiz da árvore.
2. Loop:
3. Se a lista está vazia, então fim.
4. Remover o primeiro elemento da lista. Esse elemento é chamado de SearchNode
5. Se SearchNode contém o objetivo, então finalize com SearchNode como solução e fim
6. Para cada filho do atual SearchNode, adicione esses elementos no início da lista.
2.2 Exemplo de Aplicação do Algoritmo Busca em Amplitude
O quadro 1, a seguir, apresenta um programa C que busca pela solução do 8-puzzle
utilizando a Busca em Amplitude. Esse programa foi, inicialmente, utilizado para obter os
nós da árvore representados parcialmente na Figura 4.
Destaca-se nesse quadro, a instrução da linha 195. Nessa instrução, busca-se limitar
o nível de profundidade para conter a explosão do número excessivo de tabuleiros. O
número escolhido de forma aleatória foi 5. Esse número pode ser aumentado e o algoritmo
irá buscar por soluções além do quinto nível de profundidade. Esse número não deve ser
grande devido a explosão combinatória. Em condições de teste, obteve-se um bom
desempenho com esse número indo até 15.
Quadro 1 – Exemplo de programa que utiliza a busca em Amplitude.
/*1*/ /////utiliza a busca em Amplitude.
/*2*/ #include<stdio.h>
/*3*/ #include<stdlib.h>
/*4*/ #include<string.h>
/*5*/ #define TRUE 1
/*6*/ #define FALSE 0
/*7*/
/*8*/
/*9*/
/*10*/
/*11*/
/*12*/
/*13*/
struct tabuleiro
{ int LinhasColunas [3][3];
int nivel; //nivel do tabuleiro na arvore
struct tabuleiro *next;
struct tabuleiro *father;
} *tabuleiro;
struct tabuleiro GoalState, *CurrentState;
/*14*/
/*15*/
/*16*/
/*17*/
/*18*/
/*19*/
/*20*/
/*21*/
/*22*/
void defineGoalState();
void defineCurrentState();
void inicializa();
int salvar(struct tabuleiro *t);
int ehIgual(struct tabuleiro *v1, struct tabuleiro *v2);
int insereNaLista(struct tabuleiro *v);
void copie(struct tabuleiro *origem
, struct tabuleiro *destino);
int jogar();
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*23*/
/*24*/
/*25*/
/*26*/
/*27*/
/*28*/
/*29*/
/*30*/
/*31*/
/*32*/
/*33*/
/*34*/
void defineGoalState()
{
GoalState.LinhasColunas[0][0]=1;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[0][1]=2;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[0][2]=3;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[1][0]=8;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[1][1]=0;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[1][2]=4;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[2][0]=7;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[2][1]=6;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[2][2]=5;
}
/*35*/
/*36*/
/*37*/
/*38*/
/*39*/
/*40*/
/*41*/
/*42*/
/*43*/
/*44*/
/*45*/
/*46*/
/*47*/
/*48*/
/*49*/
void defineCurrentState()
{
CurrentState = (struct tabuleiro *)
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[0][0]=1;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[0][1]=4;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[0][2]=3;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[1][0]=7;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[1][1]=0;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[1][2]=6;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[2][0]=5;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[2][1]=8;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[2][2]=2;
CurrentState->nivel=0;
}
/*50*/
/*51*/
/*52*/
/*53*/
/*54*/
/*55*/
/*56*/
/*57*/
/*58*/
/*59*/
/*60*/
/*61*/
/*62*/
void inicializa()
{
tabuleiro = NULL;
defineGoalState();
defineCurrentState();
insereNaLista(CurrentState);
FILE *fp;
if ( (fp= fopen("tabuleiro.txt","w")) == NULL)
{printf(
"\nERRO: Nao foi possivel escrever dados no arquivo");
printf("'tabuleiro.txt' !");};
fclose(fp);
}
/*63*/
/*64*/
/*65*/
/*66*/
/*67*/
/*68*/
/*69*/
/*70*/
int salvar(struct tabuleiro *t)
{
FILE *fp;
if ( (fp= fopen("tabuleiro.txt","a+")) == NULL)
{
printf(
"\nERRO: Nao foi possivel escrever dados no arquivo");
printf("'tabuleiro.txt' !");
4
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*71*/
/*72*/
/*73*/
/*74*/
/*75*/
/*76*/
/*77*/
/*78*/
/*79*/
/*80*/
/*81*/
/*82*/
/*83*/
/*84*/
/*85*/
/*86*/
/*87*/
return FALSE; /*FALSO*/
}
fprintf(fp
,"\n\nTabuleiro: Nivel %i:\n\t+---+---+---+"
,t->nivel);
for (int linha=0; linha < 3; linha++)
{ fprintf(fp,"\n\t|");
for (int coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
if ( t->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna] != 0)
{ fprintf(fp," %i |"
,t->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]);}
else { fprintf(fp,"
|");}
fprintf(fp,"\n\t+---+---+---+");
}
fclose(fp);
return TRUE;
}
/*88*/
/*89*/
/*90*/
/*91*/
/*92*/
/*93*/
/*94*/
int ehIgual(struct tabuleiro *v1, struct tabuleiro *v2)
{
for (int linha=0; linha<3; linha++)
for (int coluna=0; coluna < 3; coluna++)
if (v1->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna] !=
v2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]) {return FALSE;}
return TRUE;}
/*95*/
/*96*/
/*97*/
/*98*/
/*99*/
/*100*/
/*101*/
/*102*/
/*103*/
/*104*/
/*105*/
/*109*/
/*110*/
/*111*/
/*112*/
/*113*/
int insereNaLista(struct tabuleiro *v)
{ if (tabuleiro == NULL)
{v->next = NULL;
tabuleiro = v;
return TRUE;
}
struct tabuleiro *andarilho;
andarilho=tabuleiro;
while ((andarilho->next) != NULL)
{andarilho=andarilho->next;}
if (andarilho->next == NULL)
{ v->next = NULL; andarilho->next=v;}
return TRUE;
}
void copie(struct tabuleiro *origem
, struct tabuleiro *destino)
{ for (int linha=0; linha<3; linha++)
for ( int coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
destino->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=
origem->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
}
/*114*/
/*115*/
/*116*/
/*117*/
struct tabuleiro *retirePrimeiro()
{ struct tabuleiro *saida = tabuleiro;
tabuleiro=tabuleiro->next;
return saida;
/*106*/
/*107*/
/*108*/
5
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*118*/
}
/*119*/
/*120*/
/*121*/
/*122*/
/*123*/
/*124*/
/*125*/
/*126*/
/*127*/
/*128*/
/*129*/
/*130*/
/*131*/
/*132*/
/*133*/
/*134*/
/*135*/
/*136*/
/*137*/
/*138*/
/*139*/
int jogar()
{
int linha=0, coluna=0;
int aux;
int nivelExpandido;
CurrentState = retirePrimeiro();
nivelExpandido = CurrentState->nivel;
salvar(CurrentState);
if (ehIgual(CurrentState,&GoalState)==TRUE)
{printf("\n\n\t\tfim achei a solucao!"); exit(0);}
struct tabuleiro *aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *)
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
int achei=FALSE;
for (linha=0; linha<3; linha++)
{ for ( coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
if ( aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]
== 0){achei=TRUE; break;}
if ( achei ){break;}
}
if ((achei) && (coluna>2)){coluna=2;}
if ((achei) && (linha>2)){linha=2;}
/*140*/
/*141*/
/*142*/
/*143*/
/*144*/
/*145*/
/*146*/
/*147*/
/*148*/
/*149*/
/*150*/
/*151*/
/*152*/
// move o buraco para cima
if (linha>0)
{ aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha-1][coluna];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha-1][coluna]=
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
aux2->father = CurrentState;
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
insereNaLista(aux2);
aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *)
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
}
/*153*/
/*154*/
/*155*/
/*156*/
/*157*/
/*158*/
/*159*/
/*160*/
/*161*/
/*162*/
/*163*/
/*164*/
/*165*/
// move o buraco para direita
if (coluna<2)
{ aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna+1];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna+1]=
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
aux2->father = CurrentState;
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
insereNaLista(aux2);
aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *)
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
}
6
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*166*/
/*167*/
/*168*/
/*169*/
/*170*/
/*171*/
/*172*/
/*173*/
/*174*/
/*175*/
/*176*/
/*177*/
/*178*/
/*179*/
/*180*/
/*181*/
/*182*/
/*183*/
/*184*/
/*185*/
/*186*/
/*187*/
/*188*/
/*189*/
/*190*/
// move o buraco para baixo
if (linha<2)
{ aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha+1][coluna];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha+1][coluna]=
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
aux2->father = CurrentState;
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
insereNaLista(aux2);
aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *)
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
}
// move o buraco para esquerda
if (coluna>0)
{ aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna-1];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna-1]=
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
aux2->father = CurrentState;
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
insereNaLista(aux2);
}
return nivelExpandido;
}
/*191*/
/*192*/
/*193*/
/*194*/
/*195*/
void main(void)
{
inicializa();
int nivel = jogar();
while (nivel < 5) {nivel=jogar(); }
printf("\n ********* FIM do PROGRAMA");
/*196*/
/*197*/
}
7
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
Figura 4-Exemplo de Árvore de Jogos para o 8-puzzle
8
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
9
2.3 Pesquisa Heurística
A Figura 4, parcialmente, apresenta uma árvore. Nessa árvore são representados
alguns dos possíveis movimentos do jogo 8-puzzle. A quantidade de jogadas que podem ser
produzidas, nesse jogo, é um número muito elevado. Para problemas deste tipo, pode-se
utilizar outros tipos de buscas além das buscas em Amplitude e Profundidade. Dos
algoritmos disponíveis na literarutra, destaca-se o Best-First Search.
Nesse algoritmo, as buscas necessitam ser mais refinadas ou inteligentes. Nesse
contexto, ele utiliza uma função heurística h(jogada) como elemento “inteligente” para
identificar qual é a melhor jogada. Identificada essa melhor jogada, analisa-se ela em
primeiro lugar.
A função h(jogada) deve avaliar uma possível solução e compará-la com todas as
outras soluções possíveis. Após comparadas, seleciona-se a “melhor” solução e repte-se o
processo até encontrar a solução final. Esse algoritmo é conhecido Busca Gulosa e pertence
à categoria de algoritmos heurísticos Best-First.
Algoritmo de Busca Gulosa O Melhor Primeiro (Best-First Search)
1) Criar uma lista e adicionar o primeiro nó. Esse nó representa o estado inicial da busca
ou o nó raiz da árvore.
2) Loop:
3)
Se a lista está vazia, então fim.
4)
Remover o primeiro elemento da lista. Esse elemento é chamado de SearchNode
5)
Se SearchNode contém o objetivo, então finalize com SearchNode como solução e
fim.
6)
Para cada filho do atual SearchNode, insira esse filho de maneira ordenada na lista.
Outros algoritmos possíveis de serem utilizados nesse problema são MiniMax,
Means-End, Greedy, A*, entre outros.
2.4 Exemplo do Algoritmo de Busca Gulosa
O programa do Quadro 1 foi modificado e é apresentado no Quadro 2. Nessa
modificação a função h(jogada) foi inserida para definir um critério de ordenamento para a
lista de tabuleiros.
– h(jogada) = distância de cada peça ao seu local correto.
Com essa ordenação, cada tabuleiro analisado deverá ser o tabuleiro com maiores
chances de sucesso. Logo, deve-se ordenar a lista dos nós expandidos ou soluções em
ordem crescente a cada nó expandido da árvore. Nesse exemplo, quanto menor for o valor
de h(jogada), melhor será a solução.
/*1*/
/*2*/
/*3*/
/*4*/
/*5*/
Quadro 2 – Exemplo de programa que utiliza a Busca Gulosa.
// utiliza a Busca Gulosa .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<conio.h>
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*6*/ #define TRUE 1
/*7*/ #define FALSE 0
/*8*/ struct tabuleiro
/*9*/ { int LinhasColunas [3][3];
/*10*/
int custo;
/*11*/
int nivel;
/*12*/
int numero;
/*13*/
int numeroPai;
/*14*/
struct tabuleiro *next;
/*15*/
struct tabuleiro *father;
/*16*/
} *inicio;
/*17*/
int contador=0;
/*18*/
struct tabuleiro GoalState, *CurrentState;
/*19*/
/*20*/
/*21*/
/*22*/
/*23*/
/*24*/
/*25*/
/*26*/
/*27*/
/*28*/
/*29*/
/*30*/
/*31*/
/*32*/
void
void
void
void
int
int
int
void
/*33*/
/*34*/
/*35*/
/*36*/
/*37*/
/*38*/
/*39*/
/*40*/
/*41*/
/*42*/
/*43*/
/*44*/
/*45*/
/*46*/
/*47*/
/*48*/
/*49*/
/*50*/
/*51*/
/*52*/
/*53*/
/*54*/
/*55*/
/*56*/
int h(struct tabuleiro *v)
{ int h1=0;
int i,j,k,m;
for (i=0; i < 3; i++)
for (j=0; j < 3; j++)
{
for (k=i; k < 3; k++)
for ( m=j; m < 3; m++)
if (GoalState.LinhasColunas[i][j]
== v->LinhasColunas[k][m])
{h1 = h1 + abs(abs(k-i)+abs(m-j));}
}
return (h1);
}
void defineGoalState()
{
GoalState.LinhasColunas[0][0]=1;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[0][1]=2;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[0][2]=3;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[1][0]=8;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[1][1]=0;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[1][2]=4;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[2][0]=7;
GoalState.LinhasColunas[2][1]=6;
imprime(struct tabuleiro *t);
defineGoalState();
defineCurrentState();
inicializa();
salvar(struct tabuleiro *t);
ehIgual(struct tabuleiro *v1, struct tabuleiro *v2);
insereNaLista(struct tabuleiro *v);
copie(struct tabuleiro *origem
, struct tabuleiro *destino);
int jogar();
int insereOrdenado(struct tabuleiro *v);
int h(struct tabuleiro *v);
int jahVisitei(struct tabuleiro *v);
void imprimeCaminhoSolucao();
10
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
11
/*57*/
/*58*/
}
GoalState.LinhasColunas[2][2]=5;
/*59*/
/*60*/
/*61*/
/*62*/
/*63*/
/*64*/
/*65*/
/*66*/
/*67*/
/*68*/
/*69*/
/*70*/
/*71*/
void defineCurrentState()
{
CurrentState = (struct tabuleiro *)
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[0][0]=5;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[0][1]=0;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[0][2]=1;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[1][0]=2;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[1][1]=6;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[1][2]=8;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[2][0]=7;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[2][1]=3;
CurrentState->LinhasColunas[2][2]=4;
/*72*/
/*73*/
/*74*/
/*75*/
/*76*/
/*77*/
/*78*/
/*79*/
CurrentState->next=NULL;
CurrentState->father=NULL;
CurrentState->custo=h(CurrentState);
CurrentState->nivel=0;
CurrentState->numero=contador++;
CurrentState->numeroPai=-1;
inicio=CurrentState;
}
/*80*/
/*81*/
/*82*/
/*83*/
/*84*/
/*85*/
/*86*/
/*87*/
/*88*/
/*89*/
/*90*/
/*91*/
void inicializa()
{
defineGoalState();
defineCurrentState();
FILE *fp;
if ( (fp= fopen("tabuleiro.txt","w")) == NULL)
{printf(
"\nERRO: Nao foi possivel escrever dados no arquivo");
printf("'tabuleiro.txt' !");
};
fclose(fp);
}
/*92*/
/*93*/
/*94*/
/*95*/
/*96*/
/*97*/
/*98*/
/*99*/
/*100*/
void imprimeCaminhoSolucao()
{
FILE *fp;
struct tabuleiro *solucao = CurrentState;
if ( (fp= fopen("tabuleiro.txt","a+")) == NULL)
{printf(
"\nERRO: Nao foi possivel escrever dados no arquivo");
printf("'tabuleiro.txt' !");
return;};
/*101*/
o estado
/*102*/
/*103*/
/*104*/
/*105*/
/*106*/
/*107*/
fprintf(fp, "\n Lista de tabuleiros a partir da Solucao ate
inicial:");
fclose(fp);
int x=0;
while (solucao)
{
x++;
salvar(solucao);
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
12
/*108*/
/*109*/
/*110*/
/*111*/
/*112*/
/*113*/
/*114*/
solucao = solucao->father;
}
if ( (fp= fopen("tabuleiro.txt","a+")) == NULL)
{printf(
"\nERRO: Nao foi possivel escrever dados no arquivo");
printf("'tabuleiro.txt' !");
return;};
/*115*/
/*116*/
/*117*/
fprintf(fp, "\n ***** Quantidade de Tabuleiros :%i",x);
fclose(fp);
}
/*118*/
void imprime(struct tabuleiro *t)
/*119*/
{
/*120*/
printf("\n\nTabuleiro: nivel: %i custo: %i Numero:%i, Filho
de: %i\n\t+---+---+---+"
/*121*/
,t->nivel,t->custo,t->numero,t->numeroPai);
/*122*/
for (int linha=0; linha < 3; linha++)
/*123*/
{ printf("\n\t|");
/*124*/
for (int coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
/*125*/
if ( t->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna] != 0)
/*126*/
{ printf(" %i |",t->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]);}
/*127*/
else { printf("
|");}
/*128*/
printf("\n\t+---+---+---+");
/*129*/
}
/*130*/
}
/*131*/
int salvar(struct tabuleiro *t)
/*132*/
{
/*133*/
FILE *fp;
/*134*/
if (!t) return FALSE;
/*135*/
if ( (fp= fopen("tabuleiro.txt","a+")) == NULL)
/*136*/
{printf("\nERRO:
Nao
foi
possivel
escrever
arquivo");
/*137*/
printf("'tabuleiro.txt' !");
/*138*/
return FALSE; /*FALSO*/};
dados
no
/*139*/
fprintf(fp,"\n\nTabuleiro: Nivel %i: Custo(funcao h): %i
Numero: %i, Filho de : %i \n\t+---+---+---+",t->nivel,t->custo,t>numero,t->numeroPai);
/*140*/
for (int linha=0; linha < 3; linha++)
/*141*/
{ fprintf(fp,"\n\t|");
/*142*/
for (int coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
/*143*/
if ( t->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna] != 0)
/*144*/
{ fprintf(fp," %i |",t->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]);}
/*145*/
else { fprintf(fp,"
|");}
/*146*/
fprintf(fp,"\n\t+---+---+---+");
/*147*/
}
/*148*/
fclose(fp);
/*149*/
return TRUE;
/*150*/
}
/*151*/
/*152*/
/*153*/
/*154*/
/*155*/
int ehIgual(struct tabuleiro *v1, struct tabuleiro *v2)
{
for (int linha=0; linha<3; linha++)
for (int coluna=0; coluna < 3; coluna++)
if
(v1->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]
!=
v2-
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
>LinhasColunas[linha][coluna])
/*156*/
{return FALSE;}
/*157*/
return TRUE;
/*158*/
}
/*159*/
/*160*/
/*161*/
/*162*/
int jahVisitei(struct tabuleiro *v)
{
struct tabuleiro *andarilho = CurrentState;
if (ehIgual(CurrentState,v)) return TRUE;
/*163*/
/*164*/
/*165*/
/*166*/
/*167*/
/*168*/
/*169*/
/*170*/
while (andarilho)
{
if (ehIgual(andarilho,v)) return TRUE;
else
{ andarilho=andarilho->father; }
}
return FALSE;
}
/*171*/
/*172*/
/*173*/
/*174*/
int insereNaLista(struct tabuleiro *v)
{
return insereOrdenado(v);
}
/*175*/
/*176*/
/*177*/
/*178*/
int insereOrdenado(struct tabuleiro *v)
{
struct tabuleiro *andarilho, *anterior;
int com,com2;
/*179*/
if (jahVisitei(v)) return FALSE;
/*180*/
/*181*/
v->custo=h(v);
v->father = CurrentState;
/*182*/
/*183*/
/*184*/
/*185*/
/*186*/
/*187*/
/*188*/
/*189*/
/*190*/
anterior=NULL;
andarilho = inicio;
v->numero = contador++;
if (inicio==NULL)
{
v->next = NULL;
inicio =v;
return TRUE;
}
/*191*/
/*192*/
/*193*/
/*194*/
while(andarilho)
{
if (ehIgual(andarilho, v )) {return FALSE;}
com = v->custo - andarilho->custo;
/*195*/
/*196*/
/*197*/
/*198*/
/*199*/
/*200*/
/*201*/
/*202*/
if (com >= 0)
{ anterior=andarilho; andarilho=andarilho->next;}
else {
v->next = andarilho;
if (anterior) anterior->next = v;
else {inicio=v;}
return TRUE;
}
13
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
14
/*203*/
/*204*/
/*205*/
/*206*/
/*207*/
/*208*/
}
// insere no final.
anterior->next = v;
v->next = NULL;
return TRUE;
}
/*209*/
/*210*/
/*211*/
/*212*/
/*213*/
/*214*/
/*215*/
/*216*/
/*217*/
/*218*/
/*219*/
/*220*/
void copie(struct tabuleiro *origem
, struct tabuleiro *destino)
{
for (int linha=0; linha<3; linha++)
for ( int coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
{
destino->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=
origem->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
destino->nivel=origem->nivel;
destino->custo=origem->custo;
destino->next=origem->next;
destino->father=origem->father;
}
/*221*/
}
/*222*/
/*223*/
/*224*/
/*225*/
/*226*/
struct tabuleiro *retirePrimeiro()
{ struct tabuleiro *saida = inicio;
inicio=inicio->next;
return saida;
}
/*227*/
/*228*/
/*229*/
/*230*/
/*231*/
/*232*/
/*233*/
/*234*/
/*235*/
void vitoria(struct tabuleiro *v)
{
clrscr();
imprime(v);
if (ehIgual(v,&GoalState)==TRUE)
{printf("\n\n\t\t *****Fim achei a solucao!");
imprimeCaminhoSolucao();
exit(0);}
}
/*236*/
/*237*/
/*238*/
/*239*/
/*240*/
/*241*/
int jogar()
{
int linha=0, coluna=0;
int aux;
int nivelExpandido;
int custo=1000;
// armazena o custo da jogada!
/*242*/
/*243*/
/*244*/
CurrentState = retirePrimeiro();
vitoria(CurrentState);
nivelExpandido = CurrentState->nivel;
/*245*/
struct
tabuleiro
*aux2
malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
/*246*/
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
/*247*/
int achei=FALSE;
/*248*/
/*249*/
/*250*/
=
(struct
tabuleiro
for (linha=0; linha<3; linha++)
{ for ( coluna=0; coluna<3; coluna++)
if ( aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna] == 0)
*)
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*251*/
/*252*/
/*253*/
15
{achei=TRUE; break;}
if ( achei ){break;}
}
/*254*/
if ((achei) && (coluna>2)){coluna=2;}
(linha>2)){linha=2;}
/*255*/
// move o buraco para cima
/*256*/
if (linha>0)
/*257*/
{aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha-1][coluna];
/*258*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha-1][coluna]=aux2>LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
/*259*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
/*260*/
aux2->father = CurrentState;
/*261*/
aux2->numeroPai = CurrentState->numero;
/*262*/
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
if
((achei)
&&
/*263*/
if (insereNaLista(aux2))
/*264*/
{ if (custo > aux2->custo) custo = aux2->custo;
/*265*/
if (CurrentState->next == NULL) CurrentState->next = aux2;
/*266*/
}
/*267*/
aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *) malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
/*268*/
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
/*269*/
}
/*270*/
// move o buraco para direita
/*271*/
if (coluna<2)
/*272*/
{aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna+1];
/*273*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna+1]=aux2>LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
/*274*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
/*275*/
aux2->father = CurrentState;
/*276*/
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
/*277*/
aux2->numeroPai = CurrentState->numero;
/*278*/
if (insereNaLista(aux2))
/*279*/
{if (custo > aux2->custo) custo = aux2->custo;
/*280*/
if (CurrentState->next == NULL) CurrentState->next = aux2;
/*281*/
}
/*282*/
aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *) malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
/*283*/
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
/*284*/
}
/*285*/
// move o buraco para baixo
/*286*/
if (linha<2)
/*287*/
{aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha+1][coluna];
/*288*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha+1][coluna]=aux2>LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
/*289*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
/*290*/
aux2->father = CurrentState;
/*291*/
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
/*292*/
aux2->numeroPai = CurrentState->numero;
/*293*/
if (insereNaLista(aux2))
/*294*/
{
/*295*/
if (custo > aux2->custo) custo = aux2->custo;
/*296*/
if (CurrentState->next == NULL) CurrentState->next = aux2;
/*297*/
}
/*298*/
aux2 = (struct tabuleiro *) malloc(sizeof(struct tabuleiro));
/*299*/
copie(CurrentState,aux2);
/*300*/
}
/*301*/
// move o buraco para esquerda
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
/*302*/
if (coluna>0)
/*303*/
{aux = aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna-1];
/*304*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna-1]=aux2>LinhasColunas[linha][coluna];
/*305*/
aux2->LinhasColunas[linha][coluna]=aux;
/*306*/
aux2->father = CurrentState;
/*307*/
aux2->nivel = CurrentState->nivel+1;
/*308*/
aux2->numeroPai = CurrentState->numero;
/*309*/
if (insereNaLista(aux2))
/*310*/
{if (custo > aux2->custo) custo = aux2->custo;
/*311*/
if (CurrentState->next == NULL) CurrentState->next = aux2;
/*312*/
}
/*313*/
}
/*314*/
return custo;
/*315*/
}
/*316*/
/*317*/
/*318*/
/*319*/
/*320*/
/*321*/
/*322*/
/*323*/
/*324*/
void printFila()
{
struct tabuleiro *andarilho = inicio;
while (andarilho)
{
salvar(andarilho);
andarilho=andarilho->next;
}
}
/*325*/
/*326*/
/*327*/
/*328*/
/*329*/
/*330*/
/*331*/
/*332*/
/*333*/
void main(void)
{
inicializa();
int nivel = 0, n=0;
while ( (nivel++) < 20000)
{ jogar();
}
imprimeCaminhoSolucao();
printf("FIM!");
}
/*334*/
16
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
17
77
Figura 5-Exemplo de Execução do Programa de Busca Gulosa
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
Figura 6-Exemplo de Saída do Programa de Busca Gulosa - parte 1
18
Estrutura de Dados – IF63C
Professores Vida e Hilton
19
Figura 7-Exemplo de Saída do Programa de Busca Gulosa - parte 2
Tarefa:
1) Copie o trecho de código do Quadro 1 para o ambiente de desenvolvimento C. Compile
e execute esse programa. O programa foi capaz de encontrar a solução?
2) Modifique o programa do Quadro 1 para a busca em Profundidade.
3) Pesquise, também, outros algoritmos que estão disponíveis na literatura ou na internet
para o jogo 8-puzzle. Um bom exercício de programação é tentar implementar cada um
desses algoritmos.